We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Serum sickness
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- A type III hypersensitivity reaction
- Reactions secondary to the administration of nonprotein drugs
- Amoxicillin, cefaclor, cephalexin (Keflex), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Clinical Features
- Primary occurs 6-21 days after exposure
- 1-4 days after subsequent exposures to the same antigen
- Fever
- Arthralgia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Skin eruption (rash)
- Urticaria
- Scarlatiniform rash
- Maculopapular or purpuric lesions
- Erythema multiforme
Differential Diagnosis
- Erythema multiforme
- Mononucleosis
- Polymyositis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Tick-Borne Diseases, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
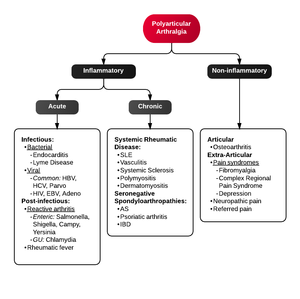
Polyarthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Serum sickness
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Serum sickness–like reactions
- Viral arthritis
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis in which labs may be suggestive but not required[1]
- Careful investigation of new medications
- List of serum sickness medications extensive
- Mild leukopenia or leukocytosis
- ESR elevation
- Mild proteinuria
- Mild hematuria
- Mild serum creatinine elevation
- Decreased C3, C4
- Other labs to obtain:
- CH50
- LFTs
- Urine electrolytes (Na, K, Cr, eosinophils)
- ESR and CRP
- HepB, HepC panel, HIV, RPR/VDRL
Management
- Discontinue antigen
- Antipyretics
- Diphenhydramamine
- Prednisone
Disposition
Admit for:
- Significant comorbidities (advanced or very young age, immunocompromised)
- Severe symptoms
- Hemodynamic instability/hypotension
- Unclear diagnosis
Prognosis
- Symptoms usually last 1-2 weeks before spontaneously subsiding
- Long-lasting sequelae generally do not occur
- Fatalities are rare and usually are due to continued administration of the antigen
References
- ↑ Alissa HM et al. Serum Sickness Workup. Dec 14, 2015. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/332032-workup#showall
Authors
Ross Donaldson, Kevin Lu, Daniel Eggeman, Neil Young, Daniel Ostermayer