We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Amiodarone
From WikEM
Contents
General
- Type: Antiarrhythmics
- Dosage Forms: 200mg
- Common Trade Names: Cordarone
Adult Dosing
- V-fib/pulseless V-tach
- Loading dose = 300mg IV bolus followed by 150mg bolus prn
- Stable V-tach or SVT
- Loading dose = 150mg IV in 100mL D5W over 10min
- Follow by infusion of 1mg/min x 6hr; 0.5mg/min thereafter
- Loading dose = 150mg IV in 100mL D5W over 10min
Pediatric Dosing
Special Populations
- Pregnancy Rating: D
- Lactation Risk Categories: Unsafe
- Renal Dosing- no adjustment
- Adult
- Pediatric
- Hepatic Dosing- caution and consider dose decrease
- Adult
- Pediatric
Indications
- Ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias
- 1st line for pulseless V-tach/V-fib
- Used for atrial arrhythmias in patients with decreased EF
Contraindications
- Allergy to class/drug
- Iodine or shellfish allergy
- Pregnancy
Adverse Reactions
- Bradycardia
- Hypotension with older solvent-based formulation. Uncommon with newer aqueous formulation.
- Prolonged QT
- Thyrotoxicosis[1]
- Between 5-20% of patients treated with amiodarone have thyrotoxicosis (higher in areas of iodine deficiency)
- Iodine-induced hyperthyroidism
- It is thought that the iodine load may unmask hyperthyroidism in patients with multinodular goiter and subclinical Graves’ disease
- Drug-induced destructive thyroiditis
- More commonly, the cytotoxic effects of amiodarone destroy thyroid cells, resulting in a release of preformed hormone.
- Amiodarone Pulmonary Toxicity
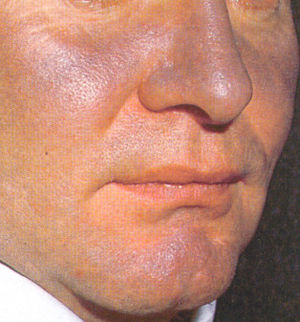
- Hyperpigmentation rash
Pharmacology
- Half-life: 58 days
- Metabolism: Liver extensively
- Excretion: Bile primarily
Mechanism of Action
- Class III - Inhibits potassium channels
- Impairs SA and AV node conduction
- Decreases automaticity
- Prolongs refractory period in accessory pathways
- Also has class I & II properties
See Also
References
- ↑ Rosen's 8th Edition