Direct Reading and Sensor Technologies

Overview
Direct-reading methods and sensors are being used more frequently in many different settings ranging from personal monitoring of individual health to applications in research and in clinical practice. NIOSH began organized research in this area in 2008 with the creation of the DREAM initiative (Direct Reading Exposure Assessment Methods). NIOSH will build upon and expand the DREAM program to address lessons learned, advances in technology, and stakeholder contributions. NIOSH researchers have developed a number of direct-reading methods and monitors and are exploring new ways to use these technologies to improve occupational safety and health.
The use of sensors has increased exponentially as countless remote wireless sensors are now employed for monitoring the environment, work sites, disaster response, “smart” buildings and facilities, and in agriculture and health. Wireless data transfer based on cell phone networks and smart phone technology is enhancing the adoption of these sensors, and allowing integration of geographically disperse sensors to produce comprehensive exposure pictures. Wearable and even implantable sensors are being developed that could aid in exposure assessment and clinical practice.
NIOSH Center for Direct Reading and Sensor Technologies
The NIOSH Center for Direct Reading and Sensor Technologies (NCDRST) was established in May 2014 to coordinate research and to develop recommendations on the use of 21st century technologies in occupational safety and health. The NCDRST is a virtual center hosted by the NIOSH Division of Applied Research and Technology and the NIOSH Exposure Assessment Cross Sector Program.
NCDRST Goals
- Coordinate a national research agenda for direct-reading methods and sensor technologies;
- Develop guidance documents pertinent to direct-reading methods and sensors, including validation and performance characteristics;
- Develop training protocols; and
- Establish partnerships to collaborate in the Center’s activities.
Direct Reading and Sensor Technologies Life Cycle Approach
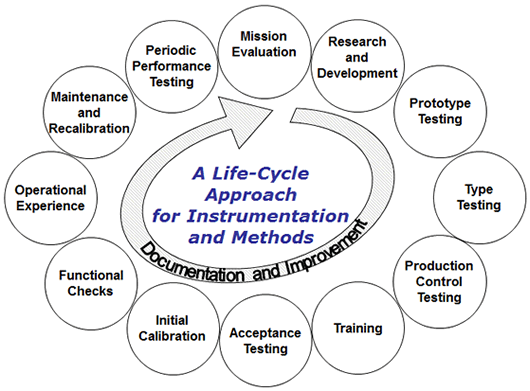
The following lifecycle approach for the development and application of direct-reading and sensor technologies shows key steps that are taken to ensure the relevance and reliability of measurements to protect workers. The cycle begins with a clear and complete identification of what needs to be measured, under what conditions it needs to be measured, and how well it needs to be measured. It also guides research and development, prototype testing, type testing, production control testing, and training needed to develop the instrument. The life cycle approach defines procedures for acceptance testing, initial calibration, functional checks, conduct and evaluation of operational experience, maintenance and recalibration, and periodic performance testing to confirm continued successful use of the instrument. Effective prototype testing ensures that the final instrument will work as intended under realistic conditions. Documentation and continuous improvement are essential at each step.
Path Forward for the 21st Century
In September 2012, The National Research Council released its report on Exposure Science in the 21st Century: A Vision and a Strategy. A major conclusion of the report was that new sensor methods and monitors will be an important driver for the future success of exposure sciences and exposure assessments. Through its activities, partnerships, and collaborations, NIOSH intends to advance the development, validation, and application of these technologies to occupational environments. Improved exposure assessments will result in enhanced health benefits for individuals and societies, but research needs must be addressed to realize this potential.
NIOSH Resources
2008 Direct Reading Exposure Assessment Methods (DREAM) Workshop
DHHS (NIOSH) Publication Number 2009-133
Shows the presentations and findings created with the support of 12 cosponsors and over 175 participants in the Direct-Reading Exposure Assessment Methods (DREAM) Workshop (November 13-14, 2008; Arlington, VA; Hilton Crystal City). The workshop gathered stakeholder input from academia, labor, management, developers, governmental agencies, and manufacturers on the research needs in the area of direct-reading methods for assessing occupational exposures.
Exposure Assessment Cross-Sector Program
Describes the field of exposure assessment. This program provides guidance to NIOSH efforts that identifies and characterizes workplace exposures, develops estimates of exposure for exposure-response and risk assessment studies, and evaluates the significance of exposure and effectiveness of intervention strategies.
http://blogs.cdc.gov/niosh-science-blog/2014/04/09/sound-apps/#_blank
The NIOSH Science Blog provides an ongoing opportunity to share the latest information about important issues for worker protection. Read more on new developments in sound measurements highlighted the responses of NIOSH noise researchers to numerous requests from stakeholders, safety professionals, and the public to address the accuracy of the many sound measurement applications available for smartphones and whether they can be relied upon to provide an accurate assessment of the ambient environment.
Components for Evaluation of Direct-Reading Monitors for Gases and Vapors
DHHS (NIOSH) Publication Number 2012-162
Expands the historical NIOSH methods for monitor development and evaluation testing to include: performance characteristics, a summary of recommended tests to evaluate the monitors, and approximations for estimating accuracy.
Addendum to Components for Evaluation of Direct-Reading Monitors for Gases and Vapors: Hazard Detection in First Responder Environments
DHHS (NIOSH) Publication Number 2012-163
Expands the applicability of the Components document by presenting methods to be used in evaluating direct-reading monitors for hazard detection in First Responder environments, including those related to incidents involving weapons of mass destruction (WMD).
NIOSHTIC 2 Database Search
This link provides the results of a search of the NIOSHTIC-2 database for citations and abstracts of NIOSH documents related to direct-reading and sensor technology.
Other Government Resources
NSI White Paper: Nanotechnology for Sensors and Sensors for Nanotechnology: Improving and Protecting Health, Safety, and the Environment
This white paper details the Nanotechnology Signature Initiative on Nanotechnology for Sensors and Sensors for Nanotechnology: Improving and Protecting Health, Safety, and the Environment. The NNI agencies recognize the considerable potential for nanotechnology to open the door to the development of inexpensive, portable devices that can rapidly detect, identify, and quantify biological and chemical substances.
Information and Contact
NIOSH invites your participation to explore and further the development of new direct reading and sensor technologies to improve the health of workers and the public.
Questions, comments, and partnerships are welcome. Please contact the NCDRST Director Gayle DeBord or Co-Director Mark Hoover.
- Page last reviewed: July 24, 2014
- Page last updated: July 24, 2014
- Content source:
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Division of Applied Research and Technology (DART)


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir