Division of Bacterial Diseases (DBD) News Bulletin
This website is archived for historical purposes and is no longer being maintained or updated.
April 16, 2013: Content on this page kept for historical reasons.
In This Issue
- Best Wishes
- Quarter 1
- Quarter 2
- Quarter 3
- Quarter 4
- 2013 Events
Winter 2012
Quarter 4

Cake promoting Get Smart Week at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Helping the World Get Smart about Antibiotics
Get Smart About Antibiotics Week 2012 highlighted the threat of antibiotic resistance and the importance of appropriate antibiotic use nationally and globally. Promoting good antibiotic stewardship and collaborating with a host of partners to educate and inform the public about appropriate antibiotic use is a year round activity of the staff of DBD’s Get Smart: Know When Antibiotics Work campaign, which works in partnership with DHQP’s Get Smart for Healthcare campaign and state-based appropriate antibiotic use campaigns and partners to increase awareness of antibiotic resistance and the importance of appropriate antibiotic use. For the past 5 years, annually in November, the program collaborates with domestic and global partners to focus even more attention on the need for appropriate antibiotic use. Get Smart About Antibiotics Week 2012 highlighted the threat of antibiotic resistance and the importance of appropriate antibiotic use nationally and globally.

RDB’s Lauri Hicks is interviewed by Jeff Hullinger of Atlanta’s 11 Alive News during Get Smart About Antibiotics Week.
DBD highlights of this year’s activities in the United States included launch of the CDC/IHI Driver Diagram and Change Package for Antibiotic Stewardship, a conceptual model to improve antibiotic use in hospitals that will reduce resistance and complications related to antibiotic use (e.g., Clostridium difficile diarrhea); Twitter chats; launch of a new 5-week television and YouTube campaign about only using antibiotics when necessary for parents of young children; release of a joint policy statement on antibiotic use; results of a Pew Health Group Poll; and information in various professional journals.

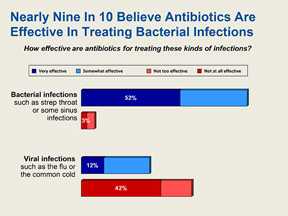
The program collaborated with the Pew Health Group on a poll to gauge Americans’ understanding of proper antibiotic use. Poll findings, released in a media briefing during Get Smart About Antibiotics Week, emphasized the importance of broad dissemination of Get Smart’s educational messages on appropriate antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance. The Pew Poll showed that nearly 9 in 10 Americans recognize antibiotics as effective treatments for fighting bacterial infections like strep throat, but more than a third mistakenly believe antibiotics are also appropriate treatments for viral infections like the common cold. The poll also showed that most Americans (79%) understand that taking antibiotics when not needed may endanger their own health, but only 47% understand that doing this can also harm others. It is important that the public understand that antibiotic-resistant bacteria can quickly spread to family members, schoolmates, and co-workers—threatening the community with a new strain of infectious disease that is more difficult to cure and more expensive to treat. Most Americans (58%) have heard either a “fair amount” or a “great deal” about antibiotic resistance. Of those who have heard a great deal, 68% believe it is a “very big problem.”
A media telebriefing was held to release a “Joint Statement on Antibiotic Resistance with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and 25 National Health Organizations” that outlines strategies to conserve and replenish antibiotic resources. In the statement, representatives from a range of fields concerned with human health jointly recognized a collective responsibility to protect the effectiveness of all antibiotics, calling for a greater coordination among all stakeholders in antibiotic effectiveness, including healthcare personnel, hospital administrators, policymakers, patients, and individuals working in medical centers, universities, and pharmaceutical companies to promote knowledge sharing and a mutual commitment to improving antibiotic use, a practice referred to as antibiotic stewardship.

Lauri Hicks and Arjun Srinivasan recording audio quotes for the Get Smart About Antibiotics Week digital press kit.
In Australia, Antibiotic Awareness Week was officially supported by the Australasian Society for Infectious Diseases, the Australian Society for Antimicrobials, the Australian Commission for Safety and Quality in Health Care, and by NPS MedicineWise as part of a 5-year campaign to address antibiotic resistance in Australia.
In Canada, an ongoing initiative, AntibioticAwareness.ca, coordinated by numerous health-related organizations across the country that had partnered last year to promote the first Antibiotic Awareness Day in Canada extended its activities to hold a Canada Antibiotic Awareness Week.
As part of European Antibiotic Awareness Day 2012, experts from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), the World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe, the Directorate-General (DG) for Research and Innovation and the DG for Health and Consumers of the European Commission held a live Twitter chat to answer questions on antibiotic resistance. Dr. Marc Sprenger, Director of ECDC, and Dr. Tom Frieden joined forces to tweet messages to mark global action to slow the spread of antimicrobial resistance threats. This is the 5th year that ECDC has held an antibiotic awareness day.

Teneva Hardy (right) acted as keyworker for the annual Combined Federal Campaign (CFC) at CDC. She has promoted campaign participation among staff in buildings 23 and 24 for 2 years to support NCIRD’s efforts to raise funds for the world’s largest and most successful annual workplace charity campaign. Here, Teneva reviews contribution options with DBD’s Tracey Pondo (left), who looks forward to supporting the campaign every year. The CFC allows federal employees and contractors to donate to a variety of organizations ranging from medical research to community improvement to youth development. NCIRD staff contributed $33, 604 to the campaign this year.
Stephen Hadler worked in the Polio Eradication Emergency Operations Center (EOC) much of the year as team lead for the Eastern Mediterranean Region, helping to guide CDC support for Pakistan and Afghanistan to implement emergency action plans to eradicate polio. Steve traveled to Afghanistan 3 times during the year to support this global health emergency. Other staff members from DBD involved in the polio eradication efforts include Sarah Meyer, who made two trips to DRC Congo and Burkina Faso, and Cindy Hatcher, who went to DRC Congo.
Helping to deliver a life-saving vaccine to 100 million

DBD has a long history of involvement in Africa’s meningitis belt and under the guidance of MVPD branch chief Nancy Messonnier (pictured below 4th row, 2nd from left) activities continue to expand. Last spring, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation funded a meeting in Dakar, Senegal co-hosted by CDC and the London School of Tropical Hygiene and Medicine during which DBD subject matter experts helped to develop research priorities for meningococcal disease in Africa. Current activities include working with ministries of health and global partners on post vaccine evaluations, lab training and other technical assistance. Staff are extremely proud to be a part of helping MenAfriVac® (the vaccine to protect against meningococcal A disease epidemics in sub Saharan Africa) to reach the 100 millionth person. The historic achievement came in early December during a seasonal immunization campaign in northern Nigeria—just two years after the vaccine was first launched in Burkina Faso. Since then, nine other countries have held vaccination campaigns to protect people from ages 1 to 29 against meningitis A. The vaccine can now be transported and stored for as long as four days without refrigeration or even an icepack—making it the first vaccine intended for use in Africa approved for this type of use, potentially setting a regulatory path that other heat-stable vaccines can follow. With the vaccination campaigns planned in Nigeria, Cameroon and Chad, by the end of this year, MenAfriVac® will have reached more than 112 million people, providing widespread and long-awaited protection against meningococcal A disease epidemics.

Rana Hajjeh (center) with CDC and hospital staff in Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), in October 2012. Rana led a team from CDC that included epidemiologists and microbiologists to assist KSA in investigating a case of a novel coronavirus diagnosed for the first time in the Kingdom. CDC worked with WHO and other international experts to determine the public health implications of this new virus. CDC assisted in building diagnostic capacity for this novel virus and provided technical guidance to health authorities, in preparation for the upcoming annual Muslim Hajj pilgrimage—the world’s largest annual religious gathering to the city of Mecca—that brings millions of people to KSA, to ensure early detection of additional cases and implementation of adequate prevention measures. No additional cases were reported during the Hajj season.
Marsha Houston represented the agency on the Global Coalition against Childhood Pneumonia, lending technical assistance to global activities for the 4th Annual World Pneumonia Day (http://worldpneumoniaday.org/). DBD’s work on pneumonia was highlighted in a CDC Connects article on November 9. Alison Patti coordinated CDC Internet and social media exposure and the November issue of CDC’s Emerging Infectious Diseases Journal featured a commentary by Rana Hajjeh and Cynthia Whitney titled “Call to Action on World Pneumonia Day”, as well as articles on results of recent research on pneumonia.

Fabiana Pimenta, a microbiologist in DBD, conducts a training session on pneumococcal detection and serotyping with lab staff at the Universidad del Valle in Guatemala City.
Lauri Hicks presented “How to improve antibiotic prescribing practices” for grand rounds at The Pennsylvania Medical Society in Harrisburg, PA.
Melissa Lewis presented “Improving disease measurement in pregnant women: a simulation approach” and Elizabeth Zell participated as a Governing Council representative for the statistics session at the 140th American Public Health Association Annual Meeting and Exposition in San Francisco, CA.
Claressa Lucas presented “The CDC Legionella Lab: 35 years of surveillance” for a seminar series at Clemson University in Clemson, SC.
Lara Misegades was interviewed by JAMA about her DTaP vaccine effectiveness paper published in late November. The video story was distributed to US and Canada television. JAMA also recorded an author monologue video with Lara that was shared with JAMA subscribers.
Matt Moore presented “Pneumococcal vaccines across the lifespan” at the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases(NFID) Vaccinology Course in Miami, FL.
The 1st International Conference of the African Society for Laboratory Medicine (ASLM) was held December 1-7, 2012 in Cape Town, South Africa. Leonard Mayer (DBD/MVDPB) presented “The use of real-time PCR for laboratory diagnosis of bacterial meningitis.” Lesley McGee (DBD/RDB) presented “Streptococcus pneumoniae, detection in bacterial meningitis.”

Anne Schuchat, Acting Director of the Center for Global Health with Rana Hajjeh at the 5th GAVI Partners Forum at the Accelerated Vaccine Initiative-Technical Assistance Consortium (AVI-TAC) in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania in December.
Leonard Mayer presented “Innovations for enhancing laboratory diagnostic capacity for vaccine-preventable diseases” at an AFRO Regional Meeting on Immunization in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania.
Tami Skoff was a keynote speaker and presented “Coughing up the facts—pertussis epidemiology and emerging trends in the U.S.” at the Annual NY Emerging Infection Program Network 2-day roadshow in Buffalo, Rochester and Albany, NY.
During the Global Meeting on Immunization Monitoring and Surveillance in Washington, DC, Chris Van Beneden presented “Use of sentinel surveillance vs. population-based surveillance to accurately monitor the impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine” and “How best to present data from the IB VPD network? Common mistakes and suggestions for improvement.” For the Scientific Symposium on the Introduction of New Vaccines held in Haiti, Chris presented “Accelerating life-saving vaccine introduction—lessons from the Hib Initiative” and “Impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in the U.S. following universal vaccine introduction.”
A new manual, Measuring impact of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influnzae type b conjugate vaccination (WHO/IVB/12.08), that describes approaches to measuring vaccine impact and a framework for determining the best methodology for use in different settings was posted on the WHO website (http://www.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/75835/1/WHO_IVB_12.08_eng.pdf). The manual was written by experts from the GAVI AVI-TAC Special Studies consortium and led by CDC/NCIRD scientists.

Tamara Pilishvili recorded a Medscape video discussing recommendations for pneumococcal conjugate and polysaccharide vaccine use for adults with high risk medical conditions.
Jonas Winchell and Stephanie Schrag presented at the ANISA (Aetiology of Neonatal Sepsis in Southeast Asia) Third Investigators’ Meeting in Phuket,Thailand. Jonas discussed further optimizations of the molecular testing procedures and TAC cards and Stephanie discussed progress on the Technical Advisory Group recommendations and presented on the project’s preliminary analysis of the multisite data. Cynthia Whitney and Lesley McGee also attended. ANISA is currently enrolling pregnant women and their newborns in Pakistan, Bangladesh, and India.
Elizabeth Zell and Tamara Pilishvili presented at the Vaccine Effectiveness (VE) Methods meeting in London, England. Rana Hajjeh, Jennifer Loo, Jennifer Verani, and Cindy Whitney attended sessions that discussed sources of bias in case control VE studies (Hib, pneumococcal, influenza and rotavirus vaccines), relevant studies, datasets and partners for future analytic work to understand biases, developing evaluation plans on important biases, and approaches to developing and disseminating recommendations.

Rana Hajjeh, Vance Dietz (GID/CGH), Peter Bloland (Director, CGH/DPHSWD) David Mekontso (Cameroun), Regis Mbarydaba (CAR) on a surveillance site visit to a district regional hospital in Cameroun in October.
DBD was well represented during ID Week in San Diego, CA, this year: Anna Acosta presented “Preventing pertussis in older adults: cost effectiveness analysis of a one-time tetanus toxoid-reduced diphtheria toxoid-acellular pertussis (Tdap) dose in adults aged 65 years and older”; Kathleen Dooling presented the poster “Investigation of a prolonged group A streptococcal outbreak among residents of a skilled nursing facility, Georgia, 2009–2011”; Jennifer Liang presented “Rationale for changes to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommendations on the use of tetanus toxoid-reduced diphtheria toxoid-acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccines for pregnant women in the United States”; Matt Moore presented “Impact of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on invasive disease in the US”; Manisha Patel presented “Persistence of serogroup C antibody responses following quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccination in US military personnel”; Jennifer Verani presented “Potential for further reduction of early-onset group B streptococcal disease in neonates”; and Jonathan Wortham presented “Burden of ambulatory visits and antibiotic prescribing for adults with community-acquired pneumonia—United States, 1998–2009.”

Leonard Mayer at the December African Society for Laboratory Medicine (ASLM) Conference in Cape Town, South Africa congratulates Dr. Rasmata Ouedraogo Traore, a professor of bacteriology-virology and close collaborator with DBD on its meningitis activities in Burkina Faso on receipt of an award. DBD nominated Dr. Rasmata for the ASLM Best Practice in laboratory Medicine in Africa Award for 2012. Dr. Rasmata says about the honor, “This recognition has been possible thanks to the CDC partners and commitment of Burkinabe particularly technical players in the labs.” MVPDB has a long and on-going relationship with the Ministry of Health in Burkina Faso where CDC is conducting vaccine effectiveness studies following the introduction of MenAfriVac® in 2010, and lending technical support and training for the country’s laboratories among other activities.
- Page last reviewed: April 16, 2013 (archived document)
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir