NCHS Nutrition Data
NCHS Fact Sheet, March 2017
PDF Version (310 KB)
About NCHS
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) is the nation’s principal health statistics agency, providing data to identify and address health issues. NCHS compiles statistical information to help guide public health and health policy decisions.
Collaborating with other public and private health partners, NCHS uses a variety of data collection mechanisms to obtain accurate information from multiple sources. This process provides a broad perspective on the population’s health, influences on health, and health outcomes.
Nutrition Data
For over 45 years, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), a major program of NCHS, has collected comprehensive data on health and nutrition, including dietary intakes. NHANES is an ongoing, nationally representative survey of the U.S. population that combines interviews with standardized physical examinations and laboratory tests conducted in a mobile examination center (MEC). NHANES can directly measure health conditions and provide reliable information on health and disease.
NHANES dietary data are collected via 24-hour dietary recall. At the MEC, participants provide details on food and beverages consumed on the preceding day. A second recall is obtained over the telephone 3–10 days later. Data on dietary supplement use during the past month are collected at the household interview and subsequently during the 24-hour recalls.
Federal agencies, researchers, health care providers, and policymakers use these data to assess and monitor the nutrition intake and status of the U.S. population as well as to inform nutrition policy and programs.
Recent Findings on Dietary Intake
NHANES data on dietary intake (food, beverages, and dietary supplements) are used to estimate food and nutrient intakes by the U.S. population and by specific age, gender, and racial and ethnic groups.
Energy intake and sources of energy for U.S. adults
- In 2013–2014, on average men and women consumed 2,477 and 1,825 calories on a given day. The contribution to total calories consumed from fat, carbohydrate, and protein on a given day were 34%, 47%, and 16% for men and 34%, 49%, and 16% for women.
Percentage of calories consumed from fat, carbohydrate, and protein by adults aged 20 years and over on a given day, by sex: United States, 2013–2014
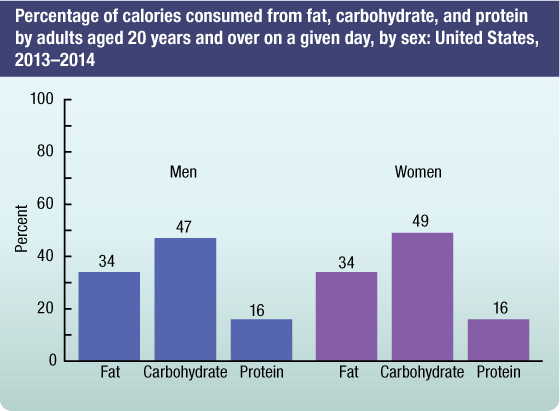
SOURCE: NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011–2012 and 2013–2014.
Sugar-sweetened beverages
The 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend reducing added sugars consumption to less than 10% of daily calories and specifically to choose beverages with no added sugars.
- Almost two-thirds of U.S. youth 2–19 years of age and approximately one-half of adults aged 20 years and over consumed at least one sugar-sweetened beverage on a given day in 2011–2014. The consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages was more common among males compared with females among both adults and children.
- In 2011–2014, U.S. adults and youth (aged 2–19 years) consumed an average of approximately 145 calories from sugar-sweetened beverages on a given day (i.e., about 7% of their total caloric intake on a given day came from sugar-sweetened beverages for both U.S. adults and youth).
Percentage of youth and adults who consumed sugar-sweetened beverages on a given day by sex: United States, 2011–2014
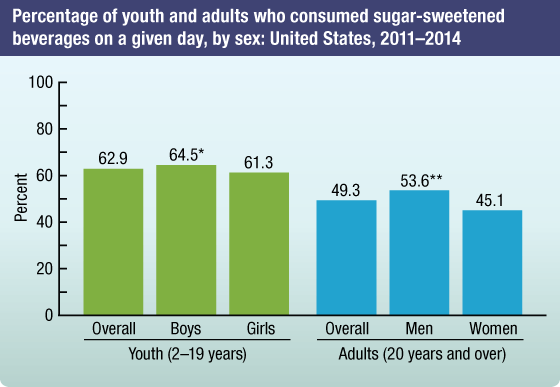
*Significantly different from girls. ** Significantly different from women.
SOURCE: NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011–2012 and 2013–2014.
Dietary supplements
NHANES data from 2013–2014 show that a little more than half of adults 20 years and over (54%) reported consuming at least one dietary supplement in the past 30 days.
- The most common supplements consumed were multivitamin or multimineral products, reported by about one-third of adults.
- A greater proportion of adult women reported consuming one or more dietary supplements in the past 30 days (61%) compared to adult men (46%).
- There were no significant differences overall or by sex in the prevalence of dietary supplement use between 2011–2012 and 2013–2014.
Percentage of adults aged 20 years and over who consumed dietary supplements in the past 30 days, overall and by sex: United States, NHANES 2011–2012 and 2013–2014
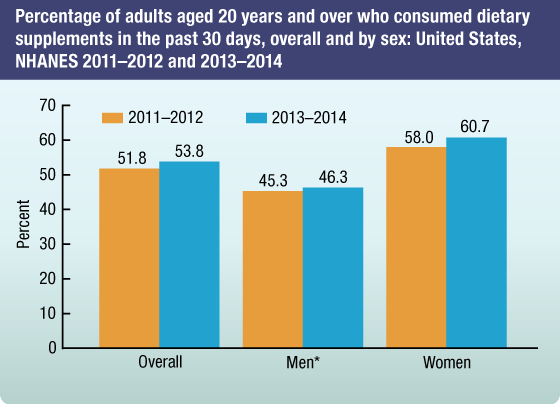
*Significantly different from women in both 2011–2012 and 2013–2014.
SOURCE: NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011–2012 and 2013–2014.
Additional nutrition findings
- Most children and adults do not eat enough dietary fiber. Based on NHANES 2013–2014 data, the mean dietary fiber intake by Americans aged 2 years and older, excluding breastfed children, was 16 grams on a given day; fiber intake of adult men and women on a given day was 18 and 15 grams, respectively. Dietary fiber intake was positively associated with income.
- During 2013–2014, 67.0% of children aged 2–19 years consumed caffeine on a given day. The percentage of children consuming caffeine on a given day increases with age: 55.3% of children aged 2–5 years, 69.1% of children aged 6–11 years, and 70.7% of children aged 12–19 years.
- In 2013–2014, about one-quarter of total calories consumed by U.S. children and adult men or women on a given day were from consumption of snacks.
- Most adults consume more sodium than recommended. In 2013–2014, the average consumption of sodium exceeded the maximum daily limit (under 2300 milligrams) for both children (aged 2–19 years) and adults (aged 20 years and over) regardless of their sex.
- In 2013–2014, over two-thirds of Americans (aged 2 years and over), reported consuming food and beverages away from home. One-third of total calories consumed by Americans on a given day were consumed away from home.
For further information about NCHS, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs.
For further information about NHANES, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm.
- Page last reviewed: April 6, 2017
- Page last updated: April 6, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir