National Survey of Family Growth
NCHS Fact Sheet, July 2017
PDF Version (872 KB)
About NCHS
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) is the nation’s principal health statistics agency, providing data to identify and address health issues. NCHS compiles statistical information to help guide public health and health policy decisions.
Collaborating with other public and private health partners, NCHS uses a variety of data collection mechanisms to obtain accurate information from multiple sources. This process provides a broad perspective on the population’s health, influences on health, and health outcomes.
National Survey of Family Growth
The National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG) collects information on families, fertility, and health from a national sample of males and females aged 15−49 in the household population of the United States.
The NSFG was conducted five times with a national sample of females aged 15-44 periodically between 1973 and 1995. A sixth periodic survey, conducted in 2002, included both males and females aged 15-44. In 2006, the NSFG shifted to a continuous, ongoing survey design, interviewing males and females. In September 2015, the age range was expanded to males and females aged 15−49.
Topics addressed include:
- Marriage, divorce, cohabitation
- Women’s pregnancy and birth history, and men’s fathering of biological children
- Breastfeeding
- Adoption and nonbiological parenting
- Contraceptive use
- Intendedness of pregnancies
- Sexual intercourse and number of sexual partners
- Family planning and related medical services
- Infertility and use of infertility services
- Attitudes on sex, parenthood, marriage, and cohabitation
- Men’s involvement as fathers with children they do and do not live with
- Other sexual behaviors (besides vaginal intercourse) that may carry risk of HIV or sexually transmitted infections, including same-sex behavior
- Sexual orientation and attraction
In 2011−2015, the most popular methods of contraception among females aged 15−44 in the United States were the pill (26%), female sterilization (23%), the male condom (15%), and long-acting reversible contraception (LARC, intrauterine devices and implants) (13%). Together, these four methods accounted for 77% of current contraceptive users.
- Current use of the pill was higher among females aged 15−19 than other age groups; female sterilization was the leading method among women aged 35−44.
- A higher percentage of Hispanic women were using a LARC method compared with non-Hispanic, White and non-Hispanic, Black women.
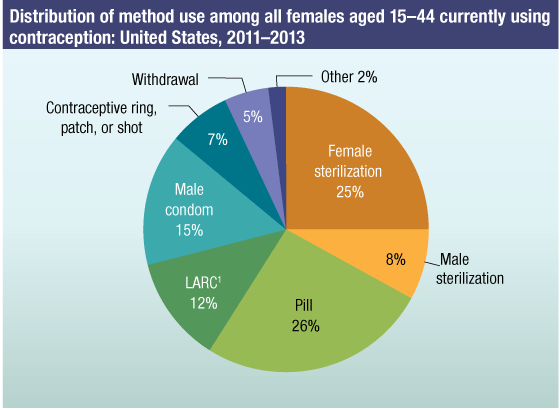
1LARC is long-acting reversible contraception and includes intrauterine devices (IUDs) and implants.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Survey of Family Growth, 2011–2015.
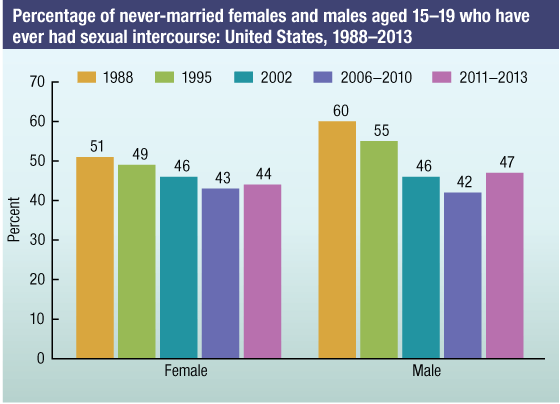
SOURCES: CDC/NCHS, National Survey of Family Growth, 1988–2013, and National Survey of Adolescent Males, 1988 and 1995.
Sexual activity among teenagers
In 2011−2015, about 2 out of every 5 never-married teenagers (aged 15–19) had ever had sexual intercourse.
- Among never married male teenagers, the percentage who ever had sexual intercourse declined from 60% in 1988 to 44% in 2011-2015. However, this percentage was not significantly different than the 42% of male teens who ever had sex in 2006-2010.
- The percentage of never-married female teenagers who ever had sexual intercourse declined from 51% in 1988 to 42% in 2011-2015. This 2011-2015 percentage was not significantly different than the 43% of female teens who ever sex in 2006-2010.
Additional findings from the 2011-2015 NSFG
- In 2011-2015, 49.5% of women and 43.8% of men aged 15-44 had ever been married.
- More than one-half of males (57%) and females (52%) aged 15–44 in 2011–2015 have cohabited at some time; 15% of women and 13% of men were currently cohabiting.
- Among singleton babies born in 2013-2015, 79% were breastfed at all, and 57% were breastfed for 3 months or longer (57%).
- Approximately 26% of first births to women aged 15−44 in 2011–2015 occurred within a cohabiting union.
- About 20% of men aged 40−44 in 2011–2015 had not fathered any children, 20% had fathered one child, 31% two, and 29% had fathered three or more children.
- In 2011-2015, 23% of women 15-44 and 16% of men 15-44 had been tested for HIV in the past year.
- In 2011−2015, 12% (7.3 million) of women aged 15−44 reported that they had ever used any infertility services.
- In 2011–2015, women on average expected to have 2.3 children in their lifetime. This estimate has decreased since 2002.
- Among men and women aged 15-44 in 2011-2015, 4% of men and 1.7% of women reported having 5 or more opposite-sex sexual partners in the past year.
Challenges and Future Opportunities
Future plans for NSFG include releasing the 2015-2017 data next year, and redesigning the survey questionnaire as needed to respond to changes in data needs in the area of reproductive health, family planning, and family formation. The survey will also continue to implement strategies to make continuous interviewing as efficient as possible in the face of declining response rates and other challenges.
For further information about NCHS and its programs, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs.
For further information on NSFG, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nsfg.htm.
- Page last reviewed: November 6, 2015
- Page last updated: October 13, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir