Health Insurance and Access to Care
NCHS Fact Sheet, February 2017
PDF Version (240 KB)
About NCHS
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) is the nation’s principal health statistics agency, providing data to identify and address health issues. NCHS compiles statistical information to help guide public health and health policy decisions.
Collaborating with other public and private health partners, NCHS uses a variety of data collection mechanisms to obtain accurate information from multiple sources. This process provides a broad perspective on the population’s health, influences on health, and health outcomes.
Health Insurance and Access to Care
Health insurance coverage is an important determinant of access to health care. Uninsured children and nonelderly adults are substantially less likely to have a usual source of health care or a recent health care visit than their insured counterparts. The majority of persons under age 65 have coverage through private employer-sponsored group health insurance. Private health insurance may also be purchased on an individual basis. Starting in 2014, U.S. adults could buy a private health insurance plan through the Health Insurance Marketplace or state-based exchanges established as part of the Affordable Care Act. Moreover, some states opted to expand Medicaid coverage to low-income adults.
Health Insurance Data
The National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) collects comprehensive data on health insurance coverage. Three estimates of lack of health insurance coverage are provided quarterly: (a) uninsured at the time of the interview, (b) uninsured at least part of the year prior to the interview, and (c) uninsured for more than a year at the time of interview. Data are also provided on public and private coverage for those currently insured, including data on enrollment through the Health Insurance Marketplace and state-based exchanges, and in consumer-directed health plans. For 2015, NHIS reported state-specific health insurance estimates for all 50 states and the District of Columbia for persons of all ages, persons under age 65, and adults aged 18−64. State-specific estimates were reported for 34 states on coverage for children aged 0–17 years.
NHIS data on uninsured adults aged 18–64 by race and ethnicity for the first 6 months of 2016 show:
- A total of 24.8% of Hispanic, 14.8% of non-Hispanic black, 8.7% of non-Hispanic white, and 7.2% of non-Hispanic Asian adults lacked health insurance coverage at the time of interview. Hispanic adults had the greatest percentage point decrease in the uninsured rate between 2013 (40.6%) and the first 6 months of 2016 (24.8%).
NHIS data on health insurance coverage for adults aged 18–64 from 1997 through the first 6 months of 2016 show:
- The percentage of uninsured decreased from 20.4% in 2013 to 12.4% in the first 6 months of 2016. During this 3-year period, corresponding increases were seen in both public and private coverage among adults aged 18–64.
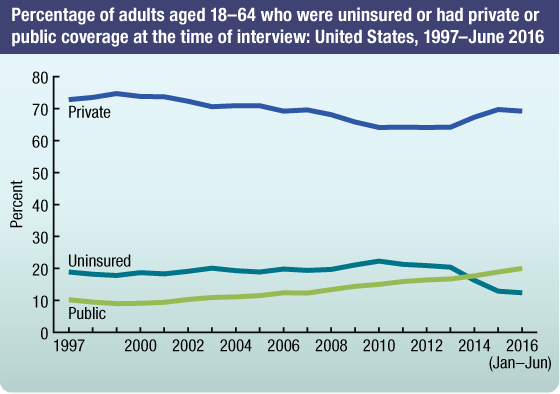
NOTE: Data are based on household interviews of a sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized population.
SOURCE: NCHS, National Health Interview Survey, 1997–2016, Family Core component.
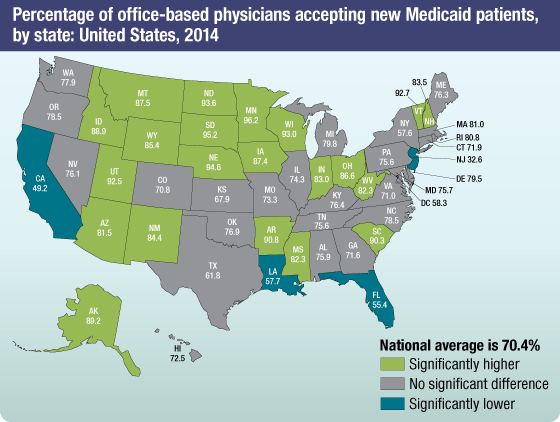
SOURCE: NCHS, National Health Care Surveys, National Electronic Health Records Survey, 2014.
Access to Care Data
Clinical experts note that with access to timely and appropriate ambulatory care, patients may be able to prevent illness, control acute episodes, or manage chronic conditions to avoid exacerbating or complicating those conditions. Although health insurance coverage levels provide a strong indication of Americans’ access to health care, other measures enhance understanding of this issue and point to solutions to improve access.
Usual place to go for medical care
NHIS data for January–June 2016 show:
- The percentage of persons of all ages who had a usual place to go for medical care decreased from 87.9% in 2003 to 85.4% in 2010, and then increased to 87.9% in January–June 2016.
Data by race and ethnicity show:
- The percentage of persons with a usual place to go for medical care by race and ethnicity in the first half of 2016 was 82.5% for Hispanic, 89.4% for non-Hispanic white, and 85.8% for non-Hispanic black persons.
Office-based physician practices
Data from NCHS’ National Health Care Surveys provide insights into access to care. The percentage of physicians accepting new patients—which varies by type of payment—is a measure of physician capacity to meet increased demand. Data for 2014 show:
- The majority of physicians reported that they accepted new patients with private insurance (91%), compared with 70% who accepted new patients with Medicaid.
- Twenty-one states had physician acceptance rates for new Medicaid patients higher than the national average of 70%.
- Physician acceptance rates for Medicaid patients were lower than the national average in four states. A previous study using NCHS data found that higher state Medicaid-to-Medicare fee ratios were correlated with greater acceptance of new Medicaid patients.
Health Insurance and Access to Care Data Sources
- National Health Interview Survey—Collects information on the nation’s health through personal household interviews that measure health status and disability, selected conditions, insurance coverage, access to care, use of health services, immunizations, health behaviors, injury, and the ability to perform daily activities. For more information, visit the NHIS website at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.
- National Health Care Surveys—A family of health care provider surveys that together obtain information about the facilities that supply health care, the services rendered, and the characteristics of the patients served. Sites surveyed include: hospitals, office-based physician practices, emergency and outpatient departments, ambulatory surgery centers, nursing homes, and home health and hospice agencies. For more information, visit the NHCS website at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhcs.
For further information about NCHS, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs.
- Page last reviewed: March 9, 2017
- Page last updated: March 9, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir