Nitrate/Nitrite Toxicity
What Are Nitrates and Nitrites?
Course: WB 2342
CE Original Date: December 5, 2013
CE Renewal Date: December 5, 2015
CE Expiration Date: December 5, 2017
Download Printer-Friendly version [PDF - 1.1 MB]
| Previous Section | Next Section |
Learning Objective |
Upon completion of this section, you will be able to
|
Introduction |
Nitrates and nitrites can be categorized into inorganic and organic forms based on their chemical structure. There are similarities and differences between these two chemical forms that affect their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and their subsequent biologic effects in humans. This course will focus on inorganic nitrates. |
Inorganic Nitrates and Nitrites |
Inorganic nitrate (NO3-) and nitrite (NO2-) are water soluble (as a result of their interaction with the positively charged portions of polar water molecules) (Figure 1) and commonly exist as salts of nitric acid and nitrous acid, respectively. They are often bound to a metal cation such as Na+ or K+ and occur naturally through the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen as part of the environmental nitrogen cycle (the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms from the environment, to organisms, and then back to the environment as illustrated in Figure 2). Inorganic nitrites are also produced endogenously through oxidation of nitrous oxide (NO) formed from the enzymatic degradation of L-arginine and through the reduction of nitrate with xanthine oxidoreductase [Omar et al. 2012; Jansson et al. 2008; Rhodes et al. 1995; Leaf et al. 1989; Green et al. 1981]. |
Organic Nitrates and Nitrites |
The organic forms of nitrates and nitrites are more complex and most are synthesized medicinal products (except ethyl nitrite) [Omar et al. 2012]. See Table 2. Organic nitrates are small non-polar hydrocarbon chains attached to a nitrooxy-radical (-ONO2; -ONO for amyl and ethyl nitrite). The addition of aliphatic or aromatic groups of variable length and volume affect the lipophilic properties of these molecules [Thatcher et al. 2004]. It has been suggested that for some molecules, the greater the number of -ONO2 groups, the greater its potency [Wenzel et al 2007] (the potency being dependent on the molecule's lipophilicity). |
Structures of Nitrate and Nitrite Ions |
Figure 1. Structures of Nitrate and Nitrite Ions
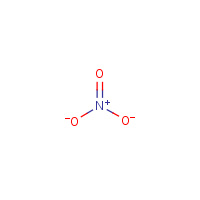
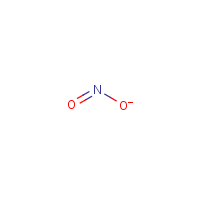 |
Key Points |
|
Progress Check |
| Previous Section | Next Section |


