Pterulone
Pterulone is a fungal metabolite. It was initially isolated from the mycelium and liquid cultures of wood-decay fungus in the genus Pterula. The compound inhibits eukaryotic respiration by targeting the mitochondrial NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
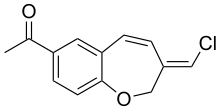
| IUPAC name
1-[(3Z)-3-(chloromethylidene)-2,3-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-7-yl]ethanone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C13H11ClO2 |
| Molar mass | 234.678 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Engler M, Anke T, Sterner O, Brandt U (1997). "Pterulinic acid and pterulone, two novel inhibitors of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) produced by a Pterula species. I. Production, isolation and biological activities". Journal of Antibiotics. 50 (4): 325–9. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.50.325. PMID 9186558.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.