Intima-media thickness
Intima–media thickness (IMT), also called intimal medial thickness, is a measurement of the thickness of tunica intima and tunica media, the innermost two layers of the wall of an artery. The measurement is usually made by external ultrasound and occasionally by internal, invasive ultrasound catheters. Measurements of the total wall thickness of blood vessels can also be done using other imaging modalities.
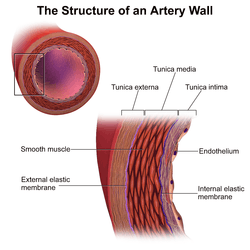
IMT is used to detect the presence of atherosclerosis in humans and, more contentiously, to track the regression, arrest or progression of atherosclerosis.[1] Ultrasound IMT measurements were first proposed and validated in vitro by Paolo Pignoli in 1984[2] and further details were subsequently published in a highly cited article.[3] The use of IMT as a non-invasive tool to track changes in arterial walls has increased substantially since the mid-1990s.[1] Although IMT is predictive of future cardiovascular events,[4] the usefulness of measuring change in IMT over time is disputed, as meta-analyses have not found that change in IMT is predictive of cardiovascular events.[5][6] As such, the use of change in IMT as a surrogate endpoint measure of drug efficacy in clinical trials, or in clinical management of cardiovascular disease, is debated.[5]
IMT is occasionally used in clinical practice, but its role is not clear.[7] After systematically reviewing the evidence base, the United States Preventive Services Task Force found no support for its routine use in stratification of risk for people at intermediate cardiovascular risk.[8] However, in 2003 the European Society of Hypertension–European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension[9] recommended the use of IMT measurements in high-risk patients to help identify target organ damage and in 2010 the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology advocated the use of IMT on intermediate risk patients if usual risk classification was not satisfactory.[10]
Measurement of IMT
IMT can be measured using external ultrasound in large arteries relatively close to the skin (e.g. the carotid, brachial, radial, or femoral arteries). External ultrasound methods have the advantage of being non-invasive, comparatively low cost and convenient. Deeper internal arteries, such as the coronary arteries require special intravascular catheters employing ultrasound or optical coherence tomography to measure IMT.[11]
The carotid artery is the usual site of measurement of IMT and consensus statements for carotid IMT have been published for adults[12] and children.[13] Often, IMT is measured in three locations: in the common carotid artery (typically at one cm proximal to the flow divider), at the bifurcation, and in the internal carotid artery.[14][15] IMT measurements of the far (deeper) wall, by ultrasound, are generally considered more reliable than measurements performed on the near (more superficial) wall;[14] although measurement of both near and far wall IMT has also been advocated.[16]
Carotid IMT has been used in many epidemiological and clinical studies and these have shown associations with several risk factors, including type 2 diabetes,[17] familial hypercholesterolemia,[18] high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglycerides,[19] rheumatoid arthritis,[20] non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,[21] and air pollution.[22] Since the 1990s, some clinical trials of lifestyle and pharmaceutical interventions have also used carotid artery IMT as a surrogate endpoint for evaluating the regression and/or progression of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease;[23] however the appropriateness of carotid IMT in this context is uncertain.[24] Although carotid intima-media thickness is strongly associated with atherosclerosis, thickening of the intima-media may not always be due to atherosclerosis. Intima-medial thickening is a complex process, depending on a variety of factors, including blood pressure,[25] local hemodynamics,[25] shear stress[25] and circumferential tensile stress.[25] Variations in IMT between different locations (e.g. the common carotid artery, the carotid bulb and the internal carotid artery) may reflect differences in local hemodynamic forces.
References
- de Groot, Eric; van Leuven, Sander I; Duivenvoorden, Raphaël; Meuwese, Marijn C; Akdim, Fatima; Bots, Michiel L; Kastelein, John JP (2008). "Measurement of carotid intima–media thickness to assess progression and regression of atherosclerosis". Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine. 5 (5): 280–288. doi:10.1038/ncpcardio1163. ISSN 1743-4297. PMID 18332891.
- Pignoli P (1984). "Ultrasound B-mode imaging for arterial wall thickness measurement". Atherosclerosis Reviews. 12: 177–184.
- Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste PL, Paoletti R (1986). "Intima plus media thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging". Circulation. 74 (6): 1399–1495. doi:10.1161/01.cir.74.6.1399. PMID 3536154.
- Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, Rosvall M, Sitzer M (January 2007). "Prediction of clinical cardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Circulation. 115 (4): 459–67. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.628875. PMID 17242284.
- Costanzo P, Perrone-Filardi P, Vassallo E, Paolillo S, Cesarano P, Brevetti G, Chiariello M (December 2010). "Does carotid intima-media thickness regression predict reduction of cardiovascular events? A meta-analysis of 41 randomized trials". J Am Coll Cardiol. 56 (24): 2006–20. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.05.059. PMID 21126642.
- Lorenz MW, Polak JF, Kavousi M, Mathiesen EB, Völzke H, Tuomainen TP, Sander D, Plichart M, Catapano AL, Robertson CM, Kiechl S, Rundek T, Desvarieux M, Lind L, Schmid C, Dasmahapatra P, Gao L, Ziegelbauer K, Bots ML, Thompson SG; on behalf of the PROG-IMT Study Group. (April 2012). "Carotid intima-media thickness progression to predict cardiovascular events in the general population (the PROG-IMT collaborative project): a meta-analysis of individual participant data". Lancet. 379 (9831): 2053–62. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60441-3. PMC 3918517. PMID 22541275.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Naqvi, Tasneem Z.; Lee, Ming-Sum (2014). "Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Plaque in Cardiovascular Risk Assessment". JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging. 7 (10): 1025–1038. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.11.014. ISSN 1936-878X. PMID 25051948.
- Helfand M, Buckley DI, Freeman M, Fu R, Rogers K, Fleming C, Humphrey LL (6 Oct 2009). "Emerging risk factors for coronary heart disease: a summary of systematic reviews conducted for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force". Ann Intern Med. 151 (7): 496–507. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-7-200910060-00010. PMID 19805772.
- European Society of Hypertension-European Society of Cardiology Guidelines Committee (June 2003). "2003 European Society of Hypertension-European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension". J. Hypertens. 21 (6): 1011–53. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000059051.65882.32 (inactive 2019-08-20). PMID 12777938.
- LPhilip Greenland, MD, FACC, FAHA (15 November 2010). "2010 ACCF/AHA Guideline for Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk in Asymptomatic Adults". Journal of the American College of Cardiology.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Kume, Teruyoshi; Akasaka, Takashi; Kawamoto, Takahiro; Watanabe, Nozomi; Toyota, Eiji; Neishi, Yoji; Sukmawan, Renan; Sadahira, Yoshito; Yoshida, Kiyoshi (August 2005). "Assessment of coronary intima--media thickness by optical coherence tomography: comparison with intravascular ultrasound". Circulation Journal. 69 (8): 903–907. doi:10.1253/circj.69.903. ISSN 1346-9843. PMID 16041157.
- Touboul, P.-J.; Hennerici, M. G.; Meairs, S.; Adams, H.; Amarenco, P.; Bornstein, N.; Csiba, L.; Desvarieux, M.; Ebrahim, S. (2012). "Mannheim carotid intima-media thickness and plaque consensus (2004-2006-2011). An update on behalf of the advisory board of the 3rd, 4th and 5th watching the risk symposia, at the 13th, 15th and 20th European Stroke Conferences, Mannheim, Germany, 2004, Brussels, Belgium, 2006, and Hamburg, Germany, 2011". Cerebrovascular Diseases (Basel, Switzerland). 34 (4): 290–296. doi:10.1159/000343145. ISSN 1421-9786. PMC 3760791. PMID 23128470.
- Dalla Pozza, Robert; Ehringer-Schetitska, Doris; Fritsch, Peter; Jokinen, Eero; Petropoulos, Andreas; Oberhoffer, Renate; Association for European Paediatric Cardiology Working Group Cardiovascular Prevention (February 2015). "Intima media thickness measurement in children: A statement from the Association for European Paediatric Cardiology (AEPC) Working Group on Cardiovascular Prevention endorsed by the Association for European Paediatric Cardiology". Atherosclerosis. 238 (2): 380–387. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.12.029. ISSN 1879-1484. PMID 25555270.
- Stein JH, Korcarz CE, Hurst RT, Lonn E, Kendall CB, Mohler ER, Najjar SS, Rembold CM, Post WS (2008). "Use of carotid ultrasound to identify subclinical vascular disease and evaluate cardiovascular disease risk: a consensus statement from the American Society of Echocardiography Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Task Force. Endorsed by the Society for Vascular Medicine". J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 21 (2): 93–111, quiz 189–90. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2007.11.011. PMID 18261694.
- Filippo Molinari; Jasjit S. Suri; Chirinjeev Kathuria (2010). Atherosclerosis Disease Management. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4419-7221-7.
- Peters, Sanne A.E.; Bots, Michiel L. (2013). "Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Studies: Study Design and Data Analysis". Journal of Stroke. 15 (1): 38–48. doi:10.5853/jos.2013.15.1.38. ISSN 2287-6391. PMC 3779675. PMID 24324938.
- Brohall G, Odén A, Fagerberg B (2006). "Carotid artery intima-media thickness in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance: a systematic review". Diabet. Med. 23 (6): 609–16. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2005.01725.x. PMID 16759301.
- Masoura C, Pitsavos C, Aznaouridis K, Skoumas I, Vlachopoulos C, Stefanadis C (2011). "Arterial endothelial function and wall thickness in familial hypercholesterolemia and familial combined hyperlipidemia and the effect of statins. A systematic review and meta-analysis". Atherosclerosis. 214 (1): 129–38. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.10.008. PMID 21074770.
- Touboul PJ, Labreuche J, Bruckert E, Schargrodsky H, Prati P, Tosetto A, Hernandez-Hernandez R, Woo KS, Silva H, Vicaut E, Amarenco P (2014). "HDL-C, triglycerides and carotid IMT: a meta-analysis of 21,000 patients with automated edge detection IMT measurement". Atherosclerosis. 232 (1): 65–71. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.10.011. PMID 24401218.
- Ambrosino P, Lupoli R, Di Minno A, Tasso M, Peluso R, Di Minno MN (2015). "Subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A meta-analysis of literature studies". Thromb. Haemost. 113 (5): 916–30. doi:10.1160/TH14-11-0921. PMID 25716931.
- Madan SA, John F, Pyrsopoulos N, Pitchumoni CS (2015). "Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and carotid artery atherosclerosis in children and adults: a meta-analysis". Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27 (11): 1237–48. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000429. PMID 26193052.
- Provost, E; Madhloum, N; Int Panis, L; De Boever, P; Nawrot, T (2015). "Carotid Intima-Media Thickness, a Marker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis, and Particulate Air Pollution Exposure: the Meta-Analytical Evidence". PLOS ONE. 10 (5): e0127014. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127014. PMC 4430520. PMID 25970426.
- Bots ML (2006). "Carotid intima-media thickness as a surrogate marker for cardiovascular disease in intervention studies". Curr Med Res Opin. 22 (11): 2181–90. doi:10.1185/030079906X148472. PMID 17076979.
- Sharma K, Blaha MJ, Blumenthal RS, Musunuru K (2009). "Clinical and research applications of carotid intima-media thickness". Am. J. Cardiol. 103 (9): 1316–20. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.01.020. PMC 2691892. PMID 19406278.
- Bartels, Susanne; Franco, Angelica Ruiz; Rundek, Tatjana (2012). "Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) and plaque from risk assessment and clinical use to genetic discoveries". Perspectives in Medicine. 1 (1–12): 139–145. doi:10.1016/j.permed.2012.01.006. ISSN 2211-968X.
- Various scholarly articles ACC AHA on Carotid IMT (Intima Media Thickness) and its utility
- Various Newscasts on Carotid IMT (Intima Media Thickness)
- Bortel L (2005). "What does intima–media thickness tell us?". Journal of Hypertension. 23: 37–39. doi:10.1097/00004872-200501000-00009.
- Wong M, Edelstein J, Wollman J, Bond MG (1993). "Ultrasonic-pathological comparison of the human arterial wall: verification of intima-media thickness". Arterioscler Thromb. 1 (4): 482–486. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.13.4.482.
- Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, Mallarini G (Feb 2010). "Carotid artery wall thickness: comparison between sonography and multi-detector row CT angiography". Neuroradiology. 52 (2): 75–82. doi:10.1007/s00234-009-0589-5. PMID 19727693.