Cross syndrome
Cross–McKusick–Breen syndrome (also known as "Cross syndrome", "hypopigmentation and microphthalmia", and "oculocerebral-hypopigmentation syndrome") is an extremely rare disorder characterized by white skin, blond hair with yellow-gray metallic sheen, small eyes with cloudy corneas, jerky nystagmus, gingival fibromatosis and severe intellectual disability and physical retardation.[2]:867–8
| Cross syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Oculocerebral hypopigmentation syndrome, Cross type[1] |
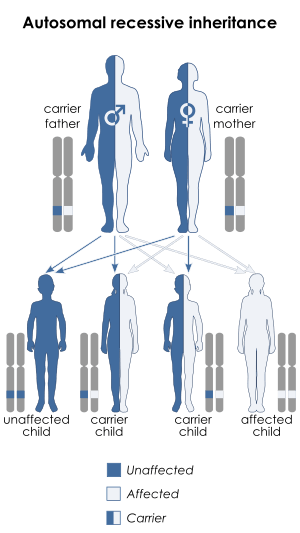 | |
| Cross syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
It was characterized in 1967.[3]
References
- RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Oculocerebral hypopigmentation syndrome, Cross type". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- Cross HE, McKusick VA, Breen W (March 1967). "A new oculocerebral syndrome with hypopigmentation". J. Pediatr. 70 (3): 398–406. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(67)80137-9. PMID 4959856.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.