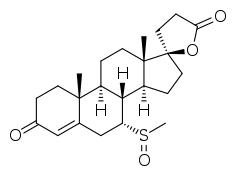
7α-Thiomethylspironolactone sulfoxide
7α-Thiomethylspironolactone sulfoxide (also known as 7α-TMS sulfoxide, 7α-thiomethylspironolactone S-oxide, or 7α-methylsulfinylspironolactone) is a metabolite of spironolactone (brand name Aldactone), an antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogen medication.[1][2][3][4][5][6] 7α-TMS sulfoxide is specifically formed from 7α-thiomethylspironolactone (7α-TMS).[1][2][4][3][5][6]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 7α-TMS sulfoxide; 7α-Thiomethylspironolactone S-oxide; 7α-Methylsulfinylspironolactone |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H32O4S |
| Molar mass | 404.565 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Cashman JR, Peña S (1988). "S-oxygenation of 7 alpha-thiomethylspironolactone by the flavin-containing monooxygenase". Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 6 (3–4): 337–48. PMID 3271645.
- Rainer F. Greger; H. Knauf; E. Mutschler (6 December 2012). Diuretics. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 194–. ISBN 978-3-642-79565-7.
- Al-Hadiya, Badraddin M.H.; Belal, Fathalla; Asiri, Yousif A.; Gubara, Othman A. (2002). "Spironolactone". 29: 261–320. doi:10.1016/S1075-6280(02)29009-6. ISSN 1075-6280. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Abshagen, U.; Rennekamp, H.; Luszpinski, G. (1976). "Pharmacokinetics of spironolactone in man". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 296 (1): 37–45. doi:10.1007/BF00498838. ISSN 0028-1298.
- Overdiek HW, Merkus FW (1987). "The metabolism and biopharmaceutics of spironolactone in man". Rev Drug Metab Drug Interact. 5 (4): 273–302. doi:10.1515/DMDI.1987.5.4.273. PMID 3333882.
- Cashman JR, Peña S (1989). "Canrenone formation via general-base-catalyzed elimination of 7 alpha-(methylthio)spironolactone S-oxide". Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2 (2): 109–13. doi:10.1021/tx00008a007. PMID 2519709.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.