We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Orbital fracture
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Types
- Blow-out Fracture
- Fracture of inferior or medial orbital walls with out fracture of orbital ridge
- Adipose tissue, inf rectus or inf oblique can entrap within maxillary or ethmoid sinus
- 33% are associated with ocular trauma
- Non Blow-out Fracture
- Lateral, inf, and sup orbital ridge fracture typically occurs with other facial fractures
- Blow-out Fracture
- Naso-orbito-ethmoid fracture
- Associated with force applied to nasal bridge
- Often accompanied by injury to lacrimal duct, dural tears, and traumatic brain injury
Clinical Features
- Findings suggestive of orbital fracture:
- Enophthalmos (globe herniation)
- Orbital rim step-off
- Crepitus
- Infraorbital anesthesia (orbital floor fracture)
- Diplopia on upward gaze
- Entrapment of inf rectus or inf oblique or orbital fat
- Injury to oculomotor nerve
- Findings suggestive of naso-orbito-ethmoid fracture
- Pain with eye movement
- Traumatic telecanthus
- Epiphora (tears spilling over lower lid)
- CSF leak
- Findings suggestive of ocular involvement:
- Retrobulbar hematoma or malignant orbital emphysema
- Exophthalmos, decreasing visual acuity, increased ocular pressure
- Ruptured globe
- Extrusion of intraocular contents, severe conjunctival hemorrhage, a tear-shaped pupil
- Orbital fissure syndrome
- Fracture of orbit involving the sup. orbital fissure
- May result in injury to oculomotor and ophthalmic divisions of CN V
- Paralysis of extraocular motions, ptosis, periorbital anesthesia
- Fracture of orbit involving the sup. orbital fissure
- Retrobulbar hematoma or malignant orbital emphysema
Differential Diagnosis
Maxillofacial Trauma
- Le Fort fractures
- Skull fracture (peds)
- Auricular hematoma
- Nasal fracture
- Zygomatic arch fracture
- Zygomaticomaxillary (tripod) fracture
- Dental trauma
- Mandible fracture
Orbital trauma
Acute
- Ruptured Globe^
- Corneal Abrasion
- Ocular foreign body
- Conjunctival laceration
- Caustic Keratoconjunctivitis^^
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
- Traumatic iritis
- Traumatic hyphema
- Retinal detachment
- Retrobulbar hemorrhage/hematoma
- Traumatic mydriasis
- Orbital fracture
- Frontal sinus fracture
- Naso-ethmoid fracture
- Inferior orbial wall fracture
- Medial orbital wall fracture
Subacute/Delayed
Evaluation
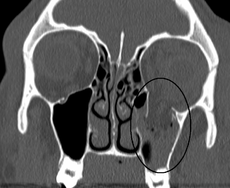
- Obtain orbital CT as initial study if significant clinical findings
- Evidence of fracture on exam
- Decreased extraocular mobility
- Decreased visual acuity or diplopia
- Severe pain
- Unable to perform adequate exam
- Look for teardrop sign on coronal view of CT
- Otherwise can obtain Waters' view first
- Shows cloudy maxillary sinus representing blood, fluid or tissue
Management
- Isolated orbital fracture
- Cephalexin 250-500mg PO QID x10d
- Decongestants
- Instructions to avoid nose blowing
- Ocular injury
- Emergent ophtho consultation
- Malignant emphysema and/or retrobulbar hemorrhage
- Extraocular Muscle Dysfunction
- May result in oculocardiac reflex → vagal symptoms
- Consider release of entrapped muscle
- Decreased extraocular movement not due to entrapment
- Consider corticosteroids
- Surgical indications include >2mm enopthalmos and/or persistent diploplia
Disposition
- Isolated orbital fracture
- Discharge with follow up in 3-10d
- Refer to ophtho for outpatient full dilated exam to rule-out unidentified retinal tears
- Naso-orbito-ethmoid fracture
- Admit