We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Difference between revisions of "Femur fracture"
From WikEM
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*Despite good care, proximal fracture 30-day all cause mortality is 22% and grows to 36% at one year<ref>Lawrence, VA, et al. Medical complications and outcomes after hip fracture repair. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162(18):2053-7.</ref> | *Despite good care, proximal fracture 30-day all cause mortality is 22% and grows to 36% at one year<ref>Lawrence, VA, et al. Medical complications and outcomes after hip fracture repair. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162(18):2053-7.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Femur fracture types}} | ||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
| − | |||
{{Hip pain DDX}} | {{Hip pain DDX}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:14, 7 May 2017
For pediatric patient see Femur fracture (peds)
Contents
Background
- Despite good care, proximal fracture 30-day all cause mortality is 22% and grows to 36% at one year[1]
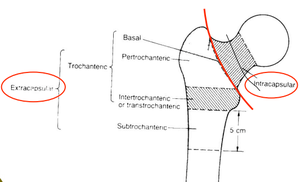
Femur fractures
Proximal
- Intracapsular
- Extracapsular
Shaft
- Mid-shaft femur fracture (all subtrochanteric)
Clinical Features
- History of trauma
- Pain, point tenderness, deformity
Differential Diagnosis
Hip pain
- Femur fracture
- Hip dislocation
- Hip bursitis
- Psoas abscess
- Piriformis syndrome
- Meralgia paresthetica
- Septic Arthritis (Hip)
- Obturator nerve entrapment
- Pelvic fractures
- Avascular necrosis of hip
Evaluation
Proximal
- Consider AP pelvis in addition to AP/lateral views to compare contralateral side
- Consider MRI if strong clinical suspicion but negative x-ray
Mid-Shaft
- Plain xrays of femur
Management
- Pain control in ED with femoral nerve blocks.
- Nerve Block: Fascia Iliaca Compartment
- 3 in 1 block (femoral, obturator, lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh)
- No difference in 2 blocks listed above, which both reduced pain scores in the ED. [2]
- Most fractures, including all displaced, are treated with ORIF
- Exception is isolated trochanteric fracture often does not require surgery
- See individual pages for further discussion
- Type and cross/screen for patients at higher risk of hemorrhage:
- Age > 75 yrs
- Initial hemoglobin < 12
- Peritrochanteric fracture
Disposition
- Generally requires admission for operative repair