We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Difference between revisions of "Patella dislocation"
From WikEM
(→Management) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
| − | * | + | *Typically occurs with trauma to an extended knee with externally rotated foot<ref>Review of Orthopaedics, 6th Edition, Mark D. Miller MD, Stephen R. Thompson MBBS MEd FRCSC, Jennifer Hart MPAS PA-C ATC, an imprint of Elsevier, Philadelphia, Copyright 2012</ref> |
| − | *Acute | + | *Acute dislocation occurs with traumatic injury, M=F, may see hemarthrosis<ref name="epi">Fithian DC, Paxton EW, Stone ML, Silva P, Davis DK, Elias DA, White LM. Epidemiology and natural history of acute patellar dislocation. AJSM 2004;32:1114-1121</ref> |
| − | *Chronic | + | *Chronic dislocation seen more commonly in women/teenage girls, typically little or no swelling<ref name="epi"></ref> |
| − | * | + | *Common associated fractures |
| + | **Medial patella facet | ||
| + | **Lateral femoral condyle | ||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
[[File:Patellar dislocation.jpg|thumb|patella dislocates laterally]] | [[File:Patellar dislocation.jpg|thumb|patella dislocates laterally]] | ||
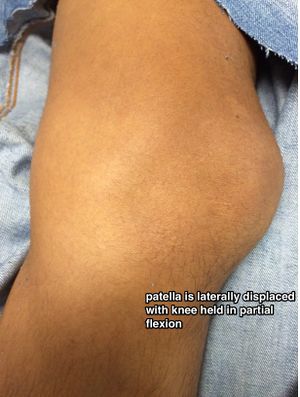
*Patella is usually displaced laterally; knee is held in flexion | *Patella is usually displaced laterally; knee is held in flexion | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Evaluation== | ==Evaluation== | ||
[[File:Patellaluxation ap 001.png|thumb]] | [[File:Patellaluxation ap 001.png|thumb]] | ||
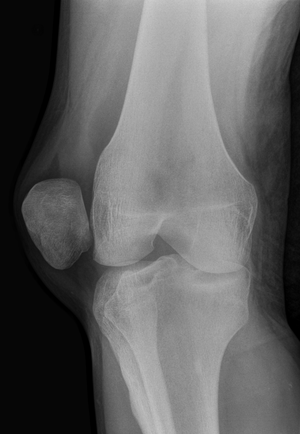
| − | * | + | *Clinical diagnosis |
| − | * | + | *May consider pre-reduction x-ray if concern for fracture (not required) |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 26: | ||
***Slowly extend and slightly hyperextend the knee and slide patella back into place. | ***Slowly extend and slightly hyperextend the knee and slide patella back into place. | ||
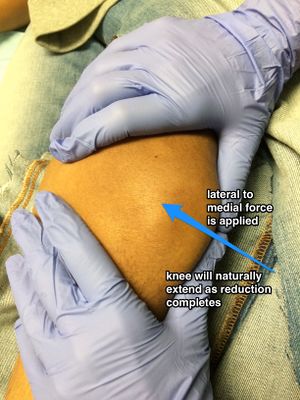
**Option #2 | **Option #2 | ||
| − | ***One provider applies slow downward pressure over the quads. This stretches out the muscle and slowly | + | ***One provider applies slow downward pressure over the quads. This stretches out the muscle and slowly straightens the leg |
| − | ***At the same time, second pulls gentle traction of the patella outward while rotating the patella back over from lateral to anterior | + | ***At the same time, second provider pulls gentle traction of the patella outward while rotating the patella back over from lateral to anterior |
| − | + | *Knee immobilizer, NSAIDs, weight-bearing as tolerated | |
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
| + | *Obtain ortho consult if unable to reduce or fracture/loose bodies seen on post-reduction x-ray | ||
| + | *Otherwise may be discharged with ortho follow-up in 1-2 weeks | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:14, 9 May 2017
Contents
Background
- Typically occurs with trauma to an extended knee with externally rotated foot[1]
- Acute dislocation occurs with traumatic injury, M=F, may see hemarthrosis[2]
- Chronic dislocation seen more commonly in women/teenage girls, typically little or no swelling[2]
- Common associated fractures
- Medial patella facet
- Lateral femoral condyle
Clinical Features
- Patella is usually displaced laterally; knee is held in flexion
Differential Diagnosis
Knee diagnoses
Acute Injury
- Knee fractures
- Patella fracture
- Tibial plateau fracture
- Knee dislocation
- Patella dislocation
- Segond fracture
- Meniscus and ligament knee injuries
- Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper's knee)
- Patellar tendon rupture
- Quadriceps tendon rupture
Nontraumatic/Subacute
- Septic Joint
- Gout
- Popliteal cyst (Baker's)
- Prepatellar bursitis (nonseptic)
- Septic bursitis
- Pes anserine bursitis
- Patellofemoral syndrome (Runner's Knee)
- Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper's knee)
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
- Arthritis
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis
- May consider pre-reduction x-ray if concern for fracture (not required)
Management
- Reduce; do not need x-rays prior to reduction. Rarely need any sedation though a dose of IV pain medication can help relax the patient
- Option #1:
- Mild flexion of hip (20-30 degrees by raising head of bed, not by propping the leg up off the bed) to relax quadriceps
- Slowly extend and slightly hyperextend the knee and slide patella back into place.
- Option #2
- One provider applies slow downward pressure over the quads. This stretches out the muscle and slowly straightens the leg
- At the same time, second provider pulls gentle traction of the patella outward while rotating the patella back over from lateral to anterior
- Option #1:
- Knee immobilizer, NSAIDs, weight-bearing as tolerated
Disposition
- Obtain ortho consult if unable to reduce or fracture/loose bodies seen on post-reduction x-ray
- Otherwise may be discharged with ortho follow-up in 1-2 weeks
References
- ↑ Review of Orthopaedics, 6th Edition, Mark D. Miller MD, Stephen R. Thompson MBBS MEd FRCSC, Jennifer Hart MPAS PA-C ATC, an imprint of Elsevier, Philadelphia, Copyright 2012
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Fithian DC, Paxton EW, Stone ML, Silva P, Davis DK, Elias DA, White LM. Epidemiology and natural history of acute patellar dislocation. AJSM 2004;32:1114-1121
See Also
Authors
Aaron Snyder, Jay, Jordan Swartz, Daniel Ostermayer, Michael Holtz, Ross Donaldson, Ted Fan, Neil Young, Claire