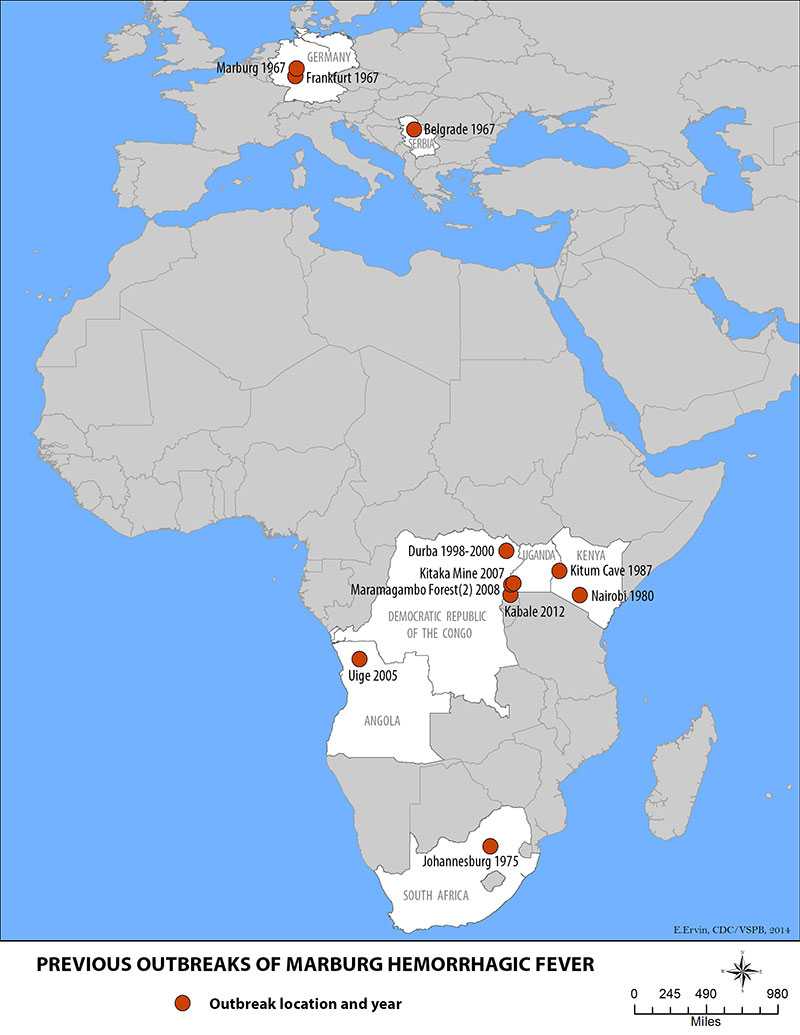
Marburg virus was first recognized in 1967, when outbreaks of hemorrhagic fever occurred simultaneously in laboratories in Marburg and Frankfurt, Germany and in Belgrade, Yugoslavia (now Serbia). Thirty-one people became ill, initially laboratory workers followed by several medical personnel and family members who had cared for them. Seven deaths were reported. The first people infected had been exposed to imported African green monkeys or their tissues while conducting research. One additional case was diagnosed retrospectively.
The reservoir host of Marburg virus is the African fruit bat, Rousettus aegyptiacus. Fruit bats infected with Marburg virus do not to show obvious signs of illness. Primates (including humans) can become infected with Marburg virus, and may develop serious disease with high mortality. Further study is needed to determine if other species may also host the virus.
- Page last reviewed: December 1, 2014
- Page last updated: December 1, 2014
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir