Wandering atrial pacemaker
Wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP) is an atrial arrhythmia that occurs when the natural cardiac pacemaker site shifts between the sinoatrial node (SA node), the atria, and/or the atrioventricular node (AV node). This shifting of the pacemaker from the SA node to adjacent tissues is identifiable on ECG Lead II by morphological changes in the P-wave; sinus beats have smooth upright P waves, while atrial beats have flattened, notched, or diphasic P-waves. It is often seen in the very young, very old, and in athletes, and rarely causes symptoms or requires treatment.[1]
| Wandering pacemaker | |
|---|---|
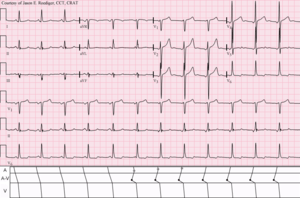 | |
| Shifting (wandering) pacemaker | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
Cause
References
- Huff, J. (2016). ECG workout: Exercises in arrhythmia interpretation (7th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.