Vorapaxar
Vorapaxar (brand name Zontivity, formerly known as SCH 530348) is a thrombin receptor (protease-activated receptor, PAR-1) antagonist based on the natural product himbacine, discovered by Schering-Plough and developed by Merck & Co.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zontivity |
| Other names | SCH-530348 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100%[1] |
| Protein binding | ≥99% |
| Metabolism | hepatic (CYP3A4 and CYP2J2) |
| Elimination half-life | 5–13 days |
| Excretion | feces (58%), urine (25%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.116.767 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
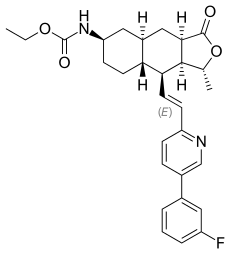
| Formula | C29H33FN2O4 |
| Molar mass | 492.58 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 278 °C (532 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Medical uses
Vorapaxar is used for persons with a history of myocardial infarction (heart attack) or persons with peripheral arterial disease. Studies have shown that this medication can reduce the rate of combined endpoint cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, and urgent coronary revascularization.[1]
Contraindications
Vorapaxar is contraindicated for people with a history of stroke, transient ischemic attack, or intracerebral hemorrhage.[1] In studies of vorapaxar on persons with prior ischemic stroke, there was an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage without an improvement in major vascular events. Vorapaxar possesses a long half life which is a problem because there is currently no treatment to reverse the antiplatelet effects of vorapaxar.[1] Because of this, it is important that vorapaxar not be used in persons with history of stroke, transient ischemic attack, or intracranial hemorrhage, or active pathological bleeding. This family of medication, PAR-1 antagonists in general has been associated with an increased risk of intracranial bleeding demonstrated by a pooled analysis of data that studied 42000 patients with history of thrombotic vascular disease or acute coronary syndrome comparing the medication and a placebo.[3]
Drug interactions
Vorapaxar is eliminated primarily by metabolism by the CYP3A enzymes. It is best to avoid any strong CYP3A4 inhibitors(ex: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, clarithromycin, nefazodone, ritonavir, saquinavir, nelfinavir, indinavir, boceprevir, telaprevir, telithromycin, and conivaptan). CYP3A4 inducers(Carbamazepine, rifampin, St. John's Wort, and Phenytoin) should also be avoided.[1]
Dose adjustment
No dose adjustment is required in persons with renal impairment.[1] No dose adjustment is required in persons with mild and moderate hepatic impairment. If the person has severe hepatic impairment, vorapaxar is not recommended due to the risk of bleeding.[1]
Mechanism of Action
Vorapaxar is a new anti-platelet drug that is part of the PAR-1 antagonist family, a new class of anti-platelet drug. It functions by inhibiting thrombin-related platelet aggregation. This mechanism works by a different pathway than other anti-platelet medications such as aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors. Unlike many other medication, vorapaxar does not affect ADP-mediated platelet aggregation, coagulation parameters, or bleeding time.[4]
Storage
Vorapaxar can be stored at 20-25 °C(68-77 °F). It is best to store vorapaxar in original packaging with the bottle tightly closed and to avoid moisture.[1]
History
In January 2011, clinical trials being conducted by Merck were halted for patients with stroke and mild heart conditions due to an increase in brain bleedings.[5] In a randomized double-blinded trial comparing vorapaxar with placebo in addition to standard therapy in 12,944 patients who had acute coronary syndromes, there was no significant reduction in a composite end point of death from cardiovascular causes, myocardial infarction, stroke, recurrent ischemia with rehospitalization, or urgent coronary revascularization. However, there was increased risk of major bleeding.[6] A trial published in February 2012, found no change in all cause mortality while decreasing the risk of cardiac death and increasing the risk of major bleeding, including intracranial hemorrhages. After two years, the data and safety monitoring board recommended discontinuation of the study treatment in people with a history of stroke owing to the risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
TRA 2°P–TIMI 50 study of vorapaxar was carried out in patients who had previously experienced a heart attack, stroke, or who had peripheral arterial disease (PAD). In this three-year study in over 26,000 patients, the addition of vorapaxar to standard of care (aspirin and/or an ADP antagonist such as clopidogrel) significantly reduced the risk of the primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, heart attack, stroke or urgent coronary revascularization by 12 percent compared to placebo plus standard of care (11.2 percent vs. 12.4 percent, p = 0.001). Vorapaxar showed the most promising result among patients with a history of heart attack. Among these patients the drug reduced the relative risk of CV death, heart attack or stroke by 20 percent. There was an increase in moderate or severe bleeding, but no statistically significant increase in fatal bleeding.[7] Vorapaxar was recommended for FDA approval on January 15, 2014.[8]
On May 5, 2014, vorapaxar obtained FDA approval.
References
- "ZONTIVITY™ (vorapaxar) Tablets 2.08 mg, for oral use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Merck & Co., Inc. Initial U.S. Approval: 05/2014. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- Chackalamannil S; Wang Y; Greenlee WJ; Hu Z; Xia Y; Ahn H-S; Boykow G; Hsieh Y; Palamanda J; Agans-Fantuzzi J; Kurowski S; Graziano M; Chintala M. Discovery of a Novel, Orally Active Himbacine-Based Thrombin Receptor Antagonist (SCH 530348) with Potent Antiplatelet Activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2008, 51, 3061–3064.
- Morrow, David A., and Mark J. Alberts. "Efficacy and Safety of Vorapaxar in Patients With Prior Ischemic Stroke." Journal of the American Heart Association (2013): 691-98. American Heart Association. Web. 2 Nov. 2014. <http://stroke.ahajournals.org/content/44/3/ 691.full.pdf+html>.
- Baker, NC; Lipinski, MJ; Lhermusier, T; Waksman, R (7 October 2014). "Overview of the 2014 food and drug administration cardiovascular and renal drugs advisory committee meeting about vorapaxar". Circulation. 130 (15): 1287–94. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.114.011471. PMID 25287768.
- Merck Blood Thinner Studies Halted in Select Patients, Bloomberg News, January 13, 2011
- Tricoci; et al. (2012). "Thrombin-Receptor Antagonist Vorapaxar in Acute Coronary Syndromes". New England Journal of Medicine. 366 (1): 20–33. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1109719. hdl:2445/49763. PMID 22077816.
- Morrow DA, Braunwald E, Bonaca MP, Ameriso SF, Dalby AJ, Fish MP, Fox KA, Lipka LJ, Liu X, Nicolau JC, Ophuis AJ, Paolasso E, Scirica BM, Spinar J, Theroux P, Wiviott SD, Strony J, Murphy SA, TRA 2P–TIMI 50 Steering Committee and, Investigators (Apr 12, 2012). "Vorapaxar in the secondary prevention of atherothrombotic events" (PDF). The New England Journal of Medicine. 366 (15): 1404–13. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1200933. hdl:10447/94482. PMID 22443427.
- "Merck Statement on FDA Advisory Committee for Vorapaxar, Merck's Investigational Antiplatelet Medicine". Merck. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
External links
- Stu Borman (2005). "Hopes Ride on Drug Candidates: Researchers reveal potential new medicines for thrombosis, anxiety, diabetes, and cancer". Chemical & Engineering News. 83 (16): 40–44. doi:10.1021/cen-v083n016.p040.