Voclosporin
Voclosporin is an experimental immunosuppressant drug being developed by Aurinia Pharmaceuticals. It is being studied as a potential treatment for lupus nephritis (LN) and uveitis.[1] It is an analog of ciclosporin that has enhanced action against calcineurin and greater metabolic stability.[2] Voclosporin was discovered by Robert T. Foster and his team at Isotechnika in the mid 1990s.[3] Isotechnika was founded in 1993 and merged with Aurinia Pharmaceuticals in 2013.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
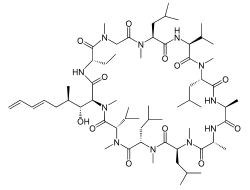
| IUPAC name
(3S,6S,9S,12R,15S,18S,21S,24S,30S,33S)-30-Ethyl-33-[(1R,2R,4E)-1-hydroxy-2-methyl-4,6-heptadien-1-yl]-6,9,18,24-tetraisobutyl-3,21-diisopropyl-1,4,7,10,12,15,19,25,28-nonamethyl-1,4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28,31-undecaazacyclotritriacontane-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29,32-undecone | |
| Other names
VCS, ISA247, Luveniq | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C63H111N11O12 |
| Molar mass | 1214.646 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Initially, voclosporin was a mixture of equal proporations of cis and trans geometric isomers of amino acid-1 modified cyclosporin. Later, in collaboration with Roche in Basel, Switzerland, voclosporin's manufacturing was changed to yield the predominantly trans isomer which possesses most of the beneficial effect of the drug (immunosuppression) in the treatment of organ transplantation and autoimmune diseases.
References
- "Luveniq Approval Status".
Luveniq (voclosporin) is a next-generation calcineurin inhibitor intended for the treatment of noninfectious uveitis involving the intermediate or posterior segments of the eye.
- "What is voclosporin?". Isotechnika. Retrieved October 19, 2012.
- U.S. Patent 6,605,593