Vincamine
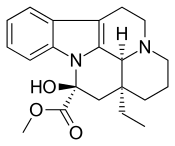
Vincamine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid found in the leaves of Vinca minor (lesser periwinkle), comprising about 25-65% of its indole alkaloids by weight. It can also be synthesized from related alkaloids.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oxybral SR |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.070 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 354.450 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Uses
Vincamine is sold in Europe as a prescription medicine for the treatment of primary degenerative and vascular dementia. In the United States, it is permitted to be sold as a dietary supplement when labeled for use in adults for six months or less.[2] Most common preparations are in the sustained release tablet forms.
Derivatives
Vinpocetine is a synthetic derivative of vincamine.[3]
References
- "Indole Alkaloids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (Fifth ed.). Wiley-VCH. 1985. p. 393. ISBN 3-527-20100-9.
- "Summary of Data for Chemical Selection: Vincamine" (PDF).
- "Vinpocetine in Dietary Supplements". FDA. 2019-06-03.
External links
- "Vincamine MSDS" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-06-08. Retrieved 2012-01-30.
- Chemical Selection Working Group. "Vincamine - 1617-90-9" (PDF). Summary of Data for Chemical Selection. NIH - United States National Institutes of Health. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-10-21. Retrieved 2007-04-23.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.