Uterine serous carcinoma
Uterine serous carcinoma (USC), is an uncommon form of endometrial cancer that typically arises in postmenopausal women. It is typically diagnosed on endometrial biopsy, prompted by post-menopausal bleeding.
| Uterine papillary serous carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Uterine papillary serous carcinoma and Uterine serous adenocarcinoma |
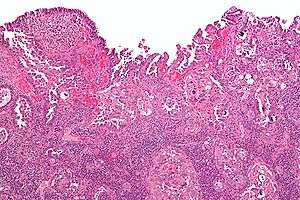 | |
| Micrograph of uterine serous papillary carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
Unlike the more common low-grade endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma, USC does not develop from endometrial hyperplasia and is not hormone-sensitive. It arises in the setting of endometrial atrophy and is classified as a type II endometrial cancer.[1]
Cause
Diagnosis
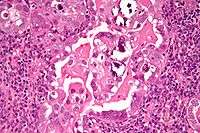
The lesion is found in patients who present typically with abnormal or postmenopausal bleeding.[2] Such bleeding is followed by further evaluation leading to a tissue diagnosis, usually done by a dilatation and curettage (D&C). A work-up to follow would look for metastasis using imaging technology including sonography and MRI. The median age at diagnosis in a study of 138 women was 67 years, of these 54 had stage I, 20 stage II, 41 stage III, and 23 stage IV disease.[3]
Histopathologically, uterine serous carcinomas is typically characterized by (1) nipple-shaped structures (papillae) with fibrovascular cores (2) marked nuclear atypia (irregularies in the nuclear membrane, enlarged nuclear size), (3) psammoma bodies and (4) cilia.
Staging
UPSC is staged like other forms of endometrial carcinoma at time of surgery using the FIGO cancer staging system.
- Stage IA: tumor is limited to less than half the myometrium
- Stage IB: invasion of more than half the myometrium
- Stage II: cervical stromal invasion
- Stage IIIA: tumor invades serosa or adnexa
- Stage IIIB: vaginal or parametrial metastasis
- Stage IIIC1: metastasis to pelvic lymph nodes
- Stage IIIC2: metastasis to para-aortic lymph nodes
- Stage IVA: invasion of the bladder or bowel
- Stage IVB: distant metastasis, including intra-abdominal or inguinal lymph nodes
Survival
In the older literature survival rates have been given as 35–50% for Stage I–II and 0–15% for Stage III and IV UPSC,[4] More recently it was reported that forty-two percent of 138 patients were found disease-free at five years.[3]
In 2009, the journal of "Gynecologic Oncology" reported the following 5-year survival rates based upon stage of cancer:
- Stage I: 50% - 80%
- Stage II: 50%
- Stage III: 20%
- Stage IV: 5% - 10% [5]
Treatment
The primary treatment is surgical. FIGO-cancer staging is done at the time of surgery which consists of peritoneal cytology, total hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, pelvic/para-aortic lymphadenectomy, and omentectomy. The tumor is aggressive and spreads quickly into the myometrium and the lymphatic system. Thus even in presumed early stages, lymphadenectomy and omentectomy should be included in the surgical approach. If the tumor has spread surgery is cytoreductive followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy.[4]
In a study to determine if adjuvant therapy should be used in patients with stage I UPSC who had undergone surgery, no increased survival was seen when radiation therapy was added versus observation, while the postsurgical treatment with chemotherapy may be beneficial but more data are needed.[6] A study of the usefulness of platinum-based chemotherapy as an adjuvant after surgery of stage I patients showed that patients with stage 1A who had no residual disease in the hysterectomy specimen had no recurrence regardless if chemotherapy was used or not, however, patients with stage 1A disease with residual disease in the hysterectomy specimen had no recurrence with platinum-based therapy, but those who had no such chemotherapy showed recurrence in 43%. Similarly, patients with stage 1B disease with chemotherapy had no recurrence, while those without chemotherapy had a high degree (77%) of recurrence.[7]
Trastuzumab
In a recent study, about 60% of USCs were found to overexpress the protein HER2/neu—the same one that is overexpressed in some breast cancers. The monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) is currently being tested as a therapy for this subset of USCs.[8]
The antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin), which is used to treat breast cancers that overexpress the HER2/neu protein, has been tried with some success in a phase II trial in women with UPSCs that overexpress HER2/neu.[8]
Prognosis
Prognosis of the UPSC is affected by age, stage, and histology as well as treatment.[3]
References
- Gründker C, Günthert AR, Emons G (2008). "Hormonal heterogeneity of endometrial cancer". Adv Exp Med Biol. 630: 166–88. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-78818-0_11. PMID 18637491.
- Sagae S, Susumu N, Viswanathan AN, Aoki D, Backes FJ, Provencher DM, Vaughan M, Creutzberg CL, Kurzeder C, Kristensen G, Lee C, Kurtz JE, Glasspool RM, Small W (November 2014). "Gynecologic Cancer InterGroup (GCIG) consensus review for uterine serous carcinoma". Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer. 24 (9 Suppl 3): S83–9. doi:10.1097/IGC.0000000000000264. PMID 25341586.
- Goldberg H, Miller RC, Abdah-Bortnyak R, Steiner M, Yildiz F, Meirovitz A, Villà S, Poortmans PM, Azria D, Zidan J, Ozsahin M, Abacioglu U, Gold DG, Amit A, Lavie O, Atahan IL, Kuten A (February 2008). "Outcome after combined modality treatment for uterine papillary serous carcinoma: a study by the Rare Cancer Network (RCN)". Gynecol. Oncol. 108 (2): 298–305. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.10.037. PMID 18096209.
- Sood BM, Jones J, Gupta S, Khabele D, Guha C, Runowicz C, Goldberg G, Fields A, Anderson P, Vikram B (September 2003). "Patterns of failure after the multimodality treatment of uterine papillary serous carcinoma". Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 57 (1): 208–16. doi:10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00531-5. PMID 12909235.
- Boruta DM, Gehrig PA, Fader AN, Olawaiye AB (October 2009). "Management of women with uterine papillary serous cancer: a Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) review". Gynecol. Oncol. 115 (1): 142–53. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2009.06.011. PMID 19592079.
- Huh WK, Powell M, Leath CA, Straughn JM, Cohn DE, Gold MA, Falkner CA, Carey DE, Herzog T, Fowler JM, Partridge EE, Kilgore LC, Alvarez RD (December 2003). "Uterine papillary serous carcinoma: comparisons of outcomes in surgical Stage I patients with and without adjuvant therapy". Gynecol. Oncol. 91 (3): 470–5. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2003.08.027. PMID 14675664.
- Kelly MG, O'malley DM, Hui P, McAlpine J, Yu H, Rutherford TJ, Azodi M, Schwartz PE (2005). "Improved survival in surgical stage I patients with uterine papillary serous carcinoma (UPSC) treated with adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy". Gynecol Oncol. 98 (3): 353–9. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.06.012. PMID 16005947.
- Santin AD, Bellone S, Roman JJ, McKenney JK, Pecorelli S (2008). "Trastuzumab treatment in patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma overexpressing HER2/neu". Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 102 (2): 128–31. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2008.04.008. PMID 18555254.