Terminal cisternae
Terminal cisternae are enlarged areas of the sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounding the transverse tubules. These discrete regions within the muscle cell store calcium (increasing the capacity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium) and release it when an action potential courses down the transverse tubules, eliciting muscle contraction. Because terminal cisternae ensure rapid calcium delivery, they are well developed in muscles that contract quickly, such as fast twitch skeletal muscle. Terminal cisternae then go on to release calcium, which binds to troponin. This releases tropomyosin, exposing active sites of the thin filament, actin.
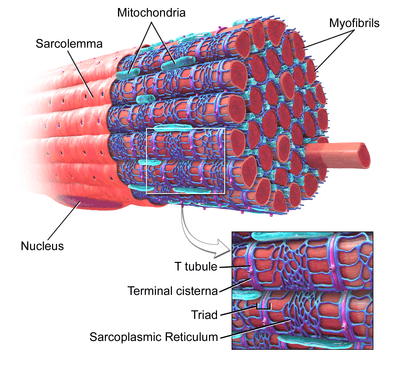
There are several mechanisms directly linked to the terminal cisternae which facilitate Excitation-Contraction coupling. When Excitation of the membrane arrives at the T-tubule nearest the muscle fiber, a Dihydropyridine (DHP) channel is activated. This is similar to a voltage gated calcium channel, but is not actually an ionotropic channel. Instead, it serves to activate Ryanodine, which will let calcium ions pass into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and triggers calcium release to the muscle fiber itself.
A T-tubule surrounded by two terminal cisternae is referred to as a " triad" in physiology. As previously explained, the terminal cisternae along with the transverse tubules are the mechanisms of transduction from a nervous impulse to an actual muscle contraction.