Sulcus (morphology)
In biological morphology and anatomy, a sulcus (pl. sulci) is a furrow or fissure. It may be a groove in the surface of a limb or an organ, notably in the surface of the brain, but also in the lungs, certain muscles (including the heart), as well as in bones, and elsewhere. Many sulci are the product of a surface fold or junction, such as in the gums, where they fold around the neck of the tooth.
Gingival sulcus at neck of mammalian tooth

Pollen grains of Cercis are sulcate, with reticulate surface.
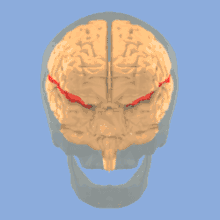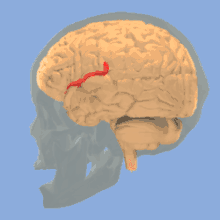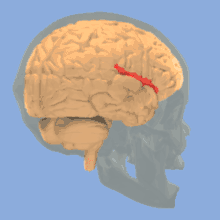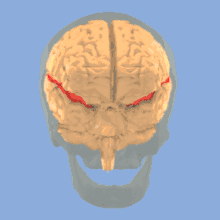
Rotating image of human brain, illustrating the lateral sulcus in the brain.
In invertebrate zoology, a sulcus is a fold, groove, or boundary, especially at the edges of sclerites or between segments.
Examples in anatomy
In the brain
Elsewhere
- anterior interventricular sulcus
- calcaneal sulcus
- coronal sulcus
- femoral sulcus or intercondylar fossa of femur
- gingival sulcus
- gluteal sulcus
- interlabial sulci
- intermammary sulcus
- intertubercular sulcus, the groove between the lesser and greater tubercules of the humerus (bone of the upper arm)
- lacrimal sulcus (sulcus lacrimalis)
- malleolar sulcus
- patellar sulcus or intercondylar fossa of femur
- posterior interventricular sulcus
- preauricular sulcus
- radial sulcus (musculospiral groove)
- sagittal sulcus
- separatoral sulcus (depression behind the brow ridges of some primates)
- sigmoid sulcus
- sulcus arteriæ vertebralis
- sulcus subtarsalis in the eyelid
- sulcus tubae auditivae
- tympanic sulcus
- urethral sulcus[1]
See also
- Fissure
- Sinus (botany)
- Sulcus sign
References
- Larkins, Christine E., and Martin J. Cohn. "Phallus development in the turtle Trachemys scripta." Sexual Development 9.1 (2015): 34-42.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.