Siphoviridae
Siphoviridae is a family of double-stranded DNA viruses in the order Caudovirales. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There are currently 313 species in this family, divided among 47 genera.[2][3] The characteristic structural features of this family are a nonenveloped head and noncontractile tail.
| Siphoviridae | |
|---|---|
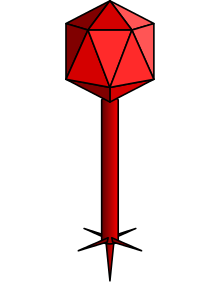 | |
| Typical structure of a siphovirus | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Phylum: | incertae sedis |
| Class: | incertae sedis |
| Order: | Caudovirales |
| Family: | Siphoviridae |
| Genera | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Structure
Viruses in Siphoviridae are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and head-tail geometries[2] (morphotype B1) or a prolate capsid (morphotype B2), and T=7 symmetry. The diameter is around 60 nm.[2] Members of this family are also characterized by their filamentous, cross-banded, noncontractile tails, usually with short terminal and subterminal fibers. Genomes are double stranded and linear, around 50kb in length,[2] containing about 70 genes. The guanine/cytosine content is usually around 52%.
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pbiunalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Yualikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Sfi1unalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Phijlunalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Che8likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Bronlikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Sap6likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Andromedalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Sfi21dtunalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Pgonelikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Lambdalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7, levo | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Skunalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Cjwunalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Corndoglikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Phifllikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Xp10likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Tunalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Wbetalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| D3112likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| 77likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Charlielikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| D3likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| T5likevirus | Head-Tail | T=13 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Tp2unalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| T5likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Reylikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Hk578likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| 3alikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Che9clikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Phietalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Tm4likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Halolikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Phic3unalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Iebhlikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Chilikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| N15likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| C5likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Phie125likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| P23likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Psimunalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Jerseylikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Spbetalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Bignuzlikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| C2likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Barnyardlikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Omegalikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| Phicbklikevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
| L5likevirus | Head-Tail | T=7 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. Replication follows the replicative transposition model. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. Translation takes place by -1 ribosomal frameshifting, and +1 ribosomal frameshifting. The virus exits the host cell by lysis, and holin/endolysin/spanin proteins.[2] Bacteria and archaea serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are passive diffusion.[2]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pbiunalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Yualikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Sfi1unalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Phijlunalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Che8likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Bronlikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Sap6likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Andromedalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Sfi21dtunalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Pgonelikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Lambdalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Skunalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Cjwunalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Corndoglikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Phifllikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Xp10likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Tunalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Wbetalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| D3112likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| 77likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Charlielikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| D3likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| T5likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Tp2unalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| T5likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Reylikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Hk578likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| 3alikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Che9clikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Phietalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Tm4likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Halolikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Phic3unalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Iebhlikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Chilikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| N15likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| C5likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Phie125likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| P23likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Psimunalikevirus | Bacteria; archea | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Jerseylikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Spbetalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Bignuzlikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| C2likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Barnyardlikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Omegalikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Phicbklikevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| L5likevirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
Taxonomy
Group: dsDNA
- Family: Siphoviridae
- Genus: 3alikevirus
- Staphylococcus phage 47
- Staphylococcus phage 3a
- Staphylococcus phage 42e
- Staphylococcus phage Ipla35
- Staphylococcus phage Phi12
- Staphylococcus phage Slt
- Genus: 77likevirus
- Staphylococcus phage 13
- Staphylococcus phage 77
- Staphylococcus phage Pvl108
- Genus: Andromedalikevirus
- Bacillus phage andromeda
- Bacillus phage blastoid
- Bacillus phage curly
- Bacillus phage eoghan
- Bacillus phage finn
- Bacillus phage glittering
- Bacillus phage riggi
- Bacillus phage taylor
- Genus: Barnyardlikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage barnyard
- Mycobacterium phage konstantine
- Mycobacterium phage patience
- Mycobacterium phage predator
- Genus: Bignuzlikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage bignuz
- Mycobacterium phage jebeks
- Genus: Bronlikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage bron
- Mycobacterium phage Faith1
- Mycobacterium phage joedirt
- Mycobacterium phage rumpelstiltskin
- Genus: C2likevirus
- Lactococcus phage bIL67
- Lactococcus phage c2
- Genus: C5likevirus
- Lactobacillus phage c5
- Lactobacillus phage LLKu
- Genus: Charlielikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage charlie
- Mycobacterium phage redi
- Genus: Che8likevirus
- Mycobacterium phage ardmore
- Mycobacterium phage avani
- Mycobacterium phage boomer
- Mycobacterium phage Che8
- Mycobacterium phage Che9d
- Mycobacterium phage deadp
- Mycobacterium phage dlane
- Mycobacterium phage dorothy
- Mycobacterium phage dotproduct
- Mycobacterium phage drago
- Mycobacterium phage fruitloop
- Mycobacterium phage gumbie
- Mycobacterium phage ibhubesi
- Mycobacterium phage Llij
- Mycobacterium phage mozy
- Mycobacterium phage mutaforma13
- Mycobacterium phage Pacc40
- Mycobacterium phage PMC
- Mycobacterium phage ramsey
- Mycobacterium phage rockyhorror
- Mycobacterium phage SG4
- Mycobacterium phage shauna1
- Mycobacterium phage shilan
- Mycobacterium phage spartacus
- Mycobacterium phage taj
- Mycobacterium phage tweety
- Mycobacterium phage wee
- Mycobacterium phage yoshi
- Genus: Che9clikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage babsiella
- Mycobacterium phage brujita
- Mycobacterium phage Che9c
- Genus: Chilikevirus
- Salmonella phage Chi
- Salmonella phage FSLSP030
- Salmonella phage FSLSP088
- Salmonella phage iEPS5
- Salmonella phage SPN19
- Genus: Cjwunalikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage 244
- Mycobacterium phage Bask21
- Mycobacterium phage CJW1
- Mycobacterium phage eureka
- Mycobacterium phage kostya
- Mycobacterium phage porky
- Mycobacterium phage pumpkin
- Mycobacterium phage sirduracell
- Mycobacterium phage toto
- Genus: Corndoglikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage corndog
- Mycobacterium phage firecracker
- Genus: D3112likevirus
- Pseudomonas phage D3112
- Pseudomonas phage DMS3
- Pseudomonas phage FHA0480
- Pseudomonas phage LPB1
- Pseudomonas phage MP22
- Pseudomonas phage MP29
- Pseudomonas phage MP38
- Pseudomonas phage PA1phi
- Genus: D3likevirus
- Pseudomonas phage D3
- Pseudomonas phage PMG1
- Genus: Halolikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage halo
- Mycobacterium phage liefie
- Genus: Hk578likevirus
- Enterobacteria phage JL1
- Enterobacteria phage SSL2009a
- Escherichia phage HK578
- Shigella phage EP23
- Sodalis phage SO1
- Genus: Iebhlikevirus
- Bacillus phage 250
- Bacillus phage IEBH
- Genus: Jerseylikevirus
- Salmonella phage Ent1
- Salmonella phage jersey
- Salmonella phage SE2
- Salmonella phage SETP3
- Salmonella phage SS3e
- Salmonella phage wksl3
- Genus: L5likevirus
- Mycobacterium phage alma
- Mycobacterium phage arturo
- Mycobacterium phage astro
- Mycobacterium phage backyardigan
- Mycobacterium phage BBPiebs31
- Mycobacterium phage benedict
- Mycobacterium phage bethlehem
- Mycobacterium phage billknuckles
- Mycobacterium phage bruns
- Mycobacterium phage Bxb1
- Mycobacterium phage Bxz2
- Mycobacterium phage Che12
- Mycobacterium phage cuco
- Mycobacterium phage D29
- Mycobacterium phage doom
- Mycobacterium phage ericb
- Mycobacterium phage euphoria
- Mycobacterium phage george
- Mycobacterium phage gladiator
- Mycobacterium phage goose
- Mycobacterium phage hammer
- Mycobacterium phage heldan
- Mycobacterium phage Jasper
- Mycobacterium phage JC27
- Mycobacterium phage jeffabunny
- Mycobacterium phage JHC117
- Mycobacterium phage KBG
- Mycobacterium phage kssjeb
- Mycobacterium phage kugel
- Mycobacterium phage L5
- Mycobacterium phage lesedi
- Mycobacterium phage LHTSCC
- Mycobacterium phage lockley
- Mycobacterium phage marcell
- Mycobacterium phage microwolf
- Mycobacterium phage mrgordo
- Mycobacterium phage museum
- Mycobacterium phage nepal
- Mycobacterium phage packman
- Mycobacterium phage peaches
- Mycobacterium phage Perseus
- Mycobacterium phage pukovnik
- Mycobacterium phage rebeuca
- Mycobacterium phage redrock
- Mycobacterium phage Ridgecb
- Mycobacterium phage rockstar
- Mycobacterium phage saintus
- Mycobacterium phage skipole
- Mycobacterium phage solon
- Mycobacterium phage switzer
- Mycobacterium phage SWU1
- Mycobacterium phage Ta17a
- Mycobacterium phage tiger
- Mycobacterium phage timshel
- Mycobacterium phage trixie
- Mycobacterium phage turbido
- Mycobacterium phage twister
- Mycobacterium phage U2
- Mycobacterium phage violet
- Mycobacterium phage wonder
- Rhodococcus phage RER2
- Rhodococcus phage RGL3
- Genus: Lambdalikevirus
- Enterobacteria phage HK022
- Enterobacteria phage HK97
- Enterobacteria phage lambda
- Genus: Omegalikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage baka
- Mycobacterium phage courthouse
- Mycobacterium phage littlee
- Mycobacterium phage omega
- Mycobacterium phage optimus
- Mycobacterium phage thibault
- Genus: P23likevirus
- Thermus phage P2345
- Thermus phage P7426
- Genus: Pbiunalikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage PBI1
- Genus: Pgonelikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage acadian
- Mycobacterium phage athena
- Mycobacterium phage chrisnmich
- Mycobacterium phage cooper
- Mycobacterium phage gadjet
- Mycobacterium phage nigel
- Mycobacterium phage oline
- Mycobacterium phage Pg1
- Mycobacterium phage pipefish
- Mycobacterium phage rosebush
- Mycobacterium phage stinger
- Mycobacterium phage zemanar
- Genus: Phic3unalikevirus
- Streptomyces phage phibt1
- Streptomyces phage phiC31
- Streptomyces phage TG1
- Genus: Phicbklikevirus
- Caulobacter phage karma
- Caulobacter phage magneto
- Caulobacter phage phicbk
- Caulobacter phage rogue
- Caulobacter phage swift
- Genus: Phie125likevirus
- Burkholderia phage phi6442
- Burkholderia phage phi1026b
- Burkholderia phage phie125
- Genus: Phietalikevirus
- Staphylococcus phage 11
- Staphylococcus phage 29
- Staphylococcus phage 37
- Staphylococcus phage 53
- Staphylococcus phage 55
- Staphylococcus phage 69
- Staphylococcus phage 71
- Staphylococcus phage 80
- Staphylococcus phage 85
- Staphylococcus phage 88
- Staphylococcus phage 92
- Staphylococcus phage 96
- Staphylococcus phage 187
- Staphylococcus phage 52a
- Staphylococcus phage 80alpha
- Staphylococcus phage Cnph82
- Staphylococcus phage Ew
- Staphylococcus phage Ipla5
- Staphylococcus phage Ipla7
- Staphylococcus phage Ipla88
- Staphylococcus phage Ph15
- Staphylococcus phage Phieta
- Staphylococcus phage Phieta2
- Staphylococcus phage Phieta3
- Staphylococcus phage phimr11
- Staphylococcus phage phimr25
- Staphylococcus phage phinm1
- Staphylococcus phage phinm2
- Staphylococcus phage phinm4
- Staphylococcus phage Sap26
- Staphylococcus phage X2
- Genus: Phifllikevirus
- Enterococcus phage phifl1
- Enterococcus phage phifl2
- Enterococcus phage phifl3
- Genus: Phijlunalikevirus
- Lactobacillus phage ATCC8014
- Lactobacillus phage phijl1
- Pediococcus phage clp1
- Genus: Reylikevirus
- Mycobacterium phage bongo
- Mycobacterium phage rey
- Genus: Sap6likevirus
- Enterococcus phage BC611
- Enterococcus phage IMEEF1
- Enterococcus phage SAP6
- Enterococcus phage VD13
- Streptococcus phage SPQS1
- Genus: Sfi1unalikevirus
- Streptococcus phage 858
- Streptococcus phage 2972
- Streptococcus phage Alq132
- Streptococcus phage O1205
- Streptococcus phage Sfi11
- Genus: Sfi21dtunalikevirus
- Streptococcus phage 7201
- Streptococcus phage Abc2
- Streptococcus phage DT1
- Streptococcus phage Sfi19
- Streptococcus phage Sfi21
- Genus: Skunalikevirus
- Lactococcus phage 712
- Lactococcus phage Ascc191
- Lactococcus phage Ascc273
- Lactococcus phage Ascc281
- Lactococcus phage Ascc465
- Lactococcus phage Ascc532
- Lactococcus phage Bibb29
- Lactococcus phage bil170
- Lactococcus phage CB13
- Lactococcus phage CB14
- Lactococcus phage CB19
- Lactococcus phage CB20
- Lactococcus phage jj50
- Lactococcus phage P2
- Lactococcus phage P008
- Lactococcus phage SK1
- Lactococcus phage Sl4
- Genus: T5likevirus
- Enterobacteria phage T5
- Escherichia phage Akfv33
- Escherichia phage Bf23
- Escherichia phage Eps7
- Escherichia phage H8
- Escherichia phage T5
- Salmonella phage Spc35
- Vibrio phage 149 (type IV)
- Genus: Tm4likevirus
- Mycobacterium phage anaya
- Mycobacterium phage angelica
- Mycobacterium phage crimd
- Mycobacterium phage fionn
- Mycobacterium phage jaws
- Mycobacterium phage larva
- Mycobacterium phage macncheese
- Mycobacterium phage pixie
- Mycobacterium phage TM4
- Genus: Tp2unalikevirus
- Bacillus phage BMBtp2
- Bacillus phage TP21
- Genus: Tunalikevirus
- Cronobacter phage Esp2949-1
- Enterobacter phage F20
- Enterobacteria phage T1
- Escherichia phage Eb49
- Escherichia phage Jk06
- Escherichia phage Rogue1
- Escherichia phage Rtp
- Escherichia phage Tls
- Shigella phage Shfl1
- Genus: Wbetalikevirus
- Bacillus phage Wbeta
- Genus: Xp10likevirus
- Xanthomonas phage CP1
- Xanthomonas phage OP1
- Xanthomonas phage phil7
- Xanthomonas phage Xop411
- Xanthomonas phage Xp10
- Genus: Yualikevirus
- Phage phiJl001
- Pseudomonas phage M6
- Pseudomonas phage Yua
Proposed genera
The organisation of genes in the genera L5likevirus, Lambdalikevirus, Phic3unalikevirus, and Psimunalikevirus and the proposed genera Sfi2likevirus, Sfi1likevirus, Sk1likevirus, and Tm4likevirus suggests that these may form a lambda supergroup (or subfamily).[5]
The following genera have been proposed but are not currently ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses:[6][7][8][9][10][11]
- Genus Cba39unalikevirus; type species: Cellulophaga phage phi39:1
- Species:
- Cellulophaga phage phi39:1
- Species:
- Genus Cba46unalikevirus; type species: Cellulophaga phage phi46:1
- Species:
- Cellulophaga phage phi46:1
- Species:
- Genus Cba18unalikevirus; type species: Cellulophaga phage phi18:1
- Species:
- Cellulophaga phage phi18:1
- Cellulophaga phage phi12:1
- Cellulophaga phage phi12:3
- Cellulophaga phage phi17:1
- Cellulophaga phage phi18:2
- Species:
- Genus Cba10unalikevirus; type species: Cellulophaga phage phi10:1
- Species:
- Cellulophaga phage phi10:1
- Cellulophaga phage phi19:1
- Species:
- Genus Cba13unalikevirus; type species: Cellulophaga phage phi13:1
- Species:
- Cellulophaga phage phi13:1
- Cellulophaga phage phi19:2
- Cellulophaga phage phiST
- Species:
- Genus Jk06likevirus; type species: Escherichia phage Jk06
- Species
- Escherichia phage Eb49
- Escherichia phage Jk06
- Escherichia phage Rogue1
- Escherichia phage AHP24
- Escherichia phage AHS24
- Escherichia phage AHP42
- Escherichia phage AKS96
- Enterobacteria phage phiJLA23
- Enterobacteria phage phiKP26
- Species
- Genus Kp36likevirus; type species: Klebsiella phage KP36
- Species
- Enterobacter phage F20
- Klebsiella phage KP36
- Species
- Genus R1tlikevirus; type species: Lactococcus phage r1t
- Species
- Lactococcus phage r1t
- Species
- Genus Rtplikevirus; type species: Escherichia phage Rtp
- Species
- Escherichia phage Rtp
- Enterobacteria phage vB_EcoS_ACG-M12
- Species
- Genus Tlslikevirus; type species: Escherichia phage Tls
- Species
- Escherichia phage Tls
- Salmonella phage FSL SP-126
- Species
Unclassified
In addition to the above viruses, many members of Siphoviridae have been grouped into an unclassified group with no genus assignment.[12] This group includes numerous phages known to infect Lactobacillus, Mycobacterium, Streptococcus, and other bacteria.
References
- Safferman, R.S.; Cannon, R.E.; Desjardins, P.R.; Gromov, B.V.; Haselkorn, R.; Sherman, L.A.; Shilo, M. (1983). "Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses of Cyanobacteria". Intervirology. 19 (2): 61–66. doi:10.1159/000149339. PMID 6408019.
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ICTV. "Virus Taxonomy: 2014 Release". Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- Lood R, Mörgelin M, Holmberg A, Rasmussen M, Collin M (2008). "Inducible Siphoviruses in superficial and deep tissue isolates of Propionibacterium acnes". BMC Microbiol. 8: 139. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-8-139. PMC 2533672. PMID 18702830.
- Brüssow H, Desiere F (2001). "Comparative phage genomics and the evolution of Siphoviridae: insights from dairy phages". Mol Microbiol. 39 (2): 213–22. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02228.x. PMID 11136444.
- Proux C, van Sinderen D, Suarez J, Garcia P, Ladero V, Fitzgerald GF, Desiere F, Brüssow H (2002). "The dilemma of phage taxonomy illustrated by comparative genomics of Sfi21-like Siphoviridae in lactic acid bacteria". J. Bacteriol. 184 (21): 6026–36. doi:10.1128/JB.184.21.6026-6036.2002. PMC 135392. PMID 12374837.
- Gutiérrez, D; Adriaenssens, EM; Martínez, B; Rodríguez, A; Lavigne, R; Kropinski, AM; García, P (11 September 2013). "Three proposed new bacteriophage genera of staphylococcal phages: "3alikevirus", "77likevirus" and "Phietalikevirus"". Archives of Virology. 159 (2): 389–98. doi:10.1007/s00705-013-1833-1. PMID 24022640.
- Taxonomy Proposals Awaiting Ratification at ICTV
- Taxonomy Proposals Pending at ICTV
- Holmfeldt, K.; Solonenko, N.; Shah, M.; Corrier, K.; Riemann, L.; Verberkmoes, N. C.; Sullivan, M. B. (2013). "Twelve previously unknown phage genera are ubiquitous in global oceans". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (31): 12798–803. doi:10.1073/pnas.1305956110. PMC 3732932. PMID 23858439.
- Niu, Y. D.; McAllister, T. A.; Nash, J. H. E.; Kropinski, A. M.; Stanford, K. (2014). "Four Escherichia coli O157:H7 Phages: A New Bacteriophage Genus and Taxonomic Classification of T1-Like Phages". PLoS ONE. 9 (6): e100426. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0100426. PMC 4070988. PMID 24963920.
- "unclassified Siphoviridae". NCBI Taxonomy.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Siphoviridae |