Pulmonary valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is the semilunar valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. Similar to the aortic valve, the pulmonary valve opens in ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery. At the end of ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle falls rapidly, the pressure in the pulmonary artery will close the pulmonary valve.
| Pulmonary valve | |
|---|---|
.svg.png) Anterior (frontal) view of the opened heart. White arrows indicate normal blood flow. | |
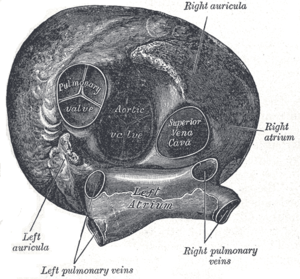 Heart seen from above. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | valva trunci pulmonalis |
| MeSH | D011664 |
| TA | A12.1.02.010 |
| FMA | 7246 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The closure of the pulmonary valve contributes the P2 component of the second heart sound (S2). The right heart is a low-pressure system, so the P2 component of the second heart sound is usually softer than the A2 component of the second heart sound. However, it is physiologically normal in some young people to hear both components separated during inhalation.
Description
- At the apex of the infundibulum, the pulmonary orifice is guarded by three semilunar cusps - two in front and one behind, with free edges projecting upward into the lumen of pulmonary trunk. The free edge of each cusp presents a fibrous nodule of semilunar cusp at the centre with two lateral thin portions, the lunule of semilunar cusp. Each cusp forms pocket like dilatation called pulmonary sinus at initial portion of pulmonary trunk
Additional images
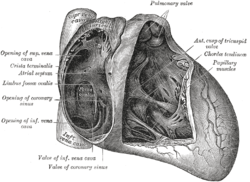 Interior of right side of heart.
Interior of right side of heart.
 Pulmonary valves
Pulmonary valves- Pulmonary valves
See also
External links
- Anatomy figure: 20:07-00 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Adult Congenital Surgery: Pulmonary Valve Replacement