Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a component of the metabolic syndrome and is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall below the threshold to diagnose diabetes mellitus. It usually does not cause symptoms but people with prediabetes often have obesity (especially abdominal or visceral obesity), dyslipidemia with high triglycerides and/or low HDL cholesterol, and hypertension.[1] It is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Prediabetes is more accurately considered an early stage of diabetes as health complications associated with type 2 diabetes often occur before the diagnosis of diabetes.
| Prediabetes | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Prediabetes can be diagnosed by measuring hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, or glucose tolerance test. Many people may be diagnosed through routine screening tests. The primary treatment approach includes lifestyle changes such as exercise and dietary adjustments. Some medications can be used to reduce the risks associated with prediabetes. There is a high rate of progression to type 2 diabetes but not everyone with prediabetes develops type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes can be a reversible condition with lifestyle changes.
Signs and symptoms
Prediabetes typically has no distinct signs or symptoms except the sole sign of high blood sugar. Patients should monitor for signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus such as increased thirst, increased urination, and feeling tired.[2]
Causes
The cause of prediabetes is multifactorial and is known to have contributions from lifestyle and genetic factors. Ultimately prediabetes occurs when control of insulin and blood glucose in the body becomes abnormal, also known as insulin resistance.[3] Risk factors for prediabetes include family history of diabetes, older age, women who have a history of gestational diabetes or high birth weight babies (greater than 9 lbs.).[4]
The increasing rates of prediabetes and diabetes suggest lifestyle and/or environmental factors that contribute to prediabetes. It remains unclear which dietary components are causative and risk is likely influenced by genetic background.[5] Lack of physical activity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes and physical activity can reduce the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes.[4]
Pathophysiology
Normal glucose homeostasis is controlled by three interrelated processes. These processes include gluconeogenesis (glucose production that occurs in the liver), uptake and utilization of glucose by the peripheral tissues of the body, and insulin secretion by the pancreatic beta islet cells. The presence of glucose in the bloodstream triggers the production and release of insulin from the pancreas' beta islet cells. The main function of insulin is to increase the rate of transport of glucose from the bloodstream into certain cells of the body, such as striated muscles, fibroblasts, and fat cells. It also is necessary for transport of amino acids, glycogen formation in the liver and skeletal muscles, triglyceride formation from glucose, nucleic acid synthesis, and protein synthesis. In individuals with prediabetes, a failure of pancreatic hormone release, failure of targeted tissues to respond to the insulin present or both leads to blood glucose rises to abnormally high levels.[6]
Diagnosis
Prediabetes can diagnosed with three different types of blood tests[7]
- Fasting blood sugar (glucose) level of:
- 110 to 125 mg/dL (6.1 mM/L to 6.9 mM/L) – WHO criteria
- 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 mM/L to 6.9 mM/L) – ADA criteria
- Glucose tolerance test: blood sugar level of 140 to 199 mg/dL (7.8 to 11.0 mM) 2 hours after ingesting a standardized 75 gram glucose solution[7]
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) between 5.7 and 6.4 percent[7]
Levels above these limits would justify a diagnosis for diabetes.
Impaired fasting glucose
Impaired fasting glycemia or impaired fasting glucose (IFG) refers to a condition in which the fasting blood glucose is elevated above what is considered normal levels but is not high enough to be classified as diabetes mellitus. It is considered a pre-diabetic state, associated with insulin resistance and increased risk of cardiovascular pathology, although of lesser risk than impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). IFG sometimes progresses to type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Fasting blood glucose levels are in a continuum within a given population, with higher fasting glucose levels corresponding to a higher risk for complications caused by the high glucose levels. Some patients with impaired fasting glucose also may be diagnosed with impaired glucose tolerance, but many have normal responses to a glucose tolerance test. Fasting glucose is helpful in identifying prediabetes when positive but has a risk of false negatives.[8]
World Health Organization (WHO) criteria for impaired fasting glucose differs from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) criteria, because the normal range of glucose is defined differently by each. Fasting plasma glucose levels 100 mg/dL (5.5 mmol/L) and higher have been shown to increase complication rates significantly, however, WHO opted to keep its upper limit of normal at under 110 mg/dL for fear of causing too many people to be diagnosed as having impaired fasting glucose, whereas the ADA lowered the upper limit of normal to a fasting plasma glucose under 100 mg/dL.
Impaired glucose tolerance
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) is diagnosed with an oral glucose tolerance test. According to the criteria of the World Health Organization and the American Diabetes Association, impaired glucose tolerance is defined as:[9][10]
- two-hour glucose levels of 140 to 199 mg per dL (7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l) on the 75-g oral glucose tolerance test. A patient is said to be under the condition of IGT when he/she has an intermediately raised glucose level after 2 hours, but less than the level that would qualify for type 2 diabetes mellitus. The fasting glucose may be either normal or mildly elevated.
From 10 to 15 percent of adults in the United States have impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose.[11]
Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin A1c is a measure of the percent of red blood cells that are glycated, or have a glucose molecule attached. This can be used as an indicator of blood glucose level over a longer period of time and is often used to diagnose prediabetes as well as diabetes. HbA1c may not accurately represent blood glucose levels and should not be used in certain medical conditions such as iron-deficiency anemia, Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency, pregnancy, hemolytic anemia, splenomegaly and end-stage renal failure.[3]
Fasting Insulin
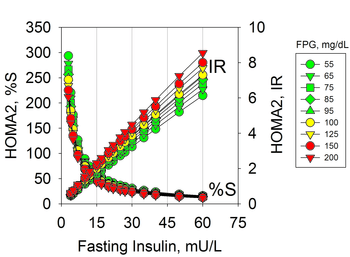
Hyperinsulinemia due to insulin resistance may occur in individuals with normal glucose levels and therefore is not diagnosed with usual tests. Hyperinsulinemia precedes prediabetes and diabetes that are characterized by hyperglycemia.[12] Insulin resistance can be diagnosed by measures of plasma insulin, both fasting or during a glucose tolerance test.[13][14] The use of fasting insulin to identify patients at risk has been proposed, but is currently not commonly used in clinical practice.[15]
The implications of hyperinsulinemia is the risk of comorbidities related to diabetes that may precede changes in blood glucose[16][17][12] including cardiovascular diseases.[18][19][20]
Screening
Fasting plasma glucose screening should begin at age 30–45 and be repeated at least every three years. Earlier and more frequent screening should be conducted in at-risk individuals. The risk factors for which are listed below:
- Family history (parent or sibling)
- Dyslipidemia (triglycerides > 200 or HDL < 35)
- Overweight or obesity (body mass index > 25)
- History of gestational diabetes or infant born with birth weight greater than 9 lb (4 kg)
- High risk ethnic group
- Hypertension (systolic blood pressure >140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure > 90 mmHg)
- Prior fasting blood glucose > 99
- Known vascular disease
- Markers of insulin resistance (PCOS, acanthosis nigricans)[21][22]
Prevention
The American College of Endocrinology (ACE) and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) have developed lifestyle intervention guidelines for preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes:
- Healthy diet (a diet with limited refined carbohydrates, added sugars, trans fats, as well as limited intake of sodium and total calories)
- Physical fitness (30–45 minutes of cardiovascular exercise per day, 3-5 days a week)
- Weight loss by as little as 5–10 percent may have a significant impact on overall health
Management
There is evidence that prediabetes is a curable disease state.[23] Although some drugs can delay the onset of diabetes, lifestyle modifications play a greater role in the prevention of diabetes.[11][24] Intensive weight loss and lifestyle intervention, if sustained, may improve glucose tolerance substantially and prevent progression from IGT to type 2 diabetes. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP)[25] study found a 16% reduction in diabetes risk for every kilogram of weight loss. Reducing weight by 7% through a low-fat diet and performing 150 minutes of exercise a week is the goal. The ADA guidelines recommend modest weight loss (5–10% body weight), moderate-intensity exercise (30 minutes daily), and smoking cessation.[26]
There are many dietary approaches that can reduce the risk of progression to diabetes. Most involve the reduction of added sugars and fats but there remains a lack of conclusive evidence proving the best approach.[27]
For patients with severe risk factors, prescription medication may be appropriate. This may be considered in patients for whom lifestyle therapy has failed, or is not sustainable, and who are at high-risk for developing type 2 diabetes.[28] Metformin[29] and acarbose help prevent the development of frank diabetes, and also have a good safety profile. Evidence also supports thiazolidinediones but there are safety concerns, and data on newer agents such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, DPP4 inhibitors or meglitinides are lacking.[30]
Prognosis
The progression to type 2 diabetes mellitus is not inevitable for those with prediabetes. The progression into diabetes mellitus from prediabetes is approximately 25% over three to five years.[31] This increases to 50% risk of progressing to diabetes over 10 years. Diabetes is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Effects of the disease may affect larger blood vessels (e.g., atherosclerosis within the larger arteries of the cardiovascular system) or smaller blood vessels, as seen with damage to the retina of the eye, damage to the kidney, and damage to the nerves.[6]
Prediabetes is a risk factor for mortality and there is evidence of cardiovascular disease developing prior to a diagnosis of diabetes.[32]
Epidemiology
Studies conducted from 1988–1994 indicated that of the total population of US in the age group 40–74 years, 34% had IFG, 15% had IGT, and 40% had prediabetes (IFG, IGT, or both). Eighteen million people (6% of the population) had type 2 diabetes in 2002.[33]
The incidence of diabetes is growing. In 2014, 29.1 million people or 9% of the US population had diabetes.[34] In 2011–2012, the prevalence of diabetes in the U.S. using hemoglobin A1C, fasting plasma glucose or the two-hour plasma glucose definition was 14% for total diabetes, 9% for diagnosed diabetes, 5% for undiagnosed diabetes and 38% for prediabetes.[35]
References
- American Diabetes Association (January 2017). "2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes". Diabetes Care. 40 (Suppl 1): S11–S24. doi:10.2337/dc17-S005. PMID 27979889.
- "Diabetes: 'Prediabetes'". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved January 27, 2009.
- Wilson, Mara Lynn (2017). "Prediabetes". Nursing Clinics of North America. 52 (4): 665–677. doi:10.1016/j.cnur.2017.07.011.
- Poltavskiy, Eduard; Kim, Dae Jung; Bang, Heejung (2016). "Comparison of screening scores for diabetes and prediabetes". Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 118: 146–153. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2016.06.022.
- Dietrich, Stefan; Jacobs, Simone; Zheng, Ju‐Sheng; Meidtner, Karina; Schwingshackl, Lukas; Schulze, Matthias B. (2019). "Gene‐lifestyle interaction on risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review". Obesity Reviews. 20 (11): 1557–1571. doi:10.1111/obr.12921. ISSN 1467-7881.
- Cotran; Kumar; Collins (1999). Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease (Saunders Sixth ed.). pp. 913–26.
- American Diabetes Association (2019). "2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019". Diabetes Care. 42 (Supplement 1): S13–S28. doi:10.2337/dc19-S002. ISSN 0149-5992.
- Nichols GA, Hillier TA, Brown JB (2007). "Progression From Newly Acquired Impaired Fasting Glusose to Type 2 Diabetes". Diabetes Care. 30 (2): 228–33. doi:10.2337/dc06-1392. PMC 1851903. PMID 17259486.
- World Health Organization. "Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications: Report of a WHO Consultation. Part 1. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus". Retrieved 2007-05-29.
- American Diabetes Association (2005). "Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus". Diabetes Care. 28 Suppl 1: S37–42. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.suppl_1.s37. PMC 3632174. PMID 15618111.
- Shobha S. Rao; Phillip Disraeli; Tamara McGregor (15 April 2004). "Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glucose". American Family Physician. 69 (8): 1961.
- Lima, Luis Mauricio TR (2017). "Subclinical Diabetes" (PDF). An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 89 (1): 591–614. doi:10.1590/0001-3765201720160394. PMID 28492735.
- Kraft, JR (1975). "Detection of Diabetes Mellitus In Situ (Occult Diabetes)". Laboratory Medicine. 6 (2): 10–22. doi:10.1093/labmed/6.2.10.
- Reaven, GM; Lerner, RL; Stern, MP; Farguhar, JW (1967). "Role of insulin in endogenous hypertriglyceridemia" (PDF). The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 46 (11): 1756–67. doi:10.1172/JCI105666. PMC 292926. PMID 6061748.
- Association, American Diabetes (1998). "Consensus Development Conference on Insulin Resistance: 5–6 November 1997". Diabetes Care. 21 (2): 310–14. doi:10.2337/diacare.21.2.310. PMID 9540000.
- Keebler ME & McGuire DK 2003 Subclinical diabetes mellitus: is it really “sub-clinical”? American Heart Journal 146 210–12. doi:10.1016/S0002-8703(03)00236-9
- Lima LMTR 2017 "Prediabetes definitions and clinical outcomes". The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 5 92–93. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30011-6
- Hanley AJG, Williams K, Stern MP & Haffner SM 2002 "Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in relation to the incidence of cardiovascular disease: the San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care 25 1177–84.
- Valenti V, Hartaigh B ó, Cho I, Schulman-Marcus J, Gransar H, Heo R, Truong QA, Shaw LJ, Knapper J, Kelkar AA et al. 2016 Absence of Coronary Artery Calcium Identifies Asymptomatic Diabetic Individuals at Low Near-Term But Not Long-Term Risk of Mortality A 15-Year Follow-Up Study of 9715 Patients. Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging 9 e003528. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003528
- DECODE Study Group, European Diabetes Epidemiology Group 2003 "Is the current definition for diabetes relevant to mortality risk from all causes and cardiovascular and noncardiovascular diseases?" Diabetes Care 26 688–696.
- "ADA: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes", Diabetes Care 27: Supp 1.515, 2004.
- "Diabetes Guidelines Taskforce: AACE Guidelines for the Management of DM", Endocrin Pract 1995, 1.149
- Eldin, W. Shehab; Emara, M.; Shoker, A. (2008-04-01). "Prediabetes: a must to recognise disease state". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 62 (4): 642–48. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2008.01705.x. ISSN 1742-1241. PMID 18266711.
- Raina Elley C, Kenealy T (December 2008). "Lifestyle interventions reduced the long-term risk of diabetes in adults with impaired glucose tolerance". Evid Based Med. 13 (6): 173. doi:10.1136/ebm.13.6.173. PMID 19043031.
- "Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP)".
- American Diabetes Association. "How to Prevent or Delay Diabetes". Archived from the original on 2009-08-22.
- Taubes, Gary (27 December 2017). "Minimal carbs, lots of fat, incredible dieting results – but not enough science". Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- UptoDate: Prediction and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus; www.utdol.com/utd/content/topic.do?topicKey=diabetes.
- Lilly M, Godwin M (Apr 2009). "Treating prediabetes with metformin: systematic review and meta-analysis". Canadian Family Physician. 55 (4): 363–69.
- "American College of Endocrinology Consensus Statement on the diagnosis and management of pre-diabetes in the continuum of hyperglycemia – When do the risks of diabetes begin?" (PDF). American College of Endocrinology Task Force on Pre-Diabetes. Retrieved 2008-07-24.
- Nathan; et al. (Mar 2007). "Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance: implications for care". Diabetes Care. 30 (3): 753–39. doi:10.2337/dc07-9920. PMID 17327355.
- Barr EL, Zimmet PZ, Welborn TA, et al. (2007). "Risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in individuals with diabetes mellitus, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance: the Australian Diabetes, Obesity, and Lifestyle Study (AusDiab)". Circulation. 116 (2): 151–57. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.685628. PMID 17576864.
- CDC: Diabetes. National Diabetes Fact Sheet; United States, 2003.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2014). "National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and its Burden in the United States, 2014". Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Archived from the original on 2016-12-02.
- Menke, Andy; Casagrande, Sarah; Geiss, Linda; Cowie, Catherine C. (2015). "Prevalence of and Trends in Diabetes Among Adults in the United States, 1988-2012". JAMA. 314 (10): 1021–9. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.10029. PMID 26348752.
Further reading
- Davies, Melanie J; Gray, I Peter (3 February 1996). "Impaired glucose tolerance". British Medical Journal. 312 (7026): 264–65. doi:10.1136/bmj.312.7026.264. PMC 2349870. PMID 8611769. – Editorial review
- Nathan, DM; Davidson, MB; DeFronzo, RA; Heine, RJ; Henry, RR; Pratley, R; Zinman, B; American Diabetes Association (March 2007). "Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance: implications for care". Diabetes Care. 30 (3): 753–59. doi:10.2337/dc07-9920. PMID 17327355.