Polymer fume fever
Polymer fume fever or fluoropolymer fever, also informally called Teflon flu, is an inhalation fever caused by the fumes released when polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, known under the trade name Teflon) reaches temperatures of 300 °C (572 °F) to 450 °C (842 °F).[1] When PTFE is heated above 450 °C the pyrolysis products are different and inhalation may cause acute lung injury.[2] Symptoms are flu-like (chills, headaches and fevers) with chest tightness and mild cough. Onset occurs about 4 to 8 hours after exposure to the pyrolysis products of PTFE. A high white blood cell count may be seen and chest x-ray findings are usually minimal.
| Polymer fume fever | |
|---|---|
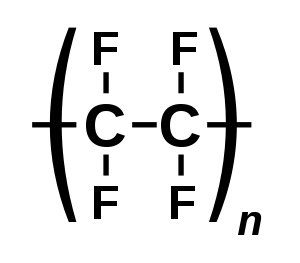 | |
| Chemical structure of Teflon, the polymer whose breakdown products cause this condition | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine |
The polymer fumes are especially harmful to certain birds whose breathing, optimized for rapidity, allows toxins which are excluded by human lungs. Fumes from Teflon in very high heat are fatal to parrots,[3] as well as some other birds (PTFE Toxicosis).[4]
See also
References
- Shusterman, D. J. (1 July 1993). "Polymer fume fever and other fluorocarbon pyrolysis-related syndromes". Occupational Medicine (Philadelphia, Pa.). 8 (3): 519–531. ISSN 0885-114X. PMID 8272977.
- Shimizu T, Hamada O, Sasaki A, Ikeda M (December 2012). "Polymer fume fever". BMJ Case Rep. 2012. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007790. PMC 4544973. PMID 23230259.
- Athan, Mattie Sue, Guide to a Well-Behaved Parrot, p. 126, Barron's Educational Service, 1993, ISBN 0-8120-4996-9.
- "Teflon Toxicity (PTFE Toxicosis) in Birds: Signs and Prevention". Retrieved 25 October 2013.