PipISB
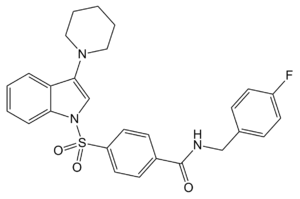
PipISB is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent and selective inverse agonist of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is highly selective for the CB1 receptor over CB2, with a Kd at CB1 of 1.5nM vs over 7000nM at CB2, has good blood-brain barrier penetration, and can be conveniently radiolabelled with either 11C or 18F, making it useful for mapping the distribution of CB1 receptors in the brain.[1][2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H26FN3O3S |
| Molar mass | 491.58 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
References
- Donohue, Sean R.; Halldin, Christer; Schou, Magnus; Hong, Jinsoo; Phebus, Lee; Chernet, Eyassu; Hitchcock, Stephen A.; Gardinier, Kevin M.; Ruley, Kevin M.; Krushinski, Joseph H.; Schaus, John; Pike, Victor W. (2008). "Radiolabeling of a high potency cannabinoid subtype-1 receptor inverse agonist, N-(4-fluoro-benzyl)-4-(3-(piperidin-1-yl-indole-1-sulfonyl)benzamide (PipISB), with carbon-11 or fluorine-18". Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals. 51 (3): 146. doi:10.1002/jlcr.1491.
- Finnema, S. J.; Donohue, S. R.; Zoghbi, S. S.; Brown, A. K.; Gulyás, B. Z.; Innis, R. B.; Halldin, C.; Pike, V. W. (2009). "Evaluation of \11C]PipISB and \18F]PipISB in monkey as candidate radioligands for imaging brain cannabinoid type-1 receptors in vivo". Synapse. 63 (1): 22–30. doi:10.1002/syn.20578. PMC 2587077. PMID 18925657.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.