Perisylvian syndrome
Perisylvian syndrome is a rare neurological disease characterized by damage to the sylvian fissure (lateral sulcus), an area in the brain involved in language and speech. The main symptoms are difficulty chewing and swallowing, low muscle tone in the face and tongue, speech and language development disorders, and epilepsy. These symptoms may also be accompanied by difficulties with mobility and intellectual disabilities.[1]
| Perisylvian syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bilateral perisylvian polymicrogyria |
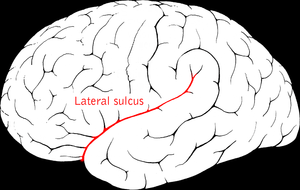 | |
| Lateral sulcus2(Sylvian fissure) | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.