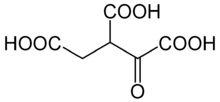
Oxalosuccinic acid
Oxalosuccinic acid is a substrate of the citric acid cycle. It is acted upon by isocitrate dehydrogenase. Salts and esters of oxalosuccinic acid are known as oxalosuccinates.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-Oxopropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.021 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C6H6O7 |
| Molar mass | 190.108 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Oxalosuccinic acid/oxalosuccinate is an unstable 6-carbon intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. It's a keto acid, formed during the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate, which is catalyzed by the enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase. Isocitrate is first oxidized by coenzyme NAD+ to form oxalosuccinic acid/oxalosuccinate.[1] Oxalosuccinic acid is both an alpha-keto and a beta-keto acid (an unstable compound) and it is the beta-ketoic property that allows the loss of carbon dioxide in the enzymatic reaction in conversion to the five-carbon molecule 2-oxoglutarate.[2]
References
- Ochoa S (May 1948). "Biosynthesis of tricarboxylic acids by carbon dioxide fixation; the preparation and properties of oxalosuccinic acid". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 174 (1): 115–22. PMID 18914069.
- Romkina AY, Kiriukhin MY (2017-04-19). "Biochemical and molecular characterization of the isocitrate dehydrogenase with dual coenzyme specificity from the obligate methylotroph Methylobacillus Flagellatus". PLOS ONE. 12 (4): e0176056. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1276056R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0176056. PMC 5397045. PMID 28423051.