Nodular melanoma
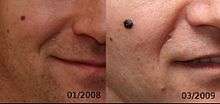
Nodular melanoma (NM) is the most aggressive form of melanoma. It tends to grow more rapidly in thickness (penetrate the skin) than in diameter. Instead of arising from a pre-existing mole, it may appear in a spot where a lesion did not previously exist . Since NM tends to grow in depth more quickly than it does in width, and can occur in a place that did not have a previous lesion, the prognosis is often worse because it takes longer for a person to be aware of the changes. NM is most often darkly pigmented; however, some NM lesions can be light brown, multicolored or even colorless (non-pigmented). A light-colored or non-pigmented NM lesion may escape detection because the appearance is not alarming, however an ulcerated and/or bleeding lesion is common.[1]:696 Polypoid melanoma is a virulent variant of nodular melanoma.[1]:696
| Nodular melanoma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Oncology, dermatology |
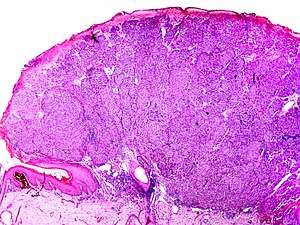
The microscopic hallmarks are:
- Dome-shaped at low power
- Epidermis thin or normal
- Dermal nodule of melanocytes with a 'pushing' growth pattern
- No "radial growth phase"
Treatment
Therapies for metastatic melanoma include the biologic immunotherapy agents ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, and nivolumab; BRAF inhibitors, such as vemurafenib and dabrafenib; and a MEK inhibitor trametinib.[2]
See also
References
- James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- Maverakis E, Cornelius LA, Bowen GM, Phan T, Patel FB, Fitzmaurice S, He Y, Burrall B, Duong C, Kloxin AM, Sultani H, Wilken R, Martinez SR, Patel F (2015). "Metastatic melanoma - a review of current and future treatment options". Acta Derm Venereol. 95 (5): 516–524. doi:10.2340/00015555-2035. PMID 25520039.