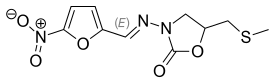
Nitrofuran
Nitrofurans are a class of drugs typically used as antibiotics or antimicrobials.[1] The defining structural component is a furan ring with a nitro group.[2]
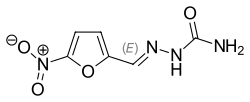
Nitrofural (nitrofurazone)
Members of this class of drugs include:
- Antibacterials (antibiotics)
- Difurazone (also known as Nitrovin) — an antibacterial growth promoter used in the animal feeds
- Furazolidone
- Nifurfoline
- Nifuroxazide
- Nifurquinazol
- Nifurtoinol
- Nifurzide
- Nitrofural (also known as nitrofurazone)
- Nitrofurantoin — a drug used to treat urinary tract infections[3]
- Ranbezolid — technically an oxazolidinone antibiotic bearing a nitrofuran group
- Antimicrobials
- Furaltadone — an antiprotozoal
- Furazidine — an antibacterial and antiprotozoal
- Furylfuramide — a formerly used food preservative
- Nifuratel — an antiprotozoal and antifungal
- Nifurtimox — an antiprotozoal
- FANFT, a potent nitrofuran derivative tumor initiator. It causes bladder tumors in all animals studied and is mutagenic to many bacteria.
References
- Chu, Pak-Sin; Lopez, Mayda I; Abraham, Ann; El Said, Kathleen R; Plakas, Steven M (2008). "Residue Depletion of Nitrofuran Drugs and Their Tissue-Bound Metabolites in Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) after Oral Dosing". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 56 (17): 8030–8034. doi:10.1021/jf801398p. PMID 18698789.
- Vass, M; Hruska, K; Franek, M (2008). "Nitrofuran antibiotics: a review on the application, prohibition and residual analysis". Veterinární Medicína. 53: 469–500. doi:10.17221/1979-VETMED.
- Huttner, Angela; Verhaegh, Els M; Harbarth, Stephan; Muller, Anouk E; Theuretzbacher, Ursula; Mouton, Johan W (2015). "Nitrofurantoin revisited: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 70 (9): 2456–2464. doi:10.1093/jac/dkv147. PMID 26066581.
External links
- Nitrofurans at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.