Nesiritide
Nesiritide (Natrecor) is the recombinant form of the 32 amino acid human B-type natriuretic peptide, which is normally produced by the ventricular myocardium. Nesiritide works to facilitate cardiovascular fluid homeostasis through counterregulation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, stimulating cyclic guanosine monophosphate, leading to smooth muscle cell relaxation.
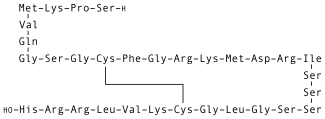 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | IV only |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C143H244N50O42S4 |
| Molar mass | 3464 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Nesiritide was believed initially to be beneficial for acute decompensated congestive heart failure. It received approval from the United States' Food and Drug Administration for this purpose in 2001 after initial non-approval. In July 2011 the results of the largest study so far for nesiritide was published in The New England Journal of Medicine. The study failed to show a difference between nesiritide and placebo on mortality or re-hospitalizations.[1]
Administration
Nesiritide is only administered intravenously, usually by bolus, followed by IV infusion. For most adults and the elderly, a normal dosage is 2 mg/kg followed by a continuous IV infusion of 0.01 mg/kg/min. This may be increased every three hours for a maximum of 0.03 mg/kg/min.
Controversy
In 2005, after several academic papers published by Jonathan Sackner-Bernstein[2][3][4] on the efficacy and side effects of Nesiritide, Johnson & Johnson met with the FDA and altered its stated plans for the drug and agreed to revise its labeling.[5][6]
Heart doctors at the Cleveland Clinic then voted unanimously not to permit the prescription of the drug to its patients.[6] Johnson and Johnson convened a panel of experts whose advice included the recommendation to conduct the large scale clinical trial that was subsequently published in 2011.[7] Following this, the United States Department of Justice announced an inquiry into the marketing of the drug[8] that led to a fine against the Scios unit of J&J.[9]
Side effects
Common side effects include:
- Low blood pressure (11% of patients)
- Headache
- Nausea
- Slow heart rate
- Kidney failure[10]
More rare side effects include:
References
- O'Connor (2011). "Effect of nesiritide in patients with acute decompensated heart failure" (PDF). New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (32): 32–43. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100171. hdl:11379/60663. PMID 21732835.
- Sackner-Bernstein, Jonathan D.; Skopicki, Hal A.; Aaronson, Keith D. (29 March 2005). "Risk of Worsening Renal Function With Nesiritide in Patients With Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure". Circulation. 111 (12): 1487–1491. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000159340.93220.E4. PMID 15781736.
- Sackner-Bernstein, Jonathan D.; Kowalski, Marcin; Fox, Marshal; Aaronson, Keith (2005-04-20). "Short-term risk of death after treatment with nesiritide for decompensated heart failure: a pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials". JAMA. 293 (15): 1900–1905. doi:10.1001/jama.293.15.1900. ISSN 1538-3598. PMID 15840865.
- Aaronson, Keith D.; Sackner-Bernstein, Jonathan (2006-09-27). "Risk of death associated with nesiritide in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure". JAMA. 296 (12): 1465–1466. doi:10.1001/jama.296.12.1465. ISSN 1538-3598. PMID 17003394.
- Saul, Stephanie (17 May 2005). "The Marketing and Success of Natrecor" – via NYTimes.com.
- Saul, Stephanie (4 May 2005). "Heart Clinic May End or Curtail Use of a Drug" – via NYTimes.com.
- Herper, Matthew. "Bitter Pill For J&J On Heart Drug" Check
|url=value (help). Forbes. - Saul, Stephanie (21 July 2005). "U.S. Looking at Marketing by Johnson & Johnson" – via NYTimes.com.
- "Johnson & Johnson Subsidiary Scios Pleads Guilty to Misbranding Heart Failure Drug Natrecor". www.justice.gov. 5 October 2011.
- "Natrecor Adverse Reactions - Epocrates Online". online.epocrates.com.
Further reading
Science or Fiction: Use of Nesiritide as a First-Line Agent? John A. Noviasky, Pharm.D., Michael Kelberman, M.D., Karen M. Whalen, B.S., Roy Guharoy, Pharm.D., William Darko, Pharm.D.