Medial pterygoid nerve
The medial pterygoid nerve (or internal pterygoid nerve) is a branch of the mandibular nerve that innervates the medial pterygoid muscle, tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani.[1]
| Medial pterygoid nerve | |
|---|---|
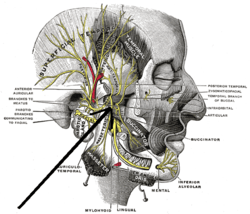 Mandibular division of the trigeminus nerve. (Internal pterygoid nerve visible but not labeled.) | |
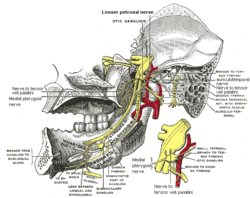 Mandibular division of trifacial nerve, seen from the middle line. Nerve to medial pterygoid labeled at bottom. | |
| Details | |
| From | Mandibular nerve |
| Innervates | Medial pterygoid, tensor veli palatini, tensor tympani |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus pterygoideus internus nervus pterygoideus medialis |
| TA | A14.2.01.066 |
| FMA | 53056 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
The nerve to the medial pterygoid muscle is a slender branch of the mandibular nerve which enters the deep surface of the muscle; it gives off one or two filaments to the otic ganglion.
The nerve provides physical support for the otic ganglion, but is neurologically distinct.
Branches
Additionally, the tensor veli palatini is innervated by the nerve to tensor veli palatini, a branch of the nerve to the medial pterygoid. Of the five paired skeletal muscles to the soft palate, tensor veli palati is the only muscle not innervated by the pharyngeal plexus.
See also
References
- Tomo, S; Nakajima, K; Tomo, I; Nodai, E; Kobayashi, S (April 1995). "The morphology and innervation of the lateral pterygoid muscle of the dog". Journal of Anatomy. 186: 435–439. PMID 7649845.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 894 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)