Negative-pressure wound therapy
Negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT), also known as a vacuum dressing or V.A.C.® dressing ("vacuum assisted closure"), is a therapeutic technique using a suction dressing to remove excess exudation and promote healing in acute or chronic wounds and second- and third-degree burns. The therapy involves the controlled application of sub-atmospheric pressure to the local wound environment,[1][2] using a sealed wound dressing connected to a vacuum pump.[3][4] The use of this technique in wound management increased dramatically over the 1990s and 2000s[5] and a large number of studies have been published examining NPWT.[6] NPWT appears to be useful for diabetic ulcers[7] and management of the open abdomen (laparotomy)[8] but further research is required for other wound types.[9]
Overview
NPWT promotes wound healing by applying a vacuum through a special sealed dressing. The continued vacuum draws out fluid from the wound and increases blood flow to the area.[3] The vacuum may be applied continuously or intermittently, depending on the type of wound being treated and the clinical objectives. Typically, the dressing is changed two to three times per week.[4] The dressings used for the technique include open-cell foam dressings and gauze, sealed with an occlusive dressing intended to contain the vacuum at the wound site.[1] Where NPWT devices allow delivery of fluids, such as saline or antibiotics to irrigate the wound,[10][11] intermittent removal of used fluid supports the cleaning and drainage of the wound bed.[12]
In 1995, Kinetic Concepts was the first company to have a NPWT product cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration.[13] Following increased use of the technique by hospitals in the US, the procedure was approved for reimbursement by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services in 2001.[1]
Technique

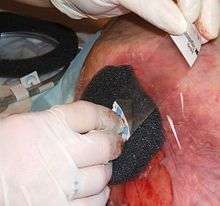
General technique for NPWT is as follows: "protect the periwound by applying a skin barrier then it should be followed by a transparent film."[14] A dressing or filler material is fitted to the contours of a wound (which is covered with a non-adherent dressing film) and the overlying foam is then sealed with a transparent film. A drainage tube is connected to the dressing through an opening of the transparent film. A vacuum tube is connected through an opening in the film drape to a canister on the side of a vacuum pump.[15] or vacuum source, turning an open wound into a controlled, closed wound[3] while removing excess fluid from the wound bed to enhance circulation and remove wound fluids. This creates a moist healing environment and reduces edema.[6] "There must be an air tight seal in order for this therapy to be successful."[14][15] The technique is usually used with chronic wounds or wounds that are expected to present difficulties while healing (such as those associated with diabetes).[4]
Three types of filler material are used over the wound surface: open-cell foam, gauze and transparent film, or honeycombed textiles with a dimpled wound contact surface.
- Foam dressings are used to fill open cavity wounds and can be cut to size to fit wounds. The foam dressing is applied, filling the wound and then a film drape is applied over the top to create a seal around the dressing.
- Open weave cotton gauze can be covered with a transparent film, and a flat drain is sandwiched in gauze and placed onto the wound. The film drape covers the wound and create a complete seal, and then the drain is connected to the pump via the tubing.[16]
- Layers of non-woven polyester, joined by a silicone elastomer, have a non-adherent wound contact surface made up of numerous small semi-rigid dome structures.[17] This solution has not completed a clinical trial as of December 2012.[18]
With all three techniques, once the dressing is sealed the vacuum pump can be set to deliver continuous or intermittent pressures, with levels of pressure depending on the device used,[15][16][19] varying between −125 and −75 mmHg depending on the material used and patient tolerance.[17][20] Pressure can be applied constantly or intermittently.[15]
The dressing type used depends on the type of wound, clinical objectives and patient. For pain sensitive patients with shallow or irregular wounds, wounds with undermining or explored tracts or tunnels, gauze may be used, while foam may be cut easily to fit a patient’s wound that has a regular contour and perform better when aggressive granulation formation and wound contraction is the desired goal.[21]
Contraindications
Contraindications for NPWT use include:[22]
- Malignancy in the wound
- Untreated osteomyelitis
- Non enteric and unexplored fistulas
- Necrotic tissue with eschar present
- Exposed blood vessels, anastomotic sites, organs and nerves in the periwound area (must avoid direct foam contact with these structures)[23]
Effectiveness
A 2007 Cochrane Review stated that the evidence comparing NPWT to alternative care was flawed and required more study, but the evidence did support improved healing and called for more, better quality research to be conducted.[9] A 2010 systematic review found "consistent evidence of the benefit of NPWT" in the treatment of diabetic ulcers of the feet. Results for bedsores were conflicting and research on mixed wounds was of poor quality, but promising. The review did not find evidence of increased significant complications. The review concluded "There is now sufficient evidence to show that NPWT is safe, and will accelerate healing, to justify its use in the treatment of diabetes-associated chronic leg wounds. There is also evidence, though of poor quality, to suggest that healing of other wounds may also be accelerated."[7]
References
- Lillis, Karin (2003). "Effective wound care requires look at total patient picture". Healthcare Purchasing News. 27 (1): 32. ISSN 0279-4799.
- Cipolla J, Baillie DR, Steinberg SM, Martin ND, Jaik NP, Lukaszczyk JJ, Stawicki SP (2008). "Negative pressure wound therapy: Unusual and innovative applications". OPUS 12 Scientist. 2 (3): 15–29.
- Moody, Yasmeen (19 July 2001). "Advances in healing chronic wounds". The Ithaca Journal. Ithaca, NY. p. 10A.
- Fogg, Erich (27 August 2009). "Best treatment of nonhealing and problematic wounds". Journal of the American Academy of Physician Assistants. 22 (8): 46, 48. doi:10.1097/01720610-200908000-00013. PMID 19725415.
- Driscoll, P (24 October 2009). "Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (Gauze and Foam)". Advanced Medical Technologies. Archived from the original on 21 August 2011.
- Gupta, Subhas; Bates-Jensen, Barbara; Gabriel, Allen; Holloway, Allen; Niezgoda, Jeffrey; Weir, Dot (2007). "Differentiating Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Devices: An Illustrative Case Series" (PDF). Wounds. 19 (1 (Supplement)): 1–9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2010. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- Xie, X.; McGregor, M.; Dendukuri, N. (November 2010). "The clinical effectiveness of negative pressure wound therapy: a systematic review". Journal of Wound Care. 19 (11): 490–5. doi:10.12968/jowc.2010.19.11.79697. PMID 21135797.
- Fitzgerald James EF (2012). "Laparostomy management using the ABThera™ open abdomen negative pressure therapy system in a grade IV open abdomen secondary to acute pancreatitis". International Wound Journal. 10: 138–144. doi:10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.00953.x.
- Ubbink, Dirk T; Westerbos, Stijn Joël; Evans, Debra; Land, Lucy; Vermeulen, Hester (2008). Ubbink, Dirk T (ed.). "Topical negative pressure for treating chronic wounds". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 16 (3): CD001898. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001898.pub2. PMID 18646080. (Retracted, see doi:10.1002/14651858.cd001898.pub3. If this is an intentional citation to a retracted paper, please replace
{{Retracted}}with{{Retracted|intentional=yes}}.) - Gerry R, Kwei S, Bayer L, Breuing KH (July 2007). "Silver-impregnated vacuum-assisted closure in the treatment of recalcitrant venous stasis ulcers". Ann Plast Surg. 59 (1): 58–62. doi:10.1097/01.sap.0000263420.70303.cc. PMID 17589262.
- Wendling, Patrice (April 2008). "Vacuum-assisted wound therapy uses expanded" (PDF). Skin & Allergy News. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 August 2011. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- Moch D, Fleischmann W, Westhauser A (1998). "Instillationsvakuumversiegelung: ein erster Erfahrungsbericht" [Instillation vacuum sealing—report of initial experiences]. Langenbecks Archiv für Chirurgie (in German). 115: 1197–9. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-45774-6_279. PMID 9931834.
- "Vacuum Assisted Closure Wound Therapy Cleared for Partial Thickness Burns". Reuters Health Medical News. 27 January 2003.
- "The Challenges of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Clinical Practice | Today's Wound Clinic". www.todayswoundclinic.com. Retrieved 20 April 2017.
- Baxter, Helena; Ballard, Kate (2001). "Vacuum-Assisted Closure". Nursing Times. 97 (35): 51–2. PMID 11957602. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- Miller, Michael S.; Brown, Rhonda; McDaniel, Cheryl (1 September 2005). "Negative pressure wound therapy options promote patient care". Biomechanics. p. 49. Archived from the original on 29 September 2011.
- Glat, Paul (8 July 2010). "The use of negative pressure wound therapy with Bio-Dome™ dressing technology". Today's Wound Clinic. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- "Negative Pressure Wound Therapy With the Engenex™-Pump and Bio-Dome™ Dressing, an Evaluation - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov". clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- Miller, Michael S. (February 2009). "Multiple approaches offer negative pressure options". Biomechanics. Archived from the original on 29 September 2011.
- Morykwas, Michael J.; Argenta, Louis C.; Shelton-Brown, Erica I.; McGuirt, Wyman (1997). "Vacuum-assisted closure: a new method for wound control and treatment". Annals of Plastic Surgery. 38 (6): 553–62. doi:10.1097/00000637-199706000-00001. PMID 9188970.
- Long, Mary Arnold; Blevins, Anne (2009). "Options in negative pressure wound therapy". Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing. 36 (2): 202–11. doi:10.1097/01.WON.0000347664.10217.2e.
- KCI clinical guidelines
- "V.A.C. Therapy Indications and Contraindications". www.activactherapy.com. Retrieved 20 April 2017.