1-Propanol
1-Propanol is a primary alcohol with the formula CH
3CH
2CH
2OH (sometimes represented as PrOH or n-PrOH). This colorless liquid is also known as propan-1-ol, 1-propyl alcohol, n-propyl alcohol, and n-propanol. It is an isomer of 2-propanol (propan-2-ol, isopropyl alcohol, isopropanol). It is formed naturally in small amounts during many fermentation processes and used as a solvent in the pharmaceutical industry, mainly for resins and cellulose esters.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propan-1-ol[1] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
Beilstein Reference |
1098242 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.679 |
| EC Number |
|
Gmelin Reference |
25616 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 1-Propanol |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1274 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C3H8O |
| Molar mass | 60.096 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | mild, alcohol-like[2] |
| Density | 0.803 g/mL |
| Melting point | −126 °C; −195 °F; 147 K |
| Boiling point | 97 to 98 °C; 206 to 208 °F; 370 to 371 K |
Solubility in water |
miscible |
| log P | 0.329 |
| Vapor pressure | 1.99 kPa (at 20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 16 |
| Basicity (pKb) | −2 |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
−45.176·10−6 cm3/mol |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.387 |
| Viscosity | 1.959 mPa·s (at 25 °C) [3] |
Dipole moment |
1.68 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
143.96 J/(K·mol) |
Std molar entropy (S |
192.8 J/(K·mol) |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−302.79…−302.29 kJ/mol |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.02156…−2.02106 MJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AX03 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  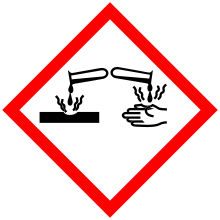  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H318, H336 |
GHS precautionary statements |
P210, P261, P280, P305+351+338 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 22 °C (72 °F; 295 K) |
Autoignition temperature |
371 °C (700 °F; 644 K) |
| Explosive limits | 2.2–13.7%[2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
2800 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 6800 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 1870 mg/kg (rat, oral)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 200 ppm (500 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 200 ppm (500 mg/m3) ST 250 ppm (625 mg/m3) [skin][2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
800 ppm[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Propane Isopropyl alcohol Propanamine Ethanol Butanol |
| Supplementary data page | |
Structure and properties |
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
Spectral data |
UV, IR, NMR, MS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
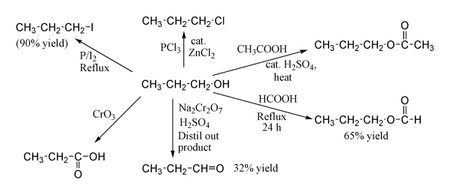
Chemical properties
1-Propanol shows the normal reactions of a primary alcohol. Thus it can be converted to alkyl halides; for example red phosphorus and iodine produce n-propyl iodide in 80% yield, while PCl
3 with catalytic ZnCl
2 gives n-propyl chloride. Reaction with acetic acid in the presence of an H
2SO
4 catalyst under Fischer esterification conditions gives propyl acetate, while refluxing propanol overnight with formic acid alone can produce propyl formate in 65% yield. Oxidation of 1-propanol with Na
2Cr
2O
7 and H
2SO
4 gives only a 36% yield of propionaldehyde, and therefore for this type of reaction higher yielding methods using PCC or the Swern oxidation are recommended. Oxidation with chromic acid yields propionic acid.
Preparation
1-Propanol is manufactured by catalytic hydrogenation of propionaldehyde. The propionaldehyde is itself produced via the oxo process, by hydroformylation of ethylene using carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst such as cobalt octacarbonyl or a rhodium complex.[5]
- H
2C=CH
2 + CO + H
2 → CH
3CH
2CH=O
- CH
3CH
2CH=O + H
2 → CH
3CH
2CH
2OH
A traditional laboratory preparation of 1-propanol involves treating n-propyl iodide with moist Ag
2O.
1-Propanol was discovered in 1853 by Gustave C. B. Chancel, who obtained it by fractional distillation of fusel oil. Indeed, 1-propanol is a major constituent of fusel oil, a by-product formed from certain amino acids when potatoes or grains are fermented to produce ethanol. This process is no longer a significant source of 1-propanol.
Safety
1-Propanol is thought to be similar to ethanol in its effects on the human body, but 2–4 times more potent. Oral LD50 in rats is 1870 mg/kg (compared to 7060 mg/kg for ethanol). It is metabolized into propionic acid. Effects include alcoholic intoxication and high anion gap metabolic acidosis. As of 2011, only one case of lethal 1-propanol poisoning was reported.[6]
Inhalation
Although this method is rare, it does exist. Propanol might be much more convenient than ethanol for inhalation because of its potency with nebulizers.
Propanol as fuel
1-propanol has high octane numbers and it is suitable for engine fuel usage. However, the production of propanol has been too expensive to make it a common fuel. The research octane number (RON) of propanol is 118 and anti-knock index (AKI) is 108.[7]
References
- Favre HA, Powell WH (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 61. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 9780854041824.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0533". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Pal A, Gaba R (2008). "Volumetric, acoustic, and viscometric studies of molecular interactions in binary mixtures of dipropylene glycol dimethyl ether with 1-alkanols at 298.15 K". J. Chem. Thermodyn. 40 (5): 818–828. doi:10.1016/j.jct.2008.01.008.
- "n-Propyl alcohol". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Papa AJ (2011). "Propanols". Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_173.pub2. ISBN 9783527303854.
- Unmack JL (2011). "N-PROPANOL Health-Base Assessment and Recommendation for HEAC" (PDF).
- "Bioalcohols". Biofuel.org.uk. 2010. Retrieved 16 Apr 2014.
Further reading
- Furniss, B. S.; Hannaford, A. J.; Smith, P. W. G.; Tatchell, A. R. (1989), Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (5th ed.), Harlow: Longman, ISBN 0-582-46236-3
- Lide DR, ed. (2006). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). TF-CRC. ISBN 0849304873.
- O'Neil MJ, ed. (2006). The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (14th ed.). Merck. ISBN 091191000X.
- Perkin WH, Kipping FS (1922). Organic Chemistry. London: W. & R. Chambers. ISBN 0080223540.
