Multiple system atrophy
Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder[1] characterized by autonomic dysfunction, tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, and postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism) and ataxia. This is caused by progressive degeneration of neurons in several parts of the brain including the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nucleus, and cerebellum.
| Multiple system atrophy | |
|---|---|
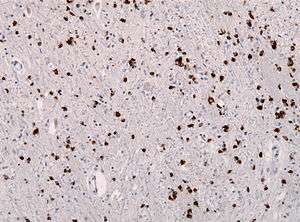 | |
| Alpha synuclein immunohistochemistry of the brain showing many glial inclusions | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Many people affected by MSA experience dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which commonly manifests as orthostatic hypotension, impotence, loss of sweating, dry mouth and urinary retention and incontinence. Palsy of the vocal cords is an important and sometimes initial clinical manifestation of the disorder.
A modified form of the alpha-synuclein protein within affected neurons may cause MSA.[2] About 55% of MSA cases occur in men, with those affected first showing symptoms at the age of 50–60 years.[3] MSA often presents with some of the same symptoms as Parkinson's disease. However, those with MSA generally show little response to the dopamine medications used to treat Parkinson's disease, and only about 9% of MSA patients with tremor had a true parkinsonian pill-rolling tremor.[4]
MSA is distinct from multisystem proteinopathy, a more common muscle wasting syndrome. It should also not be confused with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, sometimes referred to as multiple organ failure, or with multiple organ system failure, an often-fatal complication of septic shock or other very severe illnesses or injuries.
Signs and symptoms
MSA is characterized by the following, which can be present in any combination:[5][6]
- autonomic dysfunction
- parkinsonism (muscle rigidity +/ tremor and slow movement)
- cerebellar ataxia (Poor coordination/unsteady walking, double vision)
A variant with combined features of MSA and Lewy body dementia may also exist.[7] There have also been occasional instances of frontotemporal lobar degeneration associated with MSA.[8]
Initial presentation
The most common first sign of MSA is the appearance of an "akinetic-rigid syndrome" (i.e. slowness of initiation of movement resembling Parkinson's disease) found in 62% at first presentation. Other common signs at onset include problems with balance (cerebellar ataxia) found in 22% at first presentation, followed by genito-urinary symptoms (9%): both men and women often experience urgency, frequency, incomplete bladder emptying, or an inability to pass urine (retention). About 1 in 5 MSA patients experience a fall in their first year of disease.[9]
For men, the first sign can be erectile dysfunction. Women have also reported reduced genital sensitivity.[10]
Progression
As the disease progresses one of three groups of symptoms predominate. These are:
- Parkinsonism - slow, stiff movement, writing becomes small and spidery
- Cerebellar dysfunction - difficulty coordinating movement and balance
- Autonomic nervous system dysfunction - impaired automatic body functions, including one, some, or all of the following:
- postural or orthostatic hypotension, resulting in dizziness or fainting upon standing up
- urinary incontinence or urinary retention
- impotence
- constipation
- vocal cord paralysis
- dry mouth and skin
- trouble regulating body temperature due to sweating deficiency in all parts of the body
- loud snoring, abnormal breathing or inspiratory stridor during sleep
- other sleep disorders including sleep apnea, REM behavior disorder[11]
- double vision[12]
- muscle twitches[12]
- Cognitive impairment[13]
Genetics
One study found a correlation between the deletion of genes in a specific genetic region and the development of MSA in a group of Japanese patients.[14] The region in question includes the SHC2 gene which, in mice and rats, appears to have some function in the nervous system. The authors of this study hypothesized that there may be a link between the deletion of the SHC2 and the development of MSA. (See Copy-number variation for a general discussion of gene copy deletion and the variation in the number of copies of one or more sections of the DNA.)
A follow-up study was unable to replicate this finding in American MSA patients.[15] The authors of the U.S. study concluded that "Our results indicate that SHC2 gene deletions underlie few, if any, cases of well-characterized MSA in the US population. This is in contrast to the Japanese experience reported by Sasaki et al., likely reflecting heterogeneity of the disease in different genetic backgrounds."
Pathophysiology
Multiple system atrophy can be explained as cell loss and gliosis or a proliferation of astrocytes in damaged areas of the central nervous system. This damage forms a scar which is then termed a glial scar.[16] The presence of these inclusions (also known as Papp–Lantos bodies) in the movement, balance, and autonomic-control centres of the brain are the defining histopathologic hallmark of MSA.
The major filamentous component of glial and neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions is alpha-synuclein.[17] Mutations in this substance may play a role in the disease.[18] A post-translationally modified form of the protein called alpha-synuclein may be a causal agent for the disease.[2] probably caused by a primary oligodendrogliopathy.[19]
Tau proteins have been found in some glial cytoplasmic inclusions (GCI)s.[20]
Diagnosis
Clinical
Clinical diagnostic criteria were defined in 1998[21] and updated in 2007.[22] Certain signs and symptoms of MSA also occur with other disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, making the diagnosis more difficult.[23][24][25]
Radiologic
Both MRI and CT scanning may show a decrease in the size of the cerebellum and pons in those with cerebellar features (MSA-C). The putamen is hypodense on T2-weighted MRI and may show an increased deposition of iron in the Parkinsonian (MSA-P) form. In MSA-C, a "hot cross bun" sign is sometimes found; it reflects atrophy of the pontocerebellar fibers that manifest in T2 signal intensity in the atrophic pons.
MRI changes are not required to diagnose the disease as these features are often absent, especially early in the course of the disease. Additionally, the changes can be quite subtle, and are usually missed by examiners who are not experienced with MSA.
Pathologic
Pathological diagnosis can only be made at autopsy by finding abundant GCIs on histological specimens of the central nervous system.[26]
Classification
MSA is one of several neurodegenerative diseases known as synucleinopathies: they have in common an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in various parts of the brain. Other synucleinopathies include Parkinson's disease, the Lewy body dementias, and other more rare conditions.[27]
Old terminology
Historically, many terms were used to refer to this disorder, based on the predominant systems presented. These terms were discontinued by consensus in 1996 and replaced with MSA and its subtypes,[28] but awareness of these older terms and their definitions is helpful to understanding the relevant literature prior to 1996. These include striatonigral degeneration (SND), olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA), and Shy–Drager syndrome.[29] A table describing the characteristics and modern names of these conditions follows:
| Historical Name | Characteristics | Modern name and abbreviation |
| Striatonigral degeneration | predominating Parkinson's-like symptoms | MSA-P, "p" = parkinsonian subtype |
| Sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA) | characterized by progressive ataxia (an inability to coordinate voluntary muscular movements) of the gait and arms and dysarthria (difficulty in articulating words) | MSA-C, "c" = cerebellar dysfunction subtype |
| Shy–Drager syndrome | characterized by Parkinsonism plus a more pronounced failure of the autonomic nervous system.[30] | No modern equivalent – this terminology fell out of favour[31] and was not specified in the 2007 consensus paper.[22] The earlier consensus of 1998[21] referred to MSA-A, "a" = autonomic dysfunction subtype but this subtype is no longer used. |
Current terminology
The current terminology and diagnostic criteria for the disease were established at a 2007 conference of experts and set forth in a position paper.[22] This Second Consensus Statement defines two categories of MSA, based on the predominant symptoms of the disease at the time of evaluation. These are:
- MSA with predominant parkinsonism (MSA-P) - defined as MSA where extrapyramidal features predominate. It is sometimes termed striatonigral degeneration, parkinsonian variant.
- MSA with cerebellar features (MSA-C) - defined as MSA in which cerebellar ataxia predominates. It is sometimes termed sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy.
Management
Supervision
Ongoing care from a neurologist specializing in movement disorders is recommended, because the complex symptoms of MSA are often not familiar to less-specialized neurologists. Hospice/homecare services can be very useful as disability progresses.
Drug therapy
Levodopa (L-Dopa), a drug used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, improves parkinsonian symptoms in a small percentage of MSA patients. A recent trial reported that only 1.5% of MSA patients experienced any improvement at all when taking levodopa, their improvement was less than 50%, and even that improvement was a transient effect lasting less than one year. Poor response to L-Dopa has been suggested as a possible element in the differential diagnosis of MSA from Parkinson's disease.
Rehabilitation
Management by rehabilitation professionals including physiatrists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and others for difficulties with walking/movement, daily tasks, and speech problems is essential.
Physiotherapists can help to maintain the patient's mobility and will help to prevent contractures.[16] Instructing patients in gait training will help to improve their mobility and decrease their risk of falls.[32] A physiotherapist may also prescribe mobility aids such as a cane or a walker to increase the patient's safety.[32]
Speech therapists may assist in assessing, treating and supporting speech (dysarthria) and swallowing difficulties (dysphagia). Speech changes mean that alternative communication may be needed, for example communication aids or word charts.
Early intervention of swallowing difficulties is particularly useful to allow for discussion around tube feeding further in the disease progression. At some point in the progression of the disease, fluid and food modification may be implemented.
Avoidance of postural hypotension
One particularly serious problem, the drop in blood pressure upon standing up (with risk of fainting and thus injury from falling), often responds to fludrocortisone, a synthetic mineralocorticoid.[33] Another common drug treatment is the alpha-agonist midodrine.[34]
Non-drug treatments include "head-up tilt" (elevating the head of the whole bed by about 10 degrees), salt tablets or increasing salt in the diet, generous intake of fluids, and pressure (elastic) stockings. Avoidance of triggers of low blood pressure, such as hot weather, alcohol, and dehydration, are crucial.[35] The patient can be taught to move and transfer from sitting to standing slowly to decrease risk of falls and limit the effect of postural hypotension.[32] Instruction in ankle pumping helps to return blood in the legs to the systemic circulation.[32] Other preventative measures are raising the head of the bed by 8 in (20.3 cm), and the use of compression stockings and abdominal binders.[5]
Support
Social workers and occupational therapists can also help with coping with disability through the provision of equipment and home adaptations, services for caregivers and access to healthcare services, both for the person with MSA as well as family caregivers.
People affected by MSA are supported by multiple organizations, such as The Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) Coalition, and Defeat MSA.[36]
Prognosis
The average lifespan after the onset of symptoms in patients with MSA is 6–10 years.[3] Approximately 60% of patients require a wheelchair within five years of onset of the motor symptoms, and few patients survive beyond 12 years.[3] The disease progresses without remission at a variable rate. Those who present at an older age, those with parkinsonian features, and those with severe autonomic dysfunction have a poorer prognosis.[3] Those with predominantly cerebellar features and those who display autonomic dysfunction later have a better prognosis.[3]
Causes of death
The most common causes of death are sudden death and death caused by infections, which include urinary catheterization infections, feeding tube infections, and aspiration pneumonia. Some deaths are caused by cachexia, also known as wasting syndrome.[37]
Epidemiology
Multiple system atrophy is estimated to affect approximately 5 per 100,000 people. At autopsy, many patients diagnosed during life with Parkinson’s disease are found actually to have MSA, suggesting that the actual incidence of MSA is higher than that estimate.[3] While some suggest that MSA affects slightly more men than women (1.3:1), others suggest that the two sexes are equally likely to be affected.[3][5][16] The condition most commonly presents in persons aged 50–60.[3]
Notable cases
- Chef Kerry Simon died from complications of MSA.[38]
- Nikolai Andrianov was a Soviet/Russian gymnast who held the record for men for the most Olympic medals at 15 (7 gold medals, 5 silver medals, 3 bronze medals) until Michael Phelps surpassed him at the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics.[39]
- Joseph C. Howard Sr. was the first African American to serve as a United States District Judge of the United States District Court for the District of Maryland.[40]
- Singer and songwriter Johnny Cash wrote in his autobiography that he was diagnosed with Shy–Drager in 1997.[41]
Research
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy may delay the progression of neurological deficits in patients with MSA-cerebellar type.[42]
References
- "multiple system atrophy" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Peng C, Gathagan RJ, Covell DJ, Medellin C, Stieber A, Robinson JL, et al. (May 2018). "Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological α-synuclein strains in α-synucleinopathies". Nature. 557 (7706): 558–563. Bibcode:2018Natur.557..558P. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0104-4. PMC 5970994. PMID 29743672.
- Fanciulli A, Wenning GK (January 2015). "Multiple-system atrophy". N. Engl. J. Med. 372 (3): 249–63. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1311488. PMID 25587949.
- "Multiple System Atrophy Clinical Presentation". Retrieved January 7, 2018.
- Swan L, Dupont J (May 1999). "Multiple system atrophy". Phys Ther. 79 (5): 488–94. PMID 10331752.
- Burn DJ, Jaros E (December 2001). "Multiple system atrophy: cellular and molecular pathology". Mol. Pathol. 54 (6): 419–26. PMC 1187133. PMID 11724918.
- Sikorska B, Papierz W, Preusser M, Liberski PP, Budka H (2017). "Synucleinopathy with features of both multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies". Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology. 33 (1): 126–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00817.x. PMID 17239015.
- Aoki N, Boyer PJ, Lund C, Lin WL, Koga S, Ross OA, Weiner M, Lipton A, Powers JM, White CL, Dickson DW (July 2015). "Atypical multiple system atrophy is a new subtype of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: frontotemporal lobar degeneration associated with α-synuclein". Acta Neuropathol. 130 (1): 93–105. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1442-z. PMID 25962793.
- Bensimon G, Ludolph A, Agid Y, Vidailhet M, Payan C, Leigh PN (January 2009). "Riluzole treatment, survival and diagnostic criteria in Parkinson plus disorders: the NNIPPS study". Brain. 132 (Pt 1): 156–71. doi:10.1093/brain/awn291. PMC 2638696. PMID 19029129.
- Oertel WH, Wächter T, Quinn NP, Ulm G, Brandstädter D (April 2003). "Reduced genital sensitivity in female patients with multiple system atrophy of parkinsonian type". Mov. Disord. 18 (4): 430–2. doi:10.1002/mds.10384. PMID 12671951.
- Gilman S, Koeppe RA, Chervin RD, et al. (July 2003). "REM sleep behavior disorder is related to striatal monoaminergic deficit in MSA". Neurology. 61 (1): 29–34. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000073745.68744.94. PMID 12847152.
- "What is multiple system atrophy?". NIH. Retrieved November 25, 2018.
- Brown RG, Lacomblez L, Landwehrmeyer BG, Bak T, Uttner I, Dubois B, et al. (August 2010). "Cognitive impairment in patients with multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy". Brain. 133 (Pt 8): 2382–93. doi:10.1093/brain/awq158. PMID 20576697.
- Sasaki H, Emi M, Iijima H, et al. (2011). "Copy number loss of (src homology 2 domain containing)-transforming protein 2 (SHC2) gene: discordant loss in monozygotic twins and frequent loss in patients with multiple system atrophy". Mol Brain. 4: 24. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-4-24. PMC 3141657. PMID 21658278.
- Ferguson MC, Garland EM, Hedges L, Womack-Nunley B, Hamid R, Phillips JA, Shibao CA, Raj SR, Biaggioni I, Robertson D (February 2014). "SHC2 gene copy number in multiple system atrophy (MSA)". Clin. Auton. Res. 24 (1): 25–30. doi:10.1007/s10286-013-0216-8. PMC 3946192. PMID 24170347.
- Wenning GK, Colosimo C, Geser F, Poewe W (February 2004). "Multiple system atrophy". Lancet Neurol. 3 (2): 93–103. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(03)00662-8. PMID 14747001.
Wenning GK, Colosimo C, Geser F, Poewe W (March 2004). "Erratum". Lancet Neurol. 3 (3): 137. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00695-7. - Arima K, Uéda K, Sunohara N, Arakawa K, Hirai S, Nakamura M, Tonozuka-Uehara H, Kawai M (November 1998). "NACP/alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in fibrillary components of neuronal and oligodendroglial cytoplasmic inclusions in the pontine nuclei in multiple system atrophy". Acta Neuropathol. 96 (5): 439–44. doi:10.1007/s004010050917. PMID 9829806.
- Al-Chalabi A, Dürr A, Wood NW, Parkinson MH, Camuzat A, Hulot JS, Morrison KE, Renton A, Sussmuth SD, Landwehrmeyer BG, Ludolph A, Agid Y, Brice A, Leigh PN, Bensimon G (September 2009). "Genetic variants of the alpha-synuclein gene SNCA are associated with multiple system atrophy". PLoS ONE. 4 (9): e7114. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.7114A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007114. PMC 2743996. PMID 19771175.
- Stefanova N, Wenning GK (February 2016). "Review: Multiple system atrophy: emerging targets for interventional therapies". Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology. 42 (1): 20–32. doi:10.1111/nan.12304. PMC 4788141. PMID 26785838.
- Piao YS, Hayashi S, Hasegawa M, Wakabayashi K, Yamada M, Yoshimoto M, Ishikawa A, Iwatsubo T, Takahashi H (March 2001). "Co-localization of alpha-synuclein and phosphorylated tau in neuronal and glial cytoplasmic inclusions in a patient with multiple system atrophy of long duration". Acta Neuropathol. 101 (3): 285–93. doi:10.1007/s004010000292. PMID 11307630.
- Gilman S, Low PA, Quinn N, Albanese A, Ben-Shlomo Y, Fowler CJ, et al. (February 1999). "Consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy" (PDF). J. Neurol. Sci. 163 (1): 94–8. doi:10.1016/s0022-510x(98)00304-9. hdl:2027.42/41757. PMID 10223419.
- Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ, Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ, et al. (August 2008). "Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy". Neurology. 71 (9): 670–6. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000324625.00404.15. PMC 2676993. PMID 18725592.
- Vanderbilt Autonomic Dysfunction Cente. "Multiple System Atrophy / Shy Drager Syndrome". Retrieved May 29, 2010.
- "multiple system atrophy overview". 2018-09-24. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Koga S, Aoki N, Uitti RJ, van Gerpen JA, Cheshire WP, Josephs KA, Wszolek ZK, Langston JW, Dickson DW (August 2015). "When DLB, PD, and PSP masquerade as MSA: an autopsy study of 134 patients". Neurology. 85 (5): 404–12. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000001807. PMC 4534078. PMID 26138942.
- Papp MI, Kahn JE, Lantos PL (December 1989). "Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system atrophy (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome)". J. Neurol. Sci. 94 (1–3): 79–100. doi:10.1016/0022-510X(89)90219-0. PMID 2559165.
- Goedert M, Jakes R, Spillantini MG (2017). "The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years On". J Parkinsons Dis (Review). 7 (s1): S53–S71. doi:10.3233/JPD-179005. PMC 5345650. PMID 28282814.
- The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology (1996). "Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy". Neurology. 46 (5): 1470. doi:10.1212/wnl.46.5.1470. PMID 8628505.
- name="Ahmed-2012">Ahmed Z, Asi YT, Sailer A, Lees AJ, Houlden H, Revesz T, Holton JL (February 2012). "The neuropathology, pathophysiology and genetics of multiple system atrophy". Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 38 (1): 4–24. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2011.01234.x. PMID 22074330.
- Shy GM, Drager GA (1960). "A neurological syndrome associated with orthostatic hypotension: a clinical-pathologic study". Arch. Neurol. 2 (5): 511–27. doi:10.1001/archneur.1960.03840110025004. PMID 14446364.
- Schatz IJ (July 1996). "Farewell to the "Shy-Drager syndrome"". Ann. Intern. Med. 125 (1): 74–5. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-125-1-199607010-00012. PMID 8644992.
- Hardy J (2008). "Multiple system atrophy: pathophysiology, treatment and nursing care". Nurs Stand. 22 (22): 50–6, quiz 58. doi:10.7748/ns2008.02.22.22.50.c6359. PMID 18333558.
- name=MayoMSA>Multiple system atrophy (MSA) mayoclinic.org, accessed 20 May 2018
- Multiple system atrophy (MSA) mayoclinic.org, accessed 20 May 2018
- name="Shy-drager from Clinical Neurology">Aminoff MJ, Greenberg DA, Simon RP. "Chapter 7. Movement Disorders". Clinical Neurology (6th ed.).
- "Multiple System Atrophy". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). Retrieved 2019-03-01.
- Papapetropoulos, Spiridon; et al. (March 2007). "Causes of death in multiple system atrophy". J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 78 (78, 3): 327–329. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2006.103929. PMC 2117630. PMID 17308296.
- "Kerry Simon, Las Vegas 'Iron Chef' winner, dies at 60". Business Insider. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- Turner, Amanda. "Olympic Legend Andrianov Dies at 58". International Gymnast Magazine Online. Retrieved 10 December 2018.
- Cummings, Elijah (2000-09-30). "Standing up for justice". Baltimore AFRO-American. Archived from the original on 2008-05-04. Retrieved 2018-12-10.
- Cash, Johnny; Carr, Patrick (1998) [1997]. Cash: The Autobiography. New York, NY, USA: HarperCollins Publishers. pp. 400–403. ISBN 978-0061013577.
- Lee PH, Lee JE, Kim HS, Song SK, Lee HS, Nam HS, et al. (July 2012). "A randomized trial of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple system atrophy". Ann. Neurol. 72 (1): 32–40. doi:10.1002/ana.23612. PMID 22829267.
External links
- Medical Textbook: "Multiple System Atrophy" edited by Gregor Wenning and Alessandra Fanciulli
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |