MASA syndrome
MASA syndrome is a rare X-linked recessive neurological disorder on the L1 disorder spectrum belonging in the group of hereditary spastic paraplegias.[1]
| MASA syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Mental retardation-aphasia-shuffling gait-adducted thumbs syndrome |
 | |
| This condition is inherited in an x-linked recessive manner | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Signs and symptoms
The acronym "MASA" stands for the four main signs and symptoms associated with the syndrome:(1) mental retardation (mild to moderate intellectual disability), (2) aphasia (delayed onset of speech), (3) shuffling gait, and (4) adducted thumbs.[2] Affected males may also have a variable dilatation(widening) of the third heart ventricle.[2]
Genetics
MASA syndrome has been associated with variants in the L1CAM gene.[1] The symptoms are typically more intensive in males, due to the fact that males inherit only one X-chromosome.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis can be made when the clinical features have been identified, mainly the four common signs and symptoms. This can then be confirmed by single-gene sequencing, where the L1CAM gene is examined for any possible variations.[2]
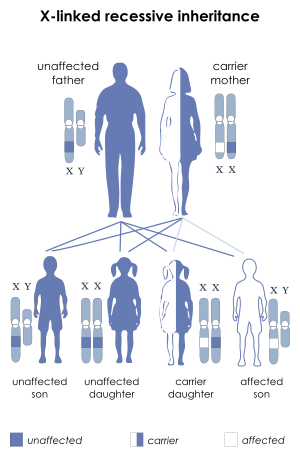
A diagnostic test prior-to-birth is possible and very reliable when the mother is a carrier of the diseased allele. First, it's necessary to determine the fetus' sex and then study the X-chromosomes inherited from the mother. The probability of transferring the variant X-chromosome to the descendants is 50% regardless of the sex of the fetus (as illustrated by the figure). Male descendants who inherit the varied X-chromosome will express the symptoms of the syndrome, on the other hand females who inherit the varied X-chromosome will become carriers of the mutated gene and will not show any symptoms or clinical features of the syndrome.[3][4]
References
- Reference, Genetics Home. "L1 syndrome". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2019-03-13.
- Stumpel, Connie; Vos, Yvonne J. (1993), Adam, Margaret P.; Ardinger, Holly H.; Pagon, Roberta A.; Wallace, Stephanie E. (eds.), "L1 Syndrome", GeneReviews®, University of Washington, Seattle, PMID 20301657, retrieved 2019-03-13
- Fransen E, Lemmon V, Van Camp G, Vits L, Coucke P, Willems PJ (1995). "CRASH syndrome: clinical spectrum of corpus callosum hypoplasia, retardation, adducted thumbs, spastic paraparesis and hydrocephalus due to mutations in one single gene, L1". European Journal of Human Genetics. 3 (5): 273–84. doi:10.1159/000472311. PMID 8556302.
- "OMIM Entry - # 303350 - MASA SYNDROME". omim.org. Retrieved 2019-03-20.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
- MASA syndrome at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
- GeneReview/NIH/UW entry on L1 Syndrome