Koilonychia
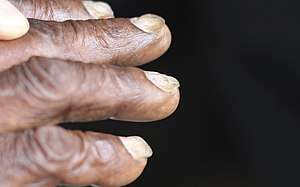
Koilonychia, also known as spoon nails,[1]:782 is a nail disease that can be a sign of hypochromic anemia, especially iron-deficiency anemia.[2]:656[3] It refers to abnormally thin nails (usually of the hand) which have lost their convexity, becoming flat or even concave in shape. In a sense, koilonychia is the opposite of nail clubbing. In early stages nails may be brittle and chip or break easily.
| Koilonychia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Spoon nails |
 | |
| Koilonychia | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Koilonychia is associated with Plummer-Vinson syndrome and iron deficiency anemia. It has also been associated with lichen planus, syphilis, and rheumatic fever. The term is from the Greek: κοῖλος, koilos, "hollow", ὄνυξ, onyx, "nail".
References
- James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- Kumar, Robbins and Cotran: Pathologic Basis of Disease, 7th ed., 2005. Saunders.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.