Istradefylline
Istradefylline, sold under the brand name Nourianz, is a medication used as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adults with Parkinson's disease (PD) experiencing "off" episodes.[1][2][3] Istradefylline reduces "off" periods resulting from long-term treatment with the antiparkinson drug levodopa.[1] An "off" episode is a time when a patient's medications are not working well, causing an increase in PD symptoms, such as tremor and difficulty walking.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nourianz |
| Other names | KW-6002 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Mainly CYP1A1, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5 |
| Elimination half-life | 64–69 hrs |
| Excretion | 68% faeces, 18% urine |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.117 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
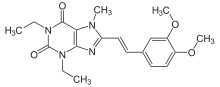
| Formula | C20H24N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 384.429 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Relatively common side effects include involuntary muscle movements (dyskinesia), constipation, hallucinations, dizziness and, much like its parent molecule caffeine, nausea and sleeplessness.[1] It is a selective antagonist at the A2A receptor.
History
It was first approved in Japan in 2013.[4]
The effectiveness of Nourianz in treating "off" episodes in patients with Parkinson's disease who are already being treated with levodopa/carbidopa was shown in four 12-week placebo-controlled clinical studies that included a total of 1,143 participants. In all four studies, people treated with Nourianz experienced a statistically significant decrease from baseline in daily "off" time compared to patients receiving a placebo.[1][2]
It was approved for medical use in the United States in 2019.[1][2] and approval was granted to Kyowa Kirin, Inc.[1]
References
- "FDA approves new add-on drug to treat off episodes in adults with Parkinson's disease". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 27 August 2019. Archived from the original on 4 September 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2019.

- "Drug Trials Snapshots: Nourianz". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 23 September 2019. Archived from the original on 20 November 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2019.

- Cabreira V, Soares-da-Silva P, Massano J (April 2019). "Contemporary Options for the Management of Motor Complications in Parkinson's Disease: Updated Clinical Review". Drugs. 79 (6): 593–608. doi:10.1007/s40265-019-01098-w. PMID 30905034.
- Dungo R, Deeks ED (June 2013). "Istradefylline: first global approval". Drugs. 73 (8): 875–82. doi:10.1007/s40265-013-0066-7. ISSN 1179-1950. PMID 23700273.
External links
- "Istradefylline". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Drug Approval Package: Nourianz". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).