Iproclozide
Iproclozide (trade names Sursum, Sinderesin) is an irreversible and selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was used as an antidepressant, but has since been discontinued.[1] It has been known to cause fulminant hepatitis and there have been at least three reported fatalities due to administration of the drug.[2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.536 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
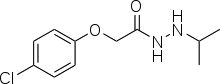
| Formula | C11H15ClN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 242.70 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
References
- Suerinck A, Suerinck E (1966). "[Depressive states in a sanatorium milieu and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. (Therapeutic results by the combination of iproclozide and chlordiazepoxide). Apropos of 146 cases]". Journal de médecine de Lyon. 47 (96): 573–586. PMID 5930723.
- Pessayre D, de Saint-Louvent P, Degott C, Bernuau J, Rueff B, Benhamou JP (1978). "Iproclozide fulminant hepatitis. Possible role of enzyme induction". Gastroenterology. 75 (3): 492–496. PMID 680506.
- Neil Kaplowitz; Laurie D. DeLeve (2003). Drug-induced liver disease. Informa Health Care. p. 455. ISBN 0-8247-0811-3. ISBN 9780824708115.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.