Instruments used in microbiology
Instrument list
| Instrument | Uses |
|---|---|
| autoclave | used for sterilization of glass ware and media |
| auto-destruct syringes | specimen collection |
| Bijou bottle | a cylindrical small glass bottle with a screw cap used as a culture medium holder |
| Biosafety cabinet | used to work with dangerous organisms and to work sterile |
| Blood collection bottle | to collect blood by venipuncture |
| Brittany | a process of free from spore-bearing bacteria |
| Bunsen burner | used to work aseptic on the bench |
| Candle jar | historically used for anaerobiosis; a lit candle was placed in as air-tight jar such that when it went out it would be because it used up all the available oxygen |
| Castaneda's medium / Castaneda's bottle | used for simultaneous solid and liquid cultures in many bottles |
| Centrifuge | to separate supernatant & pellet |
| Cragie tube | see link |
| Desiccator | to dry things |
| Durham's tube | used to detect gas production in sugar fermentation media; the tube is placed in an inverted fashion so that gases produced get trapped in it and do not float away to the surface |
| Gas-pak | releases gases to remove oxygen from a closed container, usually for anaerobiosis |
| Haemagglutination plate | for viral culture detection |
| Hungate Anaerobic tubes | for culturing of anaerobic microbes |
| Incubator | used for bacterial or fungal cultures |
| Inoculation loop: | used to inoculate test samples into culture media for bacterial or fungal cultures, antibiograms, etc. Sterilized by passing through a blue flame. |
| Laminar flow cabinet | used to work aseptic |
| Latex agglutination tiles | for serological analysis |
| Lovibond comparator | a type of a colorimeter |
| McCartney's bottle or Flat medical bottle | for simultaneous solid and liquid cultures. |
| McIntosh and Filde's anaerobic jar | production of anaerobic conditions for organisms that die in the presence of even little oxygen (anaerobiosis), e.g. tetanus bacteria |
| Microtitre plates | for ELISA |
| Nichrome wire loop | used to inoculate test samples into culture media for bacterial or fungal cultures, antibiograms, etc.; sterilized by flaming to red hot before use |
| Petri dish/agar plate | to act as a supporting container to hold the culture medium in |
| Platinum wire loop | used to inoculate test samples into culture media for bacterial or fungal cultures, antibiograms, etc.; sterilized by flaming to red hot before use |
| Pre-sterilized disposable container | specimen collection |
| Pre-sterilized disposable swabs / NIH swab / postnasal swab | specimen collection |
| Pre-sterilized disposable syringe / auto-destruct syringes | specimen collection |
| Serological test slides like those for ASO, VDRL, rheumatoid factor | vide links |
| Sterile loops | used to inoculate test samples into culture media for bacterial or fungal cultures, antibiograms, etc.; not heated before use—these are disposable pre-sterilised |
| Thermal cycler | used to amplify segments of DNA via the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process. |
| Tissue culture bottles | to grow or keep alive cells or tissue from a living organism, e.g. stem cells |
| Tuberculin syringe | as a normal syringe or to perform Mantoux test |
| Universal container | a cylindrical small glass bottle with a screw cap used as a culture medium holder |
| Vaccine bath | used to heat vaccine containing medium gently to around 45-55 degrees Celsius during vaccine production |
| Microscope | to observe microscopic specimens that cannot be seen by the naked eye. |
| Vacuum pump | to draw out the air from any closed chamber before pumping back CO2, O2 or N2, usually for anaerobiosis |
| VDRL rotator | for VDRL test |
| Specimen Dish | used to hold specimen or samples |
As well as those "used in microbiological sterilization and disinfection" (see relevant section).
Image gallery
- An inoculation loop is used to transfer bacteria for microbiological culture.
 Petri dish
Petri dish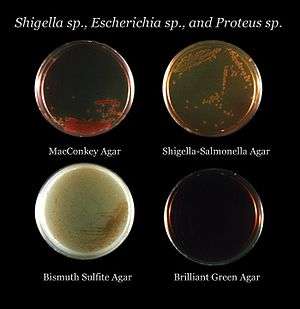 Agar plate
Agar plate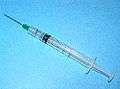 Tuberculin syringe
Tuberculin syringe Candle jar
Candle jar
References
- Textbook of Microbiology by Prof. C P Baveja, ISBN 81-7855-266-3
- Textbook of Microbiology by Ananthanarayan and Panikar, ISBN 81-250-2808-0
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.