Ibandronic acid
Ibandronic acid or ibandronate sodium is a bisphosphonate medication used in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and metastasis-associated skeletal fractures in people with cancer.[1] It may also be used to treat hypercalcemia (elevated blood calcium levels).
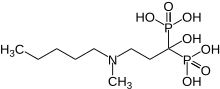 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0.6% |
| Protein binding | 90.9 to 99.5% (concentration-dependent) |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Elimination half-life | 10 to 60 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.214.537 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H23NO7P2 |
| Molar mass | 319.229 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
It was patented in 1986 by Boehringer Mannheim and approved for medical use in 1996.[2]
Medical uses
Ibandronate is indicated for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women.[3] In May 2003, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Ibandronate as a daily treatment for post-menopausal osteoporosis. The basis for this approval was a three-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial women with post-menopausal osteoporosis. Every participant also received daily oral doses of calcium and 400IUs [international units] of vitamin D. At the study's conclusion, both doses significantly reduced the occurrence risk of new vertebral fractures by 50–52 percent when compared to the effects of the placebo drug.
Ibandronate is efficacious for the prevention of metastasis-related bone fractures in multiple myeloma, breast cancer, and certain other cancers.[4]
Adverse effects
In 2008, the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a communication warning of the possibility of severe and sometimes incapacitating bone, joint or muscle pain.[5] A study conducted by the American Society of Bone and Mineral Research concluded that long-term use of bisphosphonates, including Boniva, may increase the risk of a rare but serious fracture of the femur. [6] The drug also has been associated with osteonecrosis of the jaw, relatively rare but serious condition.[7]
Pharmacology
| Bisphosphonate | Relative potency |
|---|---|
| Etidronate | 1 |
| Tiludronate | 10 |
| Pamidronate | 100 |
| Alendronate | 100-500 |
| Ibandronate | 500-1000 |
| Risedronate | 1000 |
| Zoledronate | 5000 |
Brand names
Ibandronic acid is marketed under the trade names Boniva in the USA, Bondronat in Europe, Bonviva in Asia, Bandrone in India, Ibandrix in Ecuador, Adronil in Pakistan, Bondrova in Bangladesh and Bonprove in Egypt.
References
- Bauss F, Schimmer RC (March 2006). "Ibandronate: the first once-monthly oral bisphosphonate for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis". Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 2 (1): 3–18. PMC 1661644. PMID 18360577.
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 523. ISBN 9783527607495.
- "boniva". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- Sittig HB (2012). "Pathogenesis and bisphosphonate treatment of skeletal events and bone pain in metastatic cancer: focus on ibandronate". Onkologie. 35 (6): 380–7. doi:10.1159/000338947. PMID 22722461.
- "Information for Healthcare Professionals: Bisphosphonates (marketed as Actonel, Actonel+Ca, Aredia, Boniva, Didronel, Fosamax, Fosamax+D, Reclast, Skelid, and Zometa)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 27 October 2010.
- "Drugs Commonly Prescribed for Osteoporosis Patients are Effective at Reducing Risk of Hip and Spine Fractures, But Panel Says May be Related to Unusual Thigh Bone Fractures When Used Long Term". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research=27 October 2010.
- "Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) and drug treatments for osteoporosis" (PDF). nos.org.uk. The National Osteoporosis Society.
- D., Tripathi, K. Essentials of medical pharmacology (Seventh ed.). New Delhi. ISBN 9789350259375. OCLC 868299888.
External links
- Ibandronate bound to proteins in the PDB
- Boniva Osteoporosis Treatment by GlaxoSmithKline and Roche Laboratories
- Boniva adverse events reported to the FDA