Mevalonate kinase deficiency
Mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), is an autosomal recessive [2] metabolic disorder that disrupts the biosynthesis of cholesterol and isoprenoids.[3]
| Mevalonate kinase deficiency | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Mevalonic aciduria[1] and Hyper immunoglobin D syndrome (HIDS) |
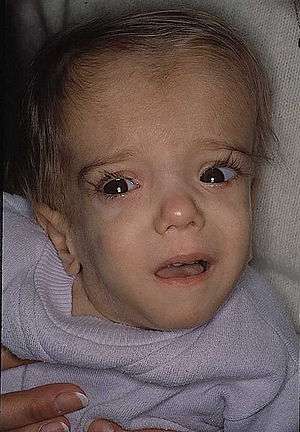 | |
| A patient with mevalonate kinase deficiency at the age of 21 months, displaying characteristic craniofacial features. | |
| Specialty | Hematology, neurology, immunology, medical genetics, endocrinology |
It is characterized by an elevated level of immunoglobin D in the blood.
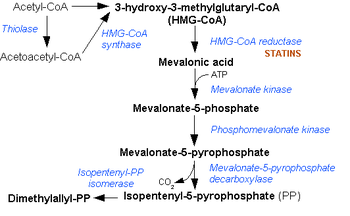
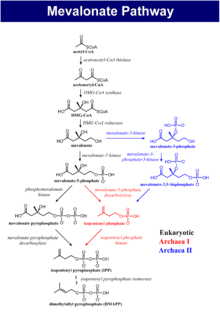
The enzyme is involved in biosynthesis of cholesterols and isoprenoids. The enzyme is necessary for the conversion of mevalonate to mevalonate-5-phosphate in the presence of Mg2+ [Harper's biochemistry manual]. Mevalonate kinase deficiency causes the accumulation of mevalonate in urine and hence the activity of the enzyme is again reduced Mevalonate kinase deficiency.[4] It was first described as HIDS in 1984.[4]
Genetics
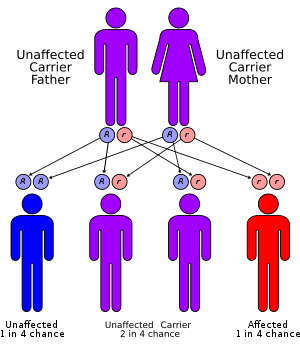
Mevalonate kinase deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that a child must inherit a defective copy of the gene from both parents to be affected.[2] It is an example of a loss-of-function mutation. The gene which codes for mevalonate kinase consists of 10 exons at locus 12q14.[5] About 63 pathological sequence variations in the gene have been characterized. The most common of these are V377I, I268T, H20P/N and P167L, present in 70% of affected individuals.[5]
Immunoglobin D
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is a protein produced by a certain type of white blood cells. There are five classes of Immunoglobin like IgG, IgA and IgM, IgE and IgD. They play an important role in the immune system. The function of IgD is still unclear.
There is a relationship between MKD and the interleukin 1beta (IL-Iβ). There is an increased IL-1β secretion and mevalonate kinase deficiency in MKD is most likely mediated by defective protein prenylation (Prenylation refers to addition of hydrophobic residues to proteins) ] and non-sterol isoprenoids, such as farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) or geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) are coupled to a target protein, which affects the activity and the cellular location. In a human monocytic MKD model it was found that the deficiency of GGPP leads to overproduction of IL-1β and defective prenylation of RhoA. This causes an increased level of Rac1 and PKB which was affecting the GTPases and B7-Glycoproteins. It was earlier found that Rac1/PI3K/PKB pathway had been linked to the pathogenesis of MKD. The inactivation of RhoA acts an inducer of IL-1β mRNA transcription independent of NLRP3- or caspase-1 activity. Due to defective RhoA there is a formation of defective mitochondria (elongated and instable) in the cell. If a defective mitochondria it is cleared in the cell by the mechanism of autophagia. But, in MKD the clearance of defective mitochondria from the cytosol is disrupted. As a result, the mitochondrial DNA starts accumulating in the cytosol which binds and activates NLRP3 which is responsible for the production of IL-1β. The activation can be direct or indirect. It can also be activated by reactive oxygen species (ROS).[6] It is known that monocytes and macrophages also produce higher levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6(IL-6) other than IL-Iβ [6] During the febrile (fever) attacks and during the attacks the C - reactive protein (CRP) also increases.[5] The CRP is released by liver which causes inflammation[13].
Hyper-IgD syndrome
Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D with recurrent fever is a periodic fever syndrome originally described in 1984 by the internist Jos van der Meer,[7] then at Leiden University Medical Centre. No more than 300 cases have been described worldwide. It is now recognised as an allelic variant of MKD.[8]
Signs and symptoms
HIDS is one of a number of periodic fever syndromes. It is characterised by attacks of fever, arthralgia, skin lesions including cyclical mouth ulcers, and diarrhea. Laboratory features include an acute phase response (elevated CRP and ESR) and markedly elevated IgD (and often IgA), although cases with normal IgD have been described.[9]
It has mainly been described in the Netherlands and France, although the international registry includes a number of cases from other countries.[9]
The differential diagnosis includes fever of unknown origin, familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) and familial Hibernian fever (or TNFα reception associated periodic syndrome/TRAPS).[9]
Cause
Virtually all people with the syndrome have mutations in the gene for mevalonate kinase, which is part of the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, an important cellular metabolic pathway.[10][11] Indeed, similar fever attacks (but normal IgD) have been described in patients with mevalonic aciduria – an inborn error of metabolism now seen as a severe form of HIDS.[9]
Pathophysiology
It is not known how mevalonate kinase mutations cause the febrile episodes, although it is presumed that other products of the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway, the prenylation chains (geranylgeraniol and farnesol) might play a role.[9]
Diagnosis
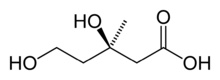
Mevalonate kinase deficiency causes an accumulation of mevalonic acid in the urine, resulting from insufficient activity of the enzyme mevalonate kinase[12] (ATP:mevalonate 5-phosphotransferase; EC 2.7.1.36).
The disorder was first described in 1985.[13]
Classified as an inborn error of metabolism, mevalonate kinase deficiency usually results in developmental delay, hypotonia, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, various dysmorphic features, mental retardation, an overall failure to thrive and several other features.
Treatment
There is no treatment for MKD. But, the inflammation and the other effects can be reduced to a certain extent.
- IL-1 targeting drugs can be used to reduce the effects of the disorder. Anakinra is antagonist to IL-1 receptors. Anakinra binds the IL-1 receptor, preventing the actions of both IL-1α and IL-1β, and it has been proved to reduce the clinical and biochemical inflammation in MKD. It can effectively decreases the frequency as well as the severity of inflammatory attacks when used on a daily basis. Disadvantages with the usage of this drug are occurrence of painful injection site reaction and as the drug is discontinued in the near future the febrile attacks start. (Examined in a 12-year-old patient).
- Canakinumab is a long acting monoclonal antibody which is directed against IL-1β has shown to be effective in reducing both frequency and severity in patients suffering from mild and severe MKD in case reports and observational case series. It reduces the physiological effects but the biochemical parameter still remain elevated (Galeotti et al. demonstrated that it is more effective than anakinra –considered 6 patients suffering from MKD).
- Anti-TNF therapy might be effective in MKD, but the effect is mostly partial and therapy failure and clinical deterioration have been described frequently in patients on infliximab or etanercept.[6] A beneficial effect of human monoclonal anti-TNFα antibody adalimumab was seen in a small number of MKD patients.
- Most MKD patients are benefited by anti-IL-1 therapy. However, anti-IL-1-resistant disease may also occur. Example. tocilizumab (a humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor). This drug is used when the patients are unresponsive towards Anakinra. (Shendi et al. treated a young woman in whom anakinra was ineffective with tocilizumab). It was found that it was effective in reducing the biochemical and clinical inflammation [30].Stoffels et al. observed reduction of frequency and severity of the inflammatory attacks, although after several months of treatment one of these two patients persistently showed mild inflammatory symptoms in the absence of biochemical inflammatory markers.
- A beneficial effect of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can be used in severe mevalonate kinase deficiency conditions (Improvement of cerebral myelinisation on MRI after allogenic stem cell transplantation was observed in one girl). But, liver transplantation did not influence febrile attacks in this patient.[6]
Treatment for HIDS
Canakinumab has been approved for treatment of HIDS and has shown to be effective.[14][15] The immunosuppressant drugs etanercept[16] and anakinra[17] have also shown to be effective. Statin drugs might decrease the level of mevalonate and are presently being investigated. A recent single case report highlighted bisphosphonates as a potential therapeutic option.[18]
Epidemiology
In the world less than 1 in 1.00.000 have HIDS [5]. 200 individuals throughout the world do suffer from MVK.[5]
Additional images
 Mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid
See also
References
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 251170
- "Mevalonate kinase deficiency".
- Mancini J, Philip N, Chabrol B, Divry P, Rolland MO, Pinsard N (May–Jun 1993). "Mevalonic aciduria in 3 siblings: a new recognizable metabolic encephalopathy". Pediatr. Neurol. 9 (3): 243–246. doi:10.1016/0887-8994(93)90095-T. PMID 8352861.
- Background information, HIDS.net, retrieved 28 August 2016
- "Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency".
- Mulders-Manders, CM; Simon, A (2015). "Hyper-IgD syndrome/mevalonate kinase deficiency: what is new?". Semin Immunopathol. 37 (4): 371–6. doi:10.1007/s00281-015-0492-6. PMC 4491100. PMID 25990874.
- van der Meer JW, Vossen JM, Radl J, et al. (May 1984). "Hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever: a new syndrome". Lancet. 1 (8386): 1087–90. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(84)92505-4. PMID 6144826.
- "OMIM Entry - * 251170 - MEVALONATE KINASE; MVK". omim.org.
- Drenth JP, van der Meer JW (December 2001). "Hereditary periodic fever". N. Engl. J. Med. 345 (24): 1748–57. doi:10.1056/NEJMra010200. PMID 11742050.
- Drenth JP, Cuisset L, Grateau G, et al. (June 1999). "Mutations in the gene encoding mevalonate kinase cause hyper-IgD and periodic fever syndrome. International Hyper-IgD Study Group". Nat. Genet. 22 (2): 178–81. doi:10.1038/9696. PMID 10369262.
- Houten SM, Kuis W, Duran M, et al. (June 1999). "Mutations in MVK, encoding mevalonate kinase, cause hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever syndrome". Nat. Genet. 22 (2): 175–7. doi:10.1038/9691. PMID 10369261.
- Bretón Martínez JR, Cánovas Martínez A, Casaña Pérez S, Escribá Alepuz J, Giménez Vázquez F (Oct 2007). "Mevalonic aciduria: report of two cases". J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 30 (5): 829. doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0618-7. PMID 17578678.
- Berger R, Smit GP, Schierbeek H, Bijsterveld K, le Coultre R (Oct 1985). "Mevalonic aciduria: an inborn error of cholesterol biosynthesis?". Clin. Chim. Acta. 152 (1–2): 219–222. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(85)90195-0. PMID 4053401.
- Aróstegui, JI; Anton, J.; Calvo, I.; Robles, A.; Speziale, A.; Joubert, Y.; Junge, G.; Yagüe, J. (2015-01-01). "Long-term efficacy and safety of Canakinumab in active Hyper-IgD syndrome (HIDS): results from an open-label study". Pediatric Rheumatology. 13 (1): O58. doi:10.1186/1546-0096-13-S1-O58. ISSN 1546-0096. PMC 4596954.
- Kozlova, A.; Mamzerova, E.; Maschan, A.; Shcherbina, A. (2014-06-01). "AB0918 Efficacy and Safety of Treatment of Children with Traps and Hids with IL1 Blocker (CANAKINUMAB)". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 73 (Suppl 2): 1103–1104. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-eular.3697. ISSN 0003-4967.
- Takada, Kazuki; Aksentijevich, Ivona; Mahadevan, Vijayabhanu; Dean, Jane A.; Kelley, Richard I.; Kastner, Daniel L. (2003-09-01). "Favorable preliminary experience with etanercept in two patients with the hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome". Arthritis and Rheumatism. 48 (9): 2645–2651. doi:10.1002/art.11218. ISSN 0004-3591. PMID 13130485.
- Rigante D, Ansuini V, Bertoni B, et al. (November 2006). "Treatment with anakinra in the hyperimmunoglobulinemia D/periodic fever syndrome". Rheumatol. Int. 27 (1): 97–100. doi:10.1007/s00296-006-0164-x. PMID 16871408.
- Cantarini, L; Vitale, A; Magnotti, F; Lucherini, O. M.; Caso, F; Frediani, B; Galeazzi, M; Rigante, D (2013). "Weekly oral alendronate in mevalonate kinase deficiency". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 8: 196. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-196. PMC 3880037. PMID 24360083.
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|
| Classification |
|
|---|
- Mevalonic aciduria at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases