Hamartoma
A hamartoma[2] is a mostly benign,[3] focal malformation that resembles a neoplasm in the tissue of its origin. While traditionally considered developmental malformation, many hamartomas have clonal chromosomal aberrations that are acquired through somatic mutations and on this basis are now considered to be neoplastic. It grows at the same rate as the surrounding tissue. It is composed of tissue elements normally found at that site, but they are growing in a disorganized manner. Hamartomas occur in many different parts of the body, and are most often asymptomatic incidentalomas (undetected until they are found incidentally on an imaging study obtained for another reason).
| Hamartoma | |
|---|---|
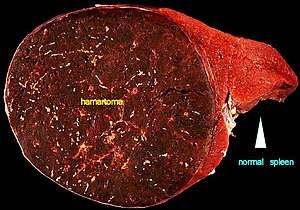 | |
| A large hamartoma of the spleen. The hamartoma is the dark circular object on the left that dominates the image. This is a cross-section; the growth is about 9 cm in diameter, while the entire spleen is about 11 cm in diameter.[1] | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics, pathology |
Additionally, the definition of hamartoma versus benign neoplasm is often unclear, since both lesions can be clonal. Lesions such as adenomas, developmental cysts, hemangiomas, lymphangiomas, and rhabdomyomas within the kidneys, lungs, or pancreas are interpreted by some experts as hamartomas while others consider them true neoplasms. Moreover, even though hamartomas show a benign histology, there is a risk of some rare but life-threatening clinical issues such as those found in neurofibromatosis type I and tuberous sclerosis.[4]
It is different from choristoma, a closely related form of heterotopia.[5][6] The two can be differentiated as follows: a hamartoma is an excess of normal tissue in a normal situation (e.g., a birthmark on the skin), while a choristoma is an excess of tissue in an abnormal situation (e.g., pancreatic tissue in the duodenum).[7][8]
Causes
Hamartomas result from an abnormal formation of normal tissue, although the underlying reasons for the abnormality are not fully understood. They grow along with, and at the same rate as, the organ from whose tissue they are made, and, unlike cancerous tumors, only rarely invade or compress surrounding structures significantly.
Diagnosis
Types
Lung
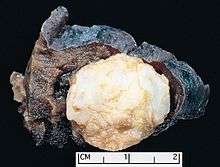
The most common hamartomas occur in the lungs. About 5–8% of all solitary lung nodules, about 75% of all benign lung tumors, are hamartomas. They almost always arise from connective tissue and are generally formed of cartilage, connective tissue, and fat cells, although they may include many other types of cells. The great majority of them form in the connective tissue on the outside of the lungs, although about 10% form deep in the linings of the bronchi. They can be worrisome, especially if situated deep in the lung, as it is sometimes difficult to make the important distinction between a hamartoma and a lung malignancy. An X-ray will often not provide a definitive diagnosis, and even a CT scan may be insufficient if the hamartoma lacks the typical cartilage and fat cells. Lung hamartomas may have popcorn-like calcifications on chest xray or computed tomography (CT scan).
Lung hamartomas are more common in men than in women, and may present additional difficulties in smokers.
Some lung hamartomas can compress surrounding lung tissue to a degree, but this is generally not debilitating and is often asymptomatic, especially for the more common peripheral growths. They are treated, if at all, by surgical resection, with an excellent prognosis: generally, the only real danger is the inherent possibility of surgical complications.
Heart
Cardiac rhabdomyomas are hamartomas composed of altered cardiac myocytes that contain large vacuoles and glycogen. They are the most common tumor of the heart in children and infants. There is a strong association between cardiac rhabdomyomas and tuberous sclerosis (characterized by hamartomas of the central nervous system, kidneys, and skin, as well as pancreatic cysts); 25-50% of patients with cardiac rhabdomyomas will have tuberous sclerosis, and up to 100% of patients with tuberous sclerosis will have cardiac masses by echocardiography. Symptoms depend on the size of the tumor, its location relative to the conduction system, and whether or not it obstructs blood flow. Symptoms are usually from congestive heart failure; in utero heart failure may occur. If patients survive infancy, their tumors may regress spontaneously; resection in symptomatic patients has good results.
Hypothalamus
One of the most troublesome hamartomas occurs on the hypothalamus. Unlike most such growths, a hypothalamic hamartoma is symptomatic; it most often causes gelastic seizures, and can cause visual problems, other seizures, rage disorders associated with hypothalamic diseases, and early onset of puberty. The symptoms typically begin in early infancy and are progressive, often into general cognitive and/or functional disability. Moreover, resection is usually difficult, as the growths are generally adjacent to, or even intertwined with, the optic nerve. Symptoms tend to be resistant to medical control; however, surgical techniques are improving and can result in immense improvement of prognosis.[9]
Kidneys, stomach, spleen, and other vascular organs
One general danger of hamartomas is that they may impinge into blood vessels, resulting in a risk of serious bleeding. Because a hamartoma typically lacks elastic tissue, it may lead to the formation of aneurysms and thus possible hemorrhage. Where a hamartoma impinges into a major blood vessel, such as the renal artery, hemorrhage must be considered life-threatening.
Angiomyolipoma of the kidney was previously considered to be a hamartoma or choristoma.
A myoepithelial hamartoma, also known as a pancreatic rest, is ectopic pancreatic tissue found in the stomach, duodenum, or proximal jejunum. When seen on upper gastrointestinal series, a pancreatic rest may appear to be a submucosal mass or gastric neoplasm. Most are asymptomatic, but they can cause dyspepsia or upper gastrointestinal bleeding.[10]
Hamartomas of the spleen are uncommon but can be dangerous. About 50% of such cases manifest abdominal pain, and they are often associated with hematologic abnormalities and spontaneous rupture.
Cowden syndrome
Considered part of the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS), which also includes Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome, Proteus syndrome, and Proteus-like syndrome, Cowden syndrome is a serious genetic disorder[11] characterized by multiple hamartomas. Usually skin hamartomas exist, and commonly (in about 66% of cases) hamartoma of the thyroid gland exists. Additional growths can form in many parts of the body, especially in bones, CNS, the eyes, the genitourinary tract, the GI tract, and mucosa. The hamartomas themselves may cause symptoms or even death, but morbidity is more often associated with increased occurrence of malignancies, usually in the breast or thyroid.
Prognosis
Hamartomas, while generally benign, can cause problems due to their location. For example, when located on the skin, especially on the face or neck, they can be very disfiguring. Cases have been reported of hamartomas the size of a small orange.[12] They may obstruct practically any organ in the body, such as the colon, eye, etc. They are particularly likely to cause major health issues when located in the hypothalamus, kidneys, lips, or spleen. They can be removed surgically if necessary, and are not likely to recur. Prognosis will depend upon the location and size of the lesion, as well as the overall health of the patient.
References
- Uthman, Ed (2 January 1999). "Hamartoma of the spleen". [Personal website]. Retrieved 30 July 2014.
- The term, from the Greek ἁμαρτία, hamartia (English translation: error), was introduced by D.P.G. Albrecht in 1904.
- "Hamartoma definition". Taber's Medical Dictionary. Retrieved 2008-09-25.
- Kumar, Abbas, Aster. Robbin's Pathologic Basis of Disease (9th ed.). p. 481.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Choristoma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Lee, Kenneth H.; Roland, Peter S. (2013). Heterotopias, Teratoma, and Choristoma. Encyclopedia of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. pp. 1179–1183. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-23499-6_642. ISBN 978-3-642-23498-9.
- Jorquera, JessicaPatricia Correa; Rubio-Palau, Josep; Cazalla, AsteriaAlbert; Rodríguez-Carunchio, Leonardo (2016). "Choristoma: A rare congenital tumor of the tongue". Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery. 6 (2): 311–313. doi:10.4103/2231-0746.200342. PMC 5343649. PMID 28299279.
- Goswamy, Monika; Tabasum, Syeda; Kudva, Praveen; Gupta, Shikha (2012). "Osseous choristoma of the periodontium". Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology. 16 (1): 120–2. doi:10.4103/0972-124X.94619. PMC 3357020. PMID 22628977.
- "Hypothalmic Hamartoma". Barrow Neurological Institute.
- Shah A, Gordon AR, Ginsberg GG, Furth EE, Levine MS. Case report: ectopic pancreatic rest in the proximal stomach mimicking gastric neoplasms. Clin Radiol. 2007 Jun;62(6):600-2. Epub 2007 Mar 26. No abstract available.
- Mutation of PTEN gene on arm 10q (~85% of cases) or rarely germline mutation in BMPR1A
- "Dermatology Images". Dermatology Image Atlas. Archived from the original on 2006-05-15.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- "Topic 28: Angiomyolipoma". eMedicine.com Radio. 2019-04-05.
- "Topic 316: Lung Hamartoma". eMedicine.com Radio. 2018-12-17.