Glomerular basement membrane
The glomerular basement membrane (GBM) of the kidney is the basal lamina layer of the glomerulus. The glomerular endothelial cells, the GBM and the filtration slits between the podocytes perform the filtration function of the glomerulus, separating the blood in the capillaries from the filtrate that forms in Bowman's capsule.[1] The GBM is a fusion of the endothelial cell and podocyte basal laminas.[2]
| Glomerular basement membrane | |
|---|---|
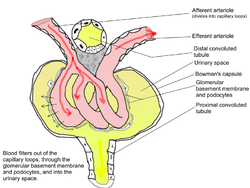 Glomerulus; note "Glomerular basement membrane and podocytes". | |
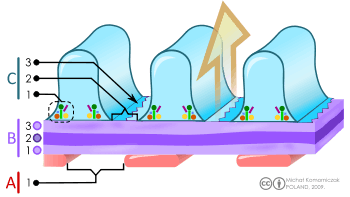 Scheme of filtration barrier (blood-urine) in the kidney. A. The endothelial cells of the glomerulus; 1. pore (fenestra). B. Glomerular basement membrane: 1. lamina rara interna 2. lamina densa 3. lamina rara externa C. Podocytes: 1. enzymatic and structural protein 2. filtration slit 3. diaphragm | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D050533 |
| FMA | 74274 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Layers
The GBM contains three layers:[3]
| Layer | Location | Composition | Function |
| lamina rara externa | adjacent to podocyte processes | heparan sulfate | blocks by charge |
| lamina densa | dark central zone | type 4 collagen and laminin | blocks by size (Molecular Weight > 70kDa) |
| lamina rara interna | adjacent to endothelial cells | heparan sulfate | blocks by charge |
The glomerular membrane consists of mesangial cells, modified pericytes that in other parts of the body separate capillaries from each other. The podocytes adjoining them have filtration slits of diameter 25 nm that are formed by the pseudopodia arising from them. The filtration slits are covered by a diaphragm that includes the transmembrane protein nephrin.
Pathology
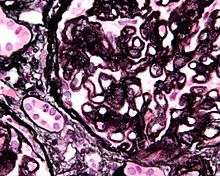
- Goodpasture's syndrome is also known as anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. Capillaries become inflamed as a result of damage to the basement membrane by antibodies to alpha 3 NC1 domain of type IV collagen.
- Nephrotic syndrome is a change in the structure of the glomerular filtration mechanism usually in the glomerular basement membrane. Some symptoms include proteinuria, hypoalbuminaemia, oedema, and hyperlipidemia.
- Diabetic glomerulosclerosis is a thickening of the basement membrane, which can become up to 4-5 times thicker than normal. Can be caused by insulin deficiency or resultant hyperglycemia.
- Alport syndrome is a X-linked hereditary nephritis caused by mutations in type IV collagen, leading to a split lamina densa of the glomerular basement membrane. It also affects the eye and inner ear.
See also
- Agrin, a protein linked to heparan sulfate
- basement membrane
- nephrin
Additional images
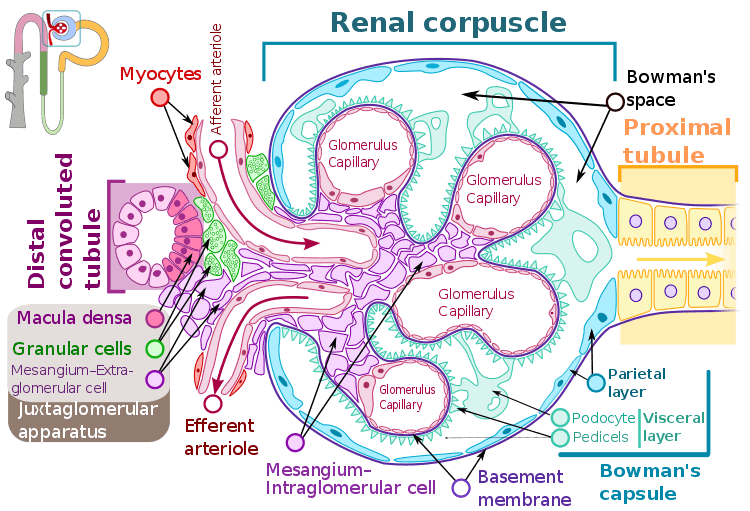 Renal corpuscle showing GBM.
Renal corpuscle showing GBM.
References
- Jarad, G.; Miner, J. H. (2009). "Update on the glomerular filtration barrier". Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension. 18 (3): 226–232. doi:10.1097/mnh.0b013e3283296044. PMC 2895306. PMID 19374010.
- Nosek, Thomas M. Essentials of Human Physiology. Section 7/7ch04/7ch04p07 - "Basement Membrane"
- JCI - New articles published
External links
- glomerular+basement+membrane at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- "The GBM and its disorders" at dmed.ed.ac.uk