Transduction (genetics)
Transduction is the process by which foreign DNA is introduced into a bacterial cell by a virus or viral vector.[1] An example is the viral transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another and hence an example of horizontal gene transfer.[2] Transduction does not require physical contact between the cell donating the DNA and the cell receiving the DNA (which occurs in conjugation), and it is DNase resistant (transformation is susceptible to DNase). Transduction is a common tool used by molecular biologists to stably introduce a foreign gene into a host cell's genome (both bacterial and mammalian cells).
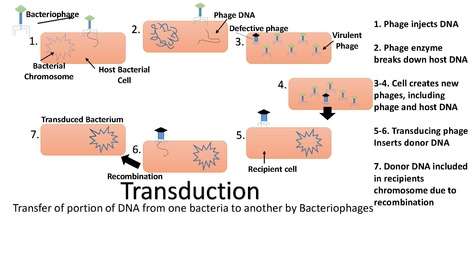
When viruses, including bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria), infect bacterial cells, their normal mode of reproduction is to harness the replicational, transcriptional, and translation machinery of the host bacterial cell to make numerous virions, or complete viral particles, including the viral DNA or RNA and the protein coat.
Discovery (bacterial transduction)
Transduction was discovered by Norton Zinder and Joshua Lederberg at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1952 in Salmonella.[3][4]
Lytic and lysogenic (temperate) cycles (bacteria)
Transduction happens through either the lytic cycle or the lysogenic cycle. If the lysogenic cycle is adopted, the phage chromosome is integrated (by covalent bonds) into the bacterial chromosome, where it can stay dormant for thousands of generations. If the lysogen is induced (by UV light for example), the phage genome is excised from the bacterial chromosome and initiates the lytic cycle, which culminates in lysis of the cell and the release of phage particles. The lytic cycle leads to the production of new phage particles which are released by lysis of the host.
Transduction as a method for transferring genetic material
Transduction by bacteriophages
The packaging of bacteriophage DNA has low fidelity. Small pieces of bacterial DNA may become packaged into the bacteriophage genome, and some bacteriophage DNA may be left behind in the bacterial genome.
There are generally three types of recombination events that can lead to this incorporation of bacterial DNA into the viral DNA, leading to two modes of genetic recombination.
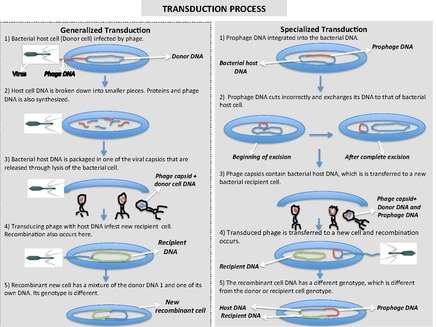
Generalized transduction
Generalized transduction is the process by which any bacterial DNA may be transferred to another bacterium via a bacteriophage. It is a rare event; a very small percentage of phage particles happen to carry a donor bacterium's DNA, on the order of 1 phage in 10,000.[3] In essence, this is the packaging of bacterial DNA into a viral envelope. This may occur in two main ways, recombination and headful packaging.
If bacteriophages undertake the lytic cycle of infection upon entering a bacterium, the virus will take control of the cell's machinery for use in replicating its own viral DNA. If by chance bacterial chromosomal DNA is inserted into the viral capsid which is usually used to encapsulate the viral DNA, the mistake will lead to generalized transduction.
If the virus replicates using 'headful packaging', it attempts to fill the nucleocapsid with genetic material. If the viral genome results in spare capacity, viral packaging mechanisms may incorporate bacterial genetic material into the new virion.
The new virus capsule now loaded with part bacterial DNA then infects another bacterial cell. This bacterial material may become recombined into another bacterium upon infection.
When the new DNA is inserted into this recipient cell it can fall to one of three fates
- The DNA will be absorbed by the cell and be recycled for spare parts.
- If the DNA was originally a plasmid, it will re-circularize inside the new cell and become a plasmid again.
- If the new DNA matches with a homologous region of the recipient cell's chromosome, it will exchange DNA material similar to the actions in bacterial recombination.
Specialized transduction
Specialized transduction is the process by which a restricted set of bacterial genes is transferred to another bacterium. The genes that get transferred (donor genes) depend on where the phage genome is located on the chromosome. Specialized transduction occurs when the prophage excises imprecisely from the chromosome so that bacterial genes lying adjacent to the prophage are included in the excised DNA. The excised DNA is then packaged into a new virus particle, which then delivers the DNA to a new bacterium, where the donor genes can be inserted into the recipient chromosome or remain in the cytoplasm, depending on the nature of the bacteriophage.
When the partially encapsulated phage material infects another cell and becomes a "prophage" (is covalently bonded into the infected cell's chromosome), the partially coded prophage DNA is called a "heterogenote".
An example of specialized transduction is λ phage in Escherichia coli.[5]
Lateral transduction
Lateral transduction is the process by which very long fragments of bacterial DNA are transferred to another bacterium. So far, this form of transduction has been only described in Staphylococcus aureus, but it can transfer more genes and at higher frequencies than generalized and specialized transduction. In lateral transduction, the prophage starts its replication before excision in a process that leads to replication of the adjacent bacterial DNA. When the replicated DNA excises from the chromosome, bacterial genes located up to several kilobases from the phage can get packaged into new virus particles that are transferred to new bacterial strains. If the transferred genetic material provides sufficient DNA for homologous recombination, the genetic material will be inserted into the recipient chromosome.
Mammalian cell transduction with viral vectors
Transduction with viral vectors can be used to insert or modify genes in mammalian cells. It is often used as a tool in basic research and is actively researched as a potential means for gene therapy. In these cases, a plasmid is constructed in which the genes to be transferred are flanked by viral sequences that are used by viral proteins to recognize and package the viral genome into viral particles. This plasmid is inserted (usually by transfection) into a producer cell together with other plasmids (DNA constructs) that carry the viral genes required for formation of infectious virions. In these producer cells, the viral proteins expressed by these packaging constructs bind the sequences on the DNA/RNA (depending on the type of viral vector) to be transferred and insert it into viral particles. For safety, none of the plasmids used contains all the sequences required for virus formation, so that simultaneous transfection of multiple plasmids is required to get infectious virions. Moreover, only the plasmid carrying the sequences to be transferred contains signals that allow the genetic materials to be packaged in virions, so that none of the genes encoding viral proteins are packaged. Viruses collected from these cells are then applied to the cells to be altered. The initial stages of these infections mimic infection with natural viruses and lead to expression of the genes transferred and (in the case of lentivirus/retrovirus vectors) insertion of the DNA to be transferred into the cellular genome. However, since the transferred genetic material does not encode any of the viral genes, these infections do not generate new viruses (the viruses are "replication-deficient").
Some enhancers have been used to improve transduction efficiency such as polybrene, protamine sulfate, retronectin, and DEAE Dextran.[6]
Medical applications
- Resistance to antibiotic drugs.
- Gene therapy: Correcting genetic diseases by direct modification of genetic errors.
See also
- Electroporation – use of an electrical field to increase cell membrane permeability.
- Phage therapy – therapeutic use of bacteriophages.
- Signal transduction
- Transfection – means of inserting DNA into a cell.
- Transformation (genetics) – means of inserting DNA into a cell.
- Viral vector – commonly used tool to deliver genetic material into cells.
References
- Transduction, Genetic at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Jones E, Hartl DL (1998). Genetics: principles and analysis. Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7637-0489-6.
- Griffiths AJ, Miller JH, Suzuki DT, Lewontin RC, Gelbart WM (2000). "Transduction". An Introduction to Genetic Analysis (7th ed.).
- Zinder ND, Lederberg J (November 1952). "Genetic exchange in Salmonella". Journal of Bacteriology. 64 (5): 679–99. PMC 169409. PMID 12999698.
- Snyder L, Peters JE, Henkin TM, Champness W (2013). "Lysogeny: the λ Paradigm and the Role of Lysogenic Conversion in Bacterial Pathogenesis". Molecular Genetics of Bacteria (4th ed.). Washington, DC: ASM Press. pp. 340–343. ISBN 9781555816278.
- Denning W, Das S, Guo S, Xu J, Kappes JC, Hel Z (March 2013). "Optimization of the transductional efficiency of lentiviral vectors: effect of sera and polycations". Molecular Biotechnology. 53 (3): 308–14. doi:10.1007/s12033-012-9528-5. PMC 3456965. PMID 22407723.
External links
- Genetic+Transduction at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview at ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- http://www.med.umich.edu/vcore/protocols/RetroviralCellScreenInfection13FEB2006.pdf (transduction protocol)
- Generalized and Specialized transduction at sdsu.edu