Gallbladder polyp
Gallbladder polyps are growths or lesions resembling growths (polypoid lesions) in the wall of the gallbladder. True polyps are abnormal accumulations of mucous membrane tissue that would normally be shed by the body. The main types of polypoid growths of the gallbladder include cholesterol polyp/cholesterosis, cholesterosis with fibrous dysplasia of gallbladder, adenomyomatosis, hyperplastic cholecystosis, and adenocarcinoma.
| Gallbladder polyp | |
|---|---|
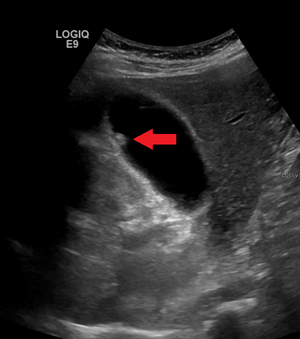 | |
| A polyp in the gall bladder as seen on ultrasound |
Signs and symptoms
Most polyps do not cause noticeable symptoms. Gallbladder polyps are usually found incidentally when examining the abdomen by ultrasound for other conditions, usually abdominal pain.
Pathology
Most small polyps (less than 1 cm) are not cancerous and may remain unchanged for years.[1] However, when small polyps occur with other conditions, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis, they are less likely to be benign.[2] Larger polyps are more likely to develop into adenocarcinomas.
Cholesterolosis is characterized by an outgrowth of the mucosal lining of the gallbladder into fingerlike projections due to the excessive accumulation of cholesterol and triglycerides within macrophages in the epithelial lining.[3] These cholesterol polyps account for most benign gallbladder polyps.
Adenomyomatosis describes a diseased state of the gallbladder in which the gallbladder wall is excessively thick, due to proliferation of subsurface cellular layer. It is characterized by deep folds into the muscularis propria. Ultrasonography may reveal the thickened gallbladder wall with intramural diverticulae, called Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses.[3]
Diagnosis
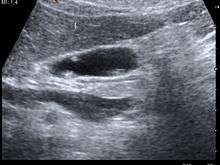
Diagnosis is typically by ultrasound or CT imaging.
Treatment
Most polyps are benign and do not need to be removed. Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is recommended when a gallbladder polyp larger than 1 cm is found, even if the person has no symptoms clearly related to the polyp. Laparoscopic surgery is an option for small or solitary polyps.
Epidemiology
Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder affect approximately 5% of the adult population.[4] The causes are uncertain, but there is a definite correlation with increasing age and the presence of gallstones (cholelithiasis). Most affected individuals do not have symptoms. The gallbladder polyps are detected during abdominal ultrasonography performed for other reasons.
The incidence of gallbladder polyps is higher among men than women. The overall prevalence among men of Chinese ancestry is 9.5%, higher than other ethnic types.[5]
References
- Lee KF, Wong J, Li JC, Lai PB (2004). "Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder". American Journal of Surgery. 188 (2): 186–90. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.11.043. PMID 15249249.
- Karlsen TH, Schrumpf E, Boberg KM (2008). "Gallbladder polyps in primary sclerosing cholangitis: not so benign". Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 24 (3): 395–9. doi:10.1097/MOG.0b013e3282f5727a. PMID 18408471.
- Owen CC, Bilhartz LE (2003). "Gallbladder polyps, cholesterolosis, adenomyomatosis, and acute acalculous cholecystitis". Semin Gastrointest Dis. 14 (4): 178–88. PMID 14719768.
- Myers RP, Shaffer EA, Beck PL (2002). "Gallbladder polyps: epidemiology, natural history and management". Can J Gastroenterol. 16 (3): 187–94. PMID 11930198.
- Lin WR, Lin DY, Tai DI, Hsieh SY, Lin CY, Sheen IS, Chiu CT (2008). "Prevalence of and risk factors for gallbladder polyps detected by ultrasonography among healthy Chinese: analysis of 34,669 cases". Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 23 (6): 965–9. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05071.x. PMID 17725602.