Ferric maltol
Ferric maltol, sold under the brand names Accrufer and Feraccru, is for the treatment of adults with low iron stores.[2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Accrufer, Feraccru |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Drug class | Hematologic agent |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
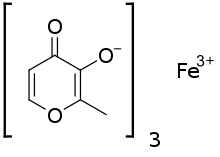
| Formula | C18H15FeO9 |
| Molar mass | 431.154 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Ferric maltol can cause serious side effects including increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease flare and iron overload in the body.[2] The most common side effects are gas, diarrhea, constipation, stool color change, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort, bloating and pain.[2]
History
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved ferric maltol in February 2016.[3]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ferric maltol in July 2019,[4][5] based on evidence from three clinical trials (Trial 1/ NCT01252221, Trial 2/NCT01340872,[6] and Trial 3/NCT02968368[7]).[2] All 295 patients had low iron stores in the body and consequent iron deficiency anemia. In the first two trials low iron was caused by patients’ inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and in the last trial, by long standing (chronic) kidney disease or CKD.[2]
Trials were conducted at 79 sites in Europe and the United States.[2]
References
- "Feraccru 30mg hard capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". electronic medicines compendium (emc). 7 February 2019. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 23 November 2019.
- "Drug Trials Snapshots: Accrufer". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 15 August 2019. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 23 November 2019.

- "Feraccru EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 23 November 2019.
- "Drug Approval Package: Accrufer". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 14 August 2019. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 23 November 2019.

- "Accrufer (ferric maltol) FDA Approval History". Drugs.com. 25 July 2019. Retrieved 23 November 2019.
- Clinical trial number NCT01340872 for "Safety and Efficacy Study of Oral Ferric Iron To Treat Iron Deficiency Anaemia in Quiescent Ulcerative Colitis (AEGIS-1) (AEGIS-1)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT02968368 for "Study With Oral Ferric Maltol for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Subjects With Chronic Kidney Disease (AEGIS-CKD)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
External links
- "Ferric maltol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM).