Estrogen conjugate
An estrogen conjugate is a conjugate of an endogenous estrogen. They occur naturally in the body as metabolites of estrogens and can be reconverted back into estrogens. They serve as a circulating reservoir for estrogen, particularly in the case of orally administered pharmaceutical estradiol. Estrogen conjugates include sulfate and/or glucuronide conjugates of estradiol, estrone, and estriol:
- Sulfated:
- Estrone 3-sulfate (E1S)
- Estradiol 3-sulfate (E2S, E2-3S) and estradiol 17β-sulfate (E2-17S)
- Estriol 3-sulfate (E3S)
- Glucuronidated:
- Estrone 3-glucuronide (E1-G)
- Estradiol 3-glucuronide (E2-3G) and estradiol 17β-glucuronide (E2-17G)
- Estriol 3-glucuronide (E3-3G), estriol 16α-glucuronide (E3-16G)
- Mixed:
- Estriol 3-sulfate 16α-glucuronide (E3-3S-16G)
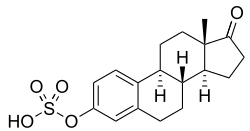
Estrone sulfate, the 3-sulfate conjugate of estrone.
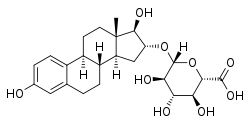
Estriol glucuronide, the 16α-glucuronide conjugate of estriol.
Estrogen conjugates are conjugated at the C3, C16α, and/or C17β positions, where hydroxyl groups are available.[1]
Estrogen conjugates have been used as pharmaceutical estrogens, as in estrone sulfate as estropipate (piperazine estrone sulfate) and in conjugated estrogens (Premarin) and conjugated estriol (Progynon, Emmenin).
See also
- Catechol estrogen
- Lipoidal estradiol
- Steroid sulfate
References
- Bhavnani, BR (January 1998). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of conjugated equine estrogens: chemistry and metabolism". Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine (New York, N.Y.). 217 (1): 6–16. doi:10.3181/00379727-217-44199. PMID 9421201.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.